Updated May 15, 2023

Definition of MySQL Index
MySQL INDEX can be said as a data organization in a database table that helps to progress the speed of the several operations taking place in MySQL and helps to optimize the database. We implement INDEX in MySQL to create indexes using one or multiple columns in a table database to have quick data access and improve the performance for organizing the data values in a specific proper manner.
MySQL INDEX denotes the indexing process to build the indexes on a database that provides the basis for quick casual lookups and proficient ordering to fetch the rows using indexes properly using phpMyAdmin. If we see practically, Indexes hold the Primary key or Index field and a pointer to every row in the database table. So, we can conclude that indexes are a kind of table.
How Does Index Work in MySQL?
Usually, you can easily generate MySQL indexes using phpMyAdmin on a local server like WAMP, XAMPP, or a live server on cPanel. B-trees store most MySQL indexes, such as UNIQUE, PRIMARY KEY, FULLTEXT, and INDEX, and they organize data in a sorted manner, facilitating sequential access, searches, inserts, and removals with logarithmic time complexity. File systems and databases benefit from B-trees as they enable efficient reading and writing of blocks of information.
In MySQL, INDEX performs the succeeding works:
- It can help quickly locate the indexing information within a database or table.
- Here, indexing in MySQL will create an innermost catalog stored by the MySQL service. It uses a catalog of table rows as it can indicate within a decimal of time using the least effort.
- It works initially by sorting the data and then works to allot identification for every row in the table.
- Indexes support examining rows corresponding to a WHERE clause with particular column values very quickly, so if the index is not functioning correctly, we must use the REINDEX command to operate and rebuild the indexes of table columns to continue the access of data.
- Eliminates rows from concern if there is any choice between more than one Indexes by selective method indexing, and thus supports the re-indexing.
- Indexes in MySQL act as a table arrangement technique because they sit atop tables and facilitate efficient query execution.
- Indexing also permits fetching rows from other related tables in RDBMS when performing JOINS and their queries properly.
How to Create an Index in MySQL?
We use the below simple syntax to complement MySQL INDEX in a MySQL Database table:
CREATE INDEX [Index_Name] ON [TableName] ([ColumnName of the TableName]);Here, the given arguments are explained below:
- Index_Name is the name of the index
- TableName is the name of the particular table
- ColumnName defines the column where the indexing will be done in the abovementioned table.
We can form a Unique Index on the table so that no two records have identical index values. The syntax is:
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX [Index_Name] ON [TableName] ([ColumnName of the TableName]);To outlook the MySQL indexes, we use the below syntax:
SHOW INDEXES FROM TableName IN DatabaseName;For using MySQL INDEX, let us first create particular indexes on tables and explain them briefly about the topic. Initially, we have taken a table named Books in the database with fields BookID, BookName, Language&Price. It holds a few data as follows:
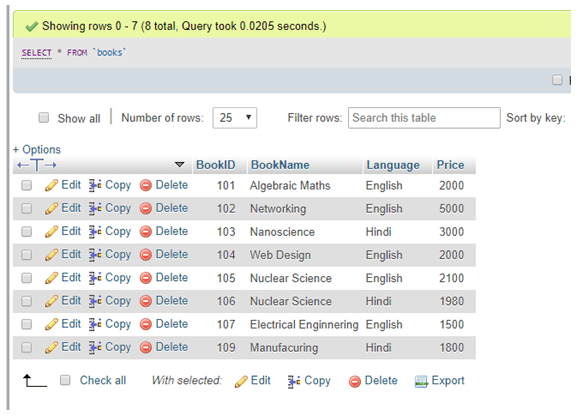
Now, the query below will discover the book whose language is English in the language column using WHERE:
SELECT BookID, BookName FROM Books WHERE Language= 'English';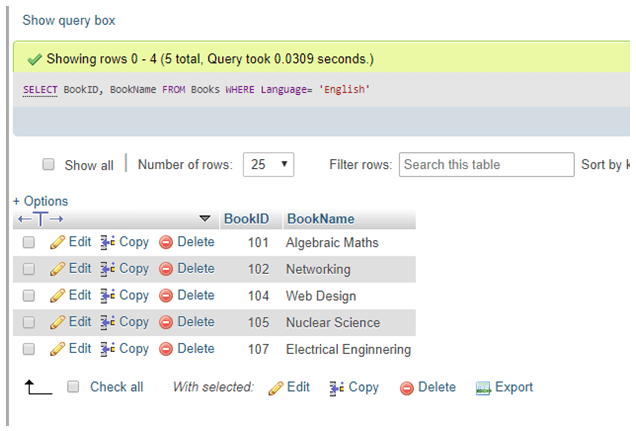
If you want to know how MySQL performed this query internally, then we apply the EXPLAIN query to the start of the previous query as follows:
EXPLAIN SELECT BookID, BookName FROM Books WHERE Language= 'English';
Here, the server must test the table containing 8 rows to execute the query.
