Updated June 2, 2023

Introduction to MSQL JSON Data Type
MYSQL is a relational database management system that is open source, and in this article, we will see how it works with JSON Data Type. We will look at how to insert JSON data type into an MYSQL table and see various functions available in MYSQL to select further and query the JSON documents or objects. From version 5.7.8, we can even store JSON data natively, and MYSQL has a whole bunch of datatype and functions to manage it.
Getting Started with JSON
JSON or JavaScript Object Notation is a format for data exchange that usually consists of objects, arrays, strings, numbers, and Booleans. This format is also language-independent, so it doesn’t matter if you use Java, SQL, kotlin, ruby, or any other language it is compatible with. To learn more information about JSON format, you can refer to https://www.json.org/json-en.html. This article will show how MYSQL interacts with JSON and what functions are available. Following is the table that we are using for the demonstration purpose to show the usage of MSQL for JSON.
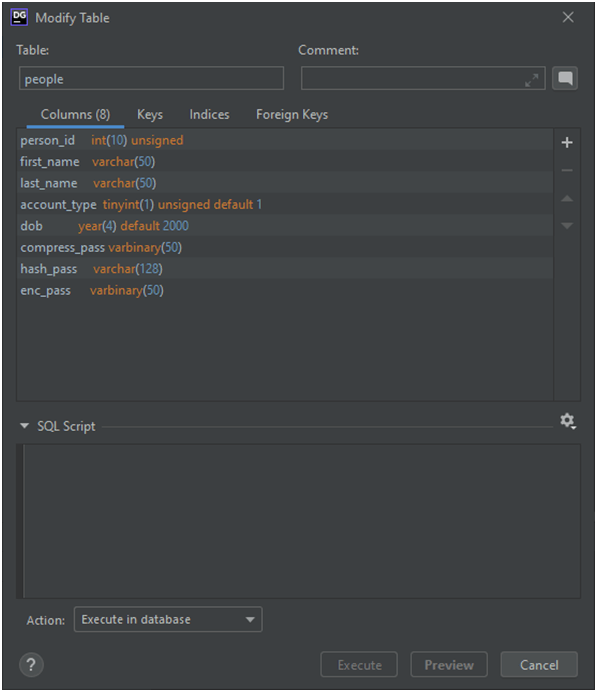
Then we will add a column with the type of JSON to store the native JSON data. The database is set up in phpMyAdmin, and for ease of access, Datagrip from Jetbrains is used for querying and altering the database.
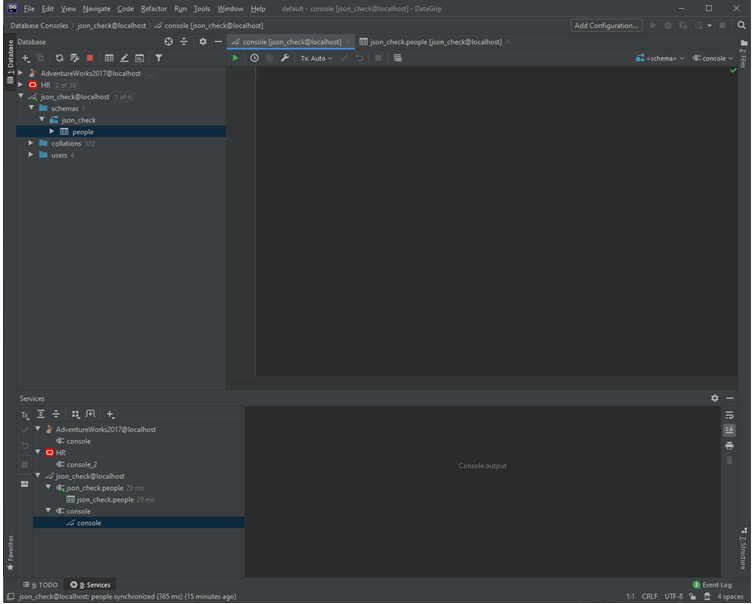
First, we will add a column person_data of the type JSON using the following query.
