Updated May 29, 2023

Introduction to MySQL INSERT IGNORE
When we want to insert the data into the MySQL database tables, we use the INSERT statement for performing this operation. Mysql provides the facility to add IGNORE keyword in the syntax of the INSERT statement. You can call this function with any number of parameters, and it will return the desired value. This is because the INSERT IGNORE statement handles the error that arrives while the addition of the duplicate record and prevents the inconsistency and redundancy of the records in the tables of Mysql.
In this article, we will learn about the general syntax of the INSERT IGNORE statement, it works, how the strict mode affects the working of the INSERT IGNORE statement, and learn the usage with the help of a few examples to make the concept clearer.
How does INSERT IGNORE work in MySQL?
When we try to insert multiple records in a particular Mysql database table using the INSERT statement, the error occurs for some reason. Mysql will terminate the execution of the query and give the error without inserting any rows in the table that we tried to insert. But when we use INSERT IGNORE instead of just inserting a statement, then Mysql will give a warning and insert all the correct records, leaving and excluding the rows that caused the error.
Syntax
The syntax of the INSERT IGNORE statement is as follows –
INSERT IGNORE INTO table(list_of_columns)
VALUES(record1),
(record2),Where list_of_columns are the comma-separated names of the column that you wish to insert in the record and the record1,record2,.. are the values of the columns that you have mentioned in the list_of_columns in the same order as they have been mentioned in the list.
Examples to Implement MySQL INSERT IGNORE
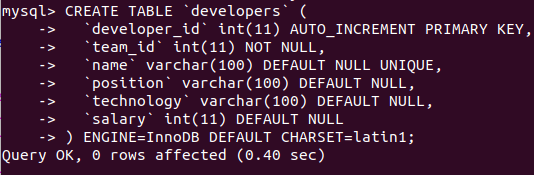
Let’s create a table named “developers” that contains one auto-incremented primary key column called “id”, one column named “name” with a unique constraint, and other necessary fields using the following query statement:
Code:
CREATE TABLE 'developers' (
'developer_id' int(11) AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
'team_id' int(11) NOT NULL,
'name' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL UNIQUE,
'position' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
'technology' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
'salary' int(11) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;Output:
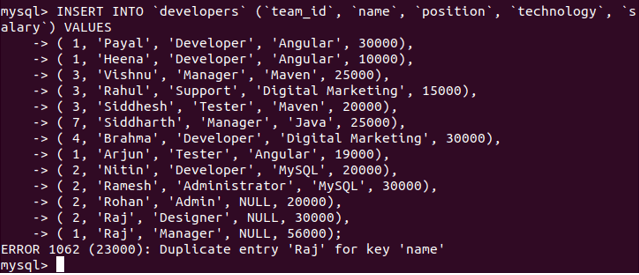
Now, we will try to insert multiple records with a single record value repeated for the name column on which we have defined the unique constraint to avoid inserting records with the same name. As inserting such records is against the rules and breaking the constraint, MySQL will issue an error saying the record with a duplicate name column value cannot be inserted. In this case, our insert query accurately specified all other columns according to the constraints and did not insert any restricted values. We can try executing the following query statement –
Code:
INSERT INTO 'developers' ('team_id', 'name', 'position', 'technology', 'salary') VALUES
( 1, 'Payal', 'Developer', 'Angular', 30000),
( 1, 'Heena', 'Developer', 'Angular', 10000),
( 3, 'Vishnu', 'Manager', 'Maven', 25000),
( 3, 'Rahul', 'Support', 'Digital Marketing', 15000),
( 3, 'Siddhesh', 'Tester', 'Maven', 20000),
( 7, 'Siddharth', 'Manager', 'Java', 25000),
( 4, 'Brahma', 'Developer', 'Digital Marketing', 30000),
( 1, 'Arjun', 'Tester', 'Angular', 19000),
( 2, 'Nitin', 'Developer', 'MySQL', 20000),
( 2, 'Ramesh', 'Administrator', 'MySQL', 30000),
( 2, 'Rohan', 'Admin', NULL, 20000),
( 2, 'Raj', 'Designer', NULL, 30000),
( 1, 'Raj', 'Manager', NULL, 56000);Output:
Let us retrieve the records of the developer’s table by using the following query statement
Code:
SELECT * FROM developers;Output:
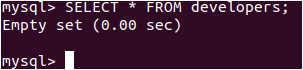
We can see that none of the records got inserted even though other than the record with the Raj name was correct. Let us now try inserting the records using the INSERT IGNORE statement instead of the INSERT statement. Our query statement will be as follows –
Code:
INSERT IGNORE INTO 'developers' ('team_id', 'name', 'position', 'technology', 'salary') VALUES
( 1, 'Payal', 'Developer', 'Angular', 30000),
( 1, 'Heena', 'Developer', 'Angular', 10000),
( 3, 'Vishnu', 'Manager', 'Maven', 25000),
( 3, 'Rahul', 'Support', 'Digital Marketing', 15000),
( 3, 'Siddhesh', 'Tester', 'Maven', 20000),
( 7, 'Siddharth', 'Manager', 'Java', 25000),
( 4, 'Brahma', 'Developer', 'Digital Marketing', 30000),
( 1, 'Arjun', 'Tester', 'Angular', 19000),
( 2, 'Nitin', 'Developer', 'MySQL', 20000),
( 2, 'Ramesh', 'Administrator', 'MySQL', 30000),
( 2, 'Rohan', 'Admin', NULL, 20000),
( 2, 'Raj', 'Designer', NULL, 30000),
( 1, 'Raj', 'Manager', NULL, 56000);Output:

