Updated June 3, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Innodb_buffer_pool_size
MySQL innodb_buffer_pool_size is one of the imperative variables for tuning, especially in the Innodb tables. Compared to MyISAM tables, the InnoDB tables indicate more sensitivity to the buffer size. Here, Innodb_buffer_pool denotes the memory space consisting of several in-memory Innodb data structures, buffers, indexes, caches, and row data.
Usually, we can say that MySQL innodb_buffer_pool_size indicates the configuration parameter in MySQL, which states the quantity of memory assigned by MySQL to the Innodb_buffer_pool. Organizing this setting based on the available system RAM is crucial as it is considered one of the essential hosting configurations in MySQL servers.
Syntax
We can show the MySQL innodb_buffer_pool_size variable through a query command with syntax given as follows:
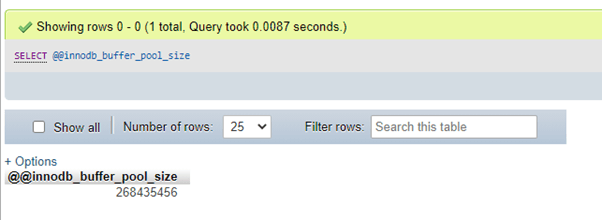
SELECT @@innodb_buffer_pool_size;In a prevailing server, a user can view the default value of MySQL innodb_buffer_pool_size through the following command query:
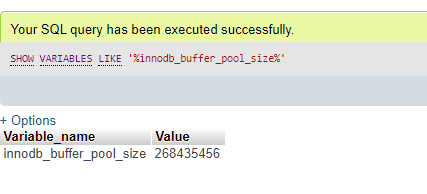
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%innodb_buffer_pool_size%';Sizing the buffer pool to accommodate the entire database is recommended. However, in practical scenarios, this may not always be possible. Therefore, it is also superior to assign about 75-80% of the total memory of the server machine present to innodb_buffer_pool_size.
You can also configure the value for the innodb_buffer_pool_size variable online in MySQL 5.7 and later versions using the following code:
SET GLOBAL innodb_buffer_pool_size = (value(in bytes));Before making any changes, it is important to note that setting the value of the above variable should be done online. If you restart the server, the configuration value may be lost. To preserve these alterations, you can track them and set the value in the configuration file named my.cnf in case of a server restart.
The configuration can be done offline in the previous versions before MySQL 5.7. The variable value can also be modified by editing the configuration file my.cnf. For this, open this file and then edit the below line of code under the code section[mysqld] and save the file:
Innodb_buffer_pool_size = X G;You can now restart the server MySQL to check the value for the new set of configurations running the following command:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%innodb_buffer_pool-size%';For online process use:
SET GLOBAL innodb_buffer_pool_size = 26843545600;For offline process use:
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 26G*For both processes, the server restart is needed.
How does the innodb_buffer_pool_size function work in MySQL?
- Caching is significant in performance optimization as it utilizes memory to accelerate access to frequently used data. However, the effectiveness of caching depends on the amount of data that needs to be accessed; retrieving data on a disk may be 100 to 100,000 times slower.
- MyISAM uses the operating system file system cache to cache the database data that frequently queries access. On the other side, Innodb implements a very altered concept. Instead of trusting OS to perform the correct thing, the Innodb regulates to cache itself – within the Innodb_buffer_pool.
- The MyISAM may perform the kind of OK with default key_buffer_size and the big data set, but then it will be crawled with default innodb_buffer_size. The Innodb buffer pool stores both index pages and data; therefore, you do not require vacant space for OS cache, so up to 70-80% of memory values frequently make logic for Innodb database-only installations.
- The same rules as for key_buffer apply to innodb_buffer_size. There is no need to allocate excessive memory to the innodb_buffer_size variable for a small dataset with no significant growth expected. It is better to optimize it based on the available memory.
- We came to know that MySQL innodb_buffer_pool is more than only a Cache; it assists multiple determinations listed below:
- Its big part is used for the process of ‘Data caching.’
- Sharing a similar buffer pool, it is used for ‘Indices caching.’
- The modified or dirty data remains buffered before it is flushed.
- InnoDB buffer pool also stores internal structures like row locks or Hash Index.
Examples of MySQL innodb_buffer_pool_size
Since MySQL innodb_buffer_pool_size denotes the total cache in the server, for setting this system variable value based on the system RAM size, we will walk through the following two tactics with the pros and cons of each:
Tactic 1: Thumb Rule Method
It defines the common practice to set the variable innodb_buffer_pool_size’s value to 70-80% of the available system RAM space. This method performs better in many cases but is not optimum in all configurations as it cannot wholly control the big RAM size or utilize it for the cache.
Tactic 2: Further Nuanced Method
Here, we will explore the internal aspects of the InnoDB buffer pool and its collaborations, as defined in the book High-Performance MySQL.
Below are the approaches to calculate the MySQL innodb_buffer_pool_size variable:
- Initially, starting with the total RAM present.
- Minus an appropriate quantity for all OS requirements.
- Minus an appropriate quantity for all MySQL requirements, such as many MySQL buffers, connection pools, replication-linked buffers, and temporary tables.
- The division of the output by 150% estimates the above needed to regulate the buffer pool.
Let us discuss some of the demonstrations using the MySQL innodb_buffer_pool_size variable query and its uses in MySQL server:
You can run the code below in the information_schema database in the server to view the innodb_buffer_pool_size value:
SELECT @@innodb_buffer_pool_size;Output:
To display the default innodb_buffer_pool_size value in the existing server:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%innodb_buffer_pool_size%';Output:
Conclusion
MySQL innodb_buffer_pool_size is an essential variable for the whole MySQL server, which has brought radical developments over the last few years in the InnoDB storage engine structures. The position of the InnoDB storage engine cultivates several times over MyISAM after Oracle acquired MySQL. Due to its ACID obedience properties, it is essential that MySQL maintenances other various pluggable storage engines. The latest enhancements in MySQL 5.7, named the configuration of online innodb_buffer_pool_size, have made it extremely flexible and helped to receive the best performance and not give long downtime.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL innodb_buffer_pool_size” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.