alter table people
add column person_data JSONThen we will use the following insert statement. Before using it make sure that person_id is a primary key and autoincrement.
insert into people(first_name, last_name, person_data)
values ('Clark', 'Kent', '{"identity": "Superman"}'),
('Bruce', 'Wayne', '{"identity": "Batman"}'),
('Bruce', 'Banner', '{"identity": "Hulk"}')In this query, we add first name, last name, and person_data, a JSON object, and add its string representation, typically in the form of key and value pairs. The value can consist of null, true, or false, but all must be in lower case and case sensitive, whereas mysql is case insensitive like Select NULL, Null, null; this all will work fine.
As we can see, our data is added in JSON form.
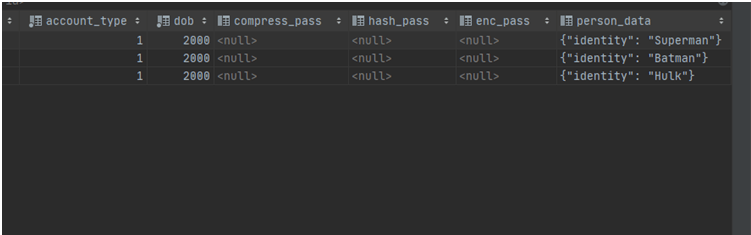
The next question is how to select the required data from the entire json data; for this, there are many helper methods in MYSQL. The first one is JSON_EXTRACT.
Syntax:
JSON_EXTRACT(json_doc, path[, path] ...)
JSON_UNQUOTE(json_val)Code:
select person_data,
JSON_EXTRACT(person_data, '$.identity') as secret_id,
JSON_UNQUOTE(JSON_EXTRACT(person_data, '$.identity')) as super_secret_id
from people
where JSON_UNQUOTE(JSON_EXTRACT(person_data, '$.identity')) = "Superman";Output:
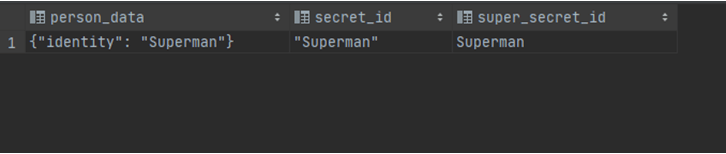
In this query, we select person_data, which is in the json format, and then we use the JSON_EXTRACT method to get the value of the identified property using a dollar symbol. It takes 2 parameters the column name or expression and the position or property. Notice that the results are in quotes. So, we can use JSON_UNQUOTE and supply the extracted value to get an unquoted value. We can even use it in the where clause to compare the value of the result.
Create Array and Objects Using MYSQL
Syntax:
JSON_ARRAY([val[, val] ...])
JSON_OBJECT([key, val[, key, val] ...])
JSON_TYPE(json_val)Code:
select json_array(1, true, "name", "2009-09-12") as array,
json_object("a", 1, "b", "Steve", "c", true, "d", "null") as object,
json_type(person_data) as type
from people;Output:

In this query, we have used three functions; JSON_ARRAY will take all the valid json types and create an array, as you can see with square brackets in the result. JSON_OBJECT will take the comma-separated key and value pairs and ensure the key is always in quotes. Then JSON_TYPE will give the data type stored; in this case, we have to store the entire json object.
Merge Functions in MYSQL for JSON
Merge functions in mysql for json are explained below:
1. Merge Patch
Syntax:
JSON_MERGE_PATCH(json_doc, json_doc[, json_doc] ...)Code:
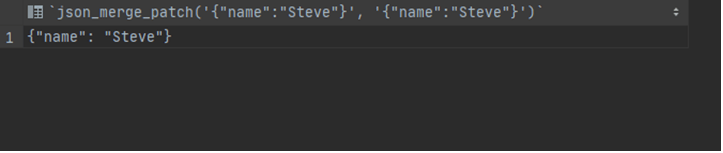
select json_merge_patch('{"name":"Steve"}', '{"name":"Steve"}');Output:
Code:
select json_merge_patch('{"name":"Steve"}', '{"name":"Dave"}');Output:

In these two queries, we have used the JSON_MERGE_PATCH function, which will merge the existing and new values by patching or replacing them. As we can see in the first query, the value is the same, and the new value is replaced in the second.