We can see that 12 rows were affected, and the query got executed with one warning. To see the warning, we can execute the following command –
Code:
SHOW WARNINGS;Output:

The warning shows that one record with the name Raj had a duplicate value for the name column having a unique constraint on it. Let us retrieve the records of the developer’s table and check which records got inserted using the following query –
Code:
SELECT * FROM developers;Output:

We can see that 12 rows got inserted when we tried to insert 13 rows, but as Raj’s record was duplicated, all the remaining rows got inserted successfully. Also, note that the autoincremented column of developer id has got values inserted beginning from 14,15 and so on because the previous 13 records that we tried to insert using just INSERT query caused an error, and then all the records that were being inserted got rollbacked leaving the sequence value associated with auto-incremented column updated to 14.
Value Exceeding the Range of the Column
When we try to insert the value that exceeds the limit of the defined column size, the INSERT statement results in an error. However, using INSERT IGNORE inserts the truncated value and warns that the range exceeded and hence value has been truncated for insertion. Consider the following example:
The length of salary columns is 11, and we try inserting 12-digit numbers using the INSERT statement gives the following output –
Code:
INSERT INTO 'developers' ('team_id', 'name', 'position', 'technology', 'salary') VALUES
( 1, 'Pihu', 'Developer', 'Angular', 300000000000);Output:

Let’s try using INSERT IGNORE statement –
Code:
INSERT IGNORE INTO 'developers' ('team_id', 'name', 'position', 'technology', 'salary') VALUES
( 1, 'Pihu', 'Developer', 'Angular', 300000000000);Output:
![]()
with warning –
Code:
SHOW WARNINGS;Output:
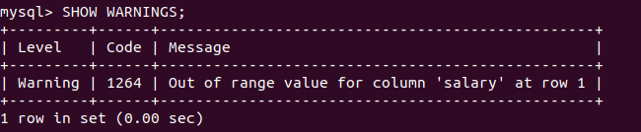
Let us retrieve and check the inserted value –
Code:
SELECT * FROM developers WHERE name='pihu';Output:

Conclusion
Using the INSERT IGNORE statement instead of just inserting statements is always a good practice. Mysql tries to adjust the values to arrange them in the correct format and inserts the correct records, excluding the ones that can cause an error.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL INSERT IGNORE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