Let us now add an index for the language column by the below statement:
CREATE INDEX Language ON Books(Language);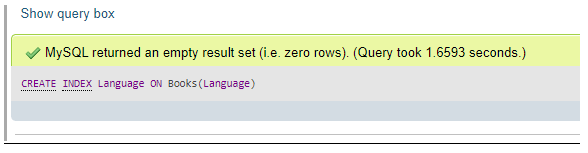
After running the query, again use the EXPLAIN statement to view the result.
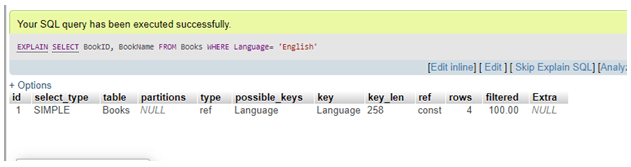
The result is clear; now, the key column in MySQL indicates that only four rows are scanned using the created index, rather than the entire table. This feature allows for more targeted and efficient data retrieval.
For example, let us view the index created on the table Books using the query below:
SHOW INDEXES FROM Books;
Thus, the index can make things easy to handle as there can be millions of records in a table, and without an index, data access can be time-consuming.
How to Alter Index in MySQL?
Note that we can define indexes for a table later even if the table is already created in a database with MySQL ALTER query:
We can write the index using the following four statements:
ALTER Table TableName ADD PRIMARY KEY (ColumName);
ALTER Table TableName ADD UNIQUE Index_Name (ColumName);
ALTER Table TableName ADD INDEX Index_Name (ColumName);
ALTER Table TableName ADD FULLTEXT Index_Name (ColumName);For example,
ALTER TABLEBooks ADD INDEX book_lang (Language);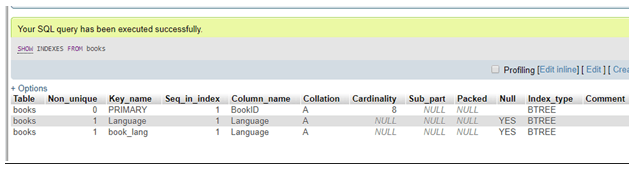
How to Delete Index in MySQL?
Again, to delete an index, we apply the following SQL statement:
DROP INDEX [Index_Name] ON [TableName] ([ColumnName of the TableName]);This command to drop an index already removes the defined indexes on a given table. Like,
DROP INDEX Book_lang ON Books;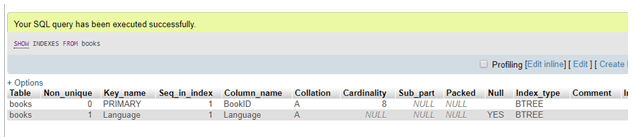
For deleting any Index, we can also use ALTER and DROP commands together as follows:
ALTER TABLE Books DROP INDEX Language;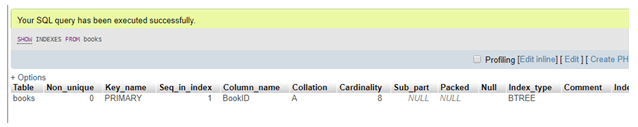
To verify the changes to confirm whether they are applied to the tables or not, we can use the SHOW INDEXES query as above.
Conclusion
Normal users cannot see MYSQL Indexes because the indexes are just applied to speed up the MySQL statements and use the Database Search Engine to discover the table records rapidly. The table in the database having indexes takes more time while using INSERT and UPDATE queries, but it is fast when we use a SELECT query on the tables. This is because when we insert or update any record, we also need to insert or update the index values.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Index” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