2. Merge Preserve
Syntax:
JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE(json_doc, json_doc[, json_doc] ...)Code:
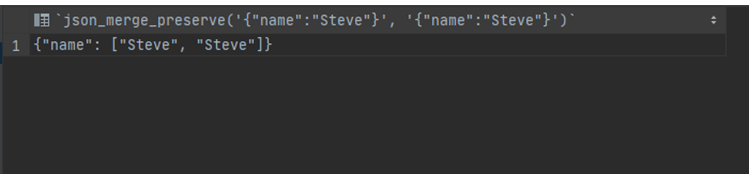
select json_merge_preserve('{"name":"Steve"}', '{"name":"Steve"}');Output:
Code:
select json_merge_preserve('{"name":"Steve"}', '{"name":"Dave"}')Output:
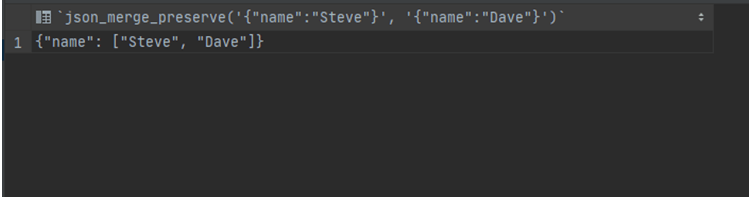
In these two queries, we preserve the old value along with the new value as we can see in the first query, the values are duplicated, and in the second query, the new value is appended.
Search JSON Values
Syntax:
JSON_CONTAINS(target, candidate[, path])Code:
SET @test_string_object = '{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": {"d": 4}}';
SET @search_value = '1';
SELECT JSON_CONTAINS(@test_string_object, @search_value, '$.a') as check_if_exist;Output:

In this query, we created one test string representing a JSON object and another variable we want to search in the object. Then we used the JSON_CONTAINS function, which takes three parameters: a target to search in, the search value, and the property. The return value is either one if found or 0 if not found. A null value is returned if any arguments are null or the path is invalid.
Syntax:
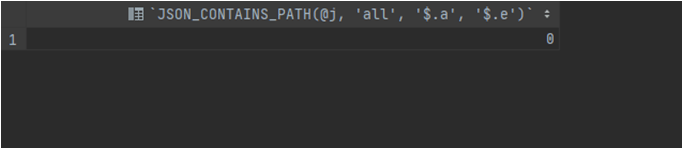
JSON_CONTAINS_PATH(json_doc, one_or_all, path[, path] ...)Code:
SET @test_string_object = '{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": {"d": 4}}';
SELECT JSON_CONTAINS_PATH(@j, 'all', '$.a', '$.e');Output:
Code:
SET @test_string_object = '{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": {"d": 4}}';
SELECT JSON_CONTAINS_PATH(@j, 'one', '$.a', '$.e');Output:
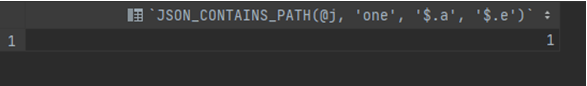
These queries utilize the JSON_CONTAINS_PATH function, which takes an input JSON and determines the existence of specified paths based on the provided arguments. It returns 1 if all paths exist or if at least one of the paths exists; otherwise, it returns 0. The first query uses all parameters, but only one path exists, which leads to a return value of 0. In the second query, only one parameter is used, and there is one existing path, resulting in a return value of 1.
Conclusion – MySQL JSON Data Type
Hopefully, now you know how to use JSON data with the MYSQL database. We have learned how to insert JSON values in an MYSQL table. We have also learned various helper methods that make it easy to manipulate the stored JSON values.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL JSON Data Type” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

