Updated May 29, 2023

Definition of MySQL Merge
MySQL Merge is a MySQL statement that allows us to update records in a specific table based on values that match from another database table. The MySQL Merge query command performs three primary query operations simultaneously. Suppose when we apply the CRUD operation commands such as INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE distinctly in our database queries. We must build up three different MySQL statements so that the data in the destination table can be modified using the corresponding rows from the database source table.
For this, the users should have SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE privileges on the database tables with which you will map to a MERGE table.
Syntax of MySQL Merge
The succeeding code of structure defines an elementary syntax for MySQL Merge statement query:
Merge TargetTableName USING SourceTableName
ON Merging_Condition
WHEN MATCHED
THEN Update_Query
WHEN NOT MATCHED
THEN Insert_Query
WHEN NOT MATCHED BY SOURCE
THEN DELETE;
Let us discuss the syntax as follows:
- Initially, we will define the target and source database tables in the MERGE clause query.
- Then, we will add the merging condition that decides how the table rows from the table source will match the table rows from the table target. This can be said as similar to a JOIN condition used in the JOIN clause. Usually, we will apply the key columns that can be either UNIQUE Key or PRIMARY Key for matching.
- After that, this merge condition provides three simple states to query as below:
- Matched: It defines the table rows that will match the Merge condition, and for this, we need to alter the table rows columns in the table target with the values from the table source. We use the UPDATE statement here.
- Not Matched: It denotes the table rows from the source table with no equivalent rows present in the target table. In this case, we should supplement the rows from the source table to the defined target table. Remember that NOT MATCHED can also be noted as NOT MATCHED BY TARGET. We will use the INSERT query here.
- Not Matched by Source: It defines the table rows in the given target table with no equivalent rows in the particular source table. We have to apply the match condition to remove or delete rows from the given target table if we want to coordinate the target table with the records from the source one. We will use the DELETE query here.
How does Merge Work in MySQL?
Assume we have two database tables: source table and target table. We need to match values from the source table and update the target table using these tables. It provides three different cases described as follows:
- The source table may include a few rows not present in the target table. Therefore, in this case, we can use the INSERT command to input rows into the target table found in the source table.
- The target table may include a few rows that are not present in the source table. Therefore, we can use the DELETE command to remove rows from the target table not found in the source table.
- In this case, we will find some table rows in the source table containing similar keys to target table rows. However, these table rows have different values in the non-key table columns. Here, we will update the table rows in the target table with the approaching values from the source table.
A MERGE table is also recognized as an anMRG_MyISAM table in the database, which denotes anassembly of comparableMyISAM tables that can be used as a single table. We can perform only SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE procedures on this group of tables. But suppose we want to drop the MERGE table; then only the MERGE specifications will be released after dropping. Here, the tables created comprise identical table columns and essential info because we cannot apply MERGE over those tables with columns packed inversely or keys having another order. In MySQL, the merge can be performed with UNION, INSERT, or JOINS on two or more tables to combine the data values based on the UNIQUE or PRIMARY keys.
Examples of MySQL Merge
We will create two tables in the database named Products and Products_Info containing product information.
CREATE TABLE Products (ProductID INT PRIMARY KEY, Product_Name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, Cost INT NOT NULL);Inserting some items as:
INSERT INTO Products(ProductID, Product_Name, Cost) VALUES
(1,'Parle G',100),
(2, 'Maggie', 112),
(3, 'GoodDay Biscuit', 150);View the table Products:
SELECT * FROM Products;Output:
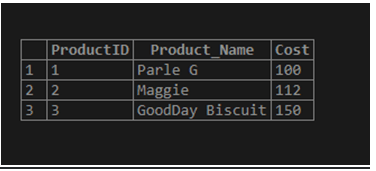
Again,
CREATE TABLE Products_Info (ProductID INT PRIMARY KEY, Product_Name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, Cost INT NOT NULL);Inserting some items as:
INSERT INTO Products_Info(ProductID, Product_Name, Cost) VALUES
(1,'Parle G', 100),
(2, 'Maggie', 112),
(3, 'GoodDay Biscuit', 115),
(4, 'Nestle Coffee', 125),
(5, 'TATA Tea', 80);View the table Products:
SELECT * FROM Products_Info;Output:
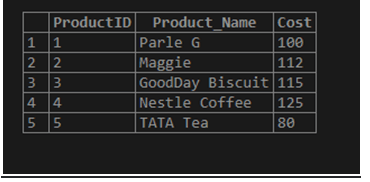
Now, with the values from the Products_Info table, which is as source table by using the MERGE statement to update data to the Products table as the target table we will use this below query in SQL because the MySQL version may not support MERGE so we will write code for it also to demonstrate:
MERGE Products t
USING Products_Info s
ON (s.ProductID = t.ProductID)
WHEN MATCHED
THEN UPDATE SET
t.Product_Name = s.Product_Name,
t.Cost = s.Cost
WHEN NOT MATCHED BY TARGET
THEN INSERT (ProductID, Product_Name,Cost)
VALUES(s.ProductID,s.Product_Name,s.Cost)
WHEN NOT MATCHED BY SOURCE
THEN DELETE;Output:
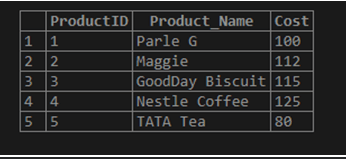
In MySQL, MERGE is not supported, and we apply INSERT…..ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE, where MySQL updates old table values based on the new ones. Hence, for MySQL, we can follow the below queries to combine two tables:
INSERT IGNORE INTO Products SELECT * FROM Products_Info;Output:
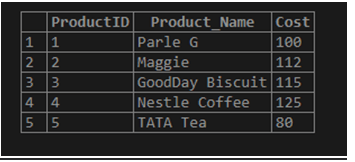
SELECT * FROM Products UNION DISTINCT SELECT * FROM Products_Info;Output:

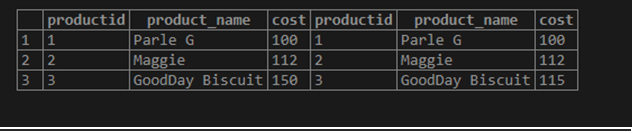
SELECT * FROM Products INNER JOIN Products_Info ON Products.ProductID = Products_Info.ProductID;Output:
Conclusion
- MySQL Merge solves a lot of problems. It helps manage log tables set easily, provides extra speed, can do the searches and repair operations proficiently, and more.
- The MySQL Merge helps map various files to a single one instantly and implements additional file descriptors. But in Merge tables, you cannot use the REPLACE query.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Merge” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

