Updated June 3, 2023
Introduction to MySQL floor
MySQL floor function is the mathematical function available in MySQL that is used for the numeric type of values. These numeric values can be either integers or floating-point numbers. If the numeric value is formatted inside the string type of value as a parameter, then that value is also allowed for floor function. In short, any value or expression deduced to the numeric value can be used as a parameter to the floor() mathematical function in MySQL. This function helps us retrieve the maximum integer value that is less or equivalent to the passed value. FLOOR() mathematical function is supported in all the versions of MySQL 4.0 and above that, including MySQL 5.0, MySQL 5.1, MySQL 5.5, MySQL 5.6, MySQL 5.7, MySQL 3.23, MySQL 4.0, and MySQL 4.1.
Syntax
Below is the syntax for the mathematical FLOOR() function in MySQL –
FLOOR(expressionOrNumber);ExpressionOrNumber – ExpressionOrNumber can be any integer, floating-point, or decimal value. If we wrap this numeric value into strings, these string values will also be accepted. Other than the direct specification of numeric value, any expression that will ultimately deduce to a numeric value is also allowed as a FLOOR() function parameter.
Return value – The FLOOR() function returns the greatest integer value that is less than or equal to the parameter value passed to the function. The return value type depends on the data type of the value passed as the parameter to the FLOOR() function. If the parameter is of integer data type, the return value is also of integer type. While in other cases, if the deduced value of the parameter of the direct specification of the parameter is of floating-point type, then the datatype of the return value is of the floating-point data type itself.
Examples
Here are the following examples mentioned below
1. Using FLOOR() function with positive values
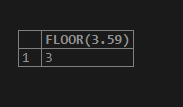
We will consider the positive numeric value say 3.59, and then use the FLOOR function to retrieve the highest integer value that is less than or equivalent to the 3.59 value. Let us execute the following SQL query statement and observe the output –
SELECT FLOOR(3.59);The output of the above query statement execution is as follows –
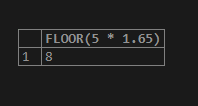
Let us consider one more example of positive value. But in this example, we will use an expression that will evaluate the value that is of numeric type. Consider the expression 5 * 1.65, whose actual value is 8.25, and use this expression in the FLOOR() function to retrieve the maximum integral value less than the passed value using the following query statement –
SELECT FLOOR(5 * 1.65);The output of the above query statement execution is as follows –
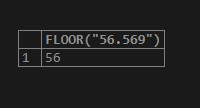
Now, we will consider a positive number wrapped as a string and use it as a FLOOR() function parameter. For example, consider the “56.569” value that is used in the following manner –
SELECT FLOOR("56.569");The output of the above query statement execution is as follows –
2. Using FLOOR() function with negative values
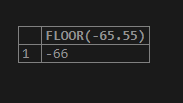
We will consider the negative numeric value say -65.55, and then use the FLOOR function to retrieve the highest integer value that is less than or equivalent to the -65.55 value. Let us execute the following SQL query statement and observe the output –
SELECT FLOOR(-65.55);The output of the above query statement execution is as follows –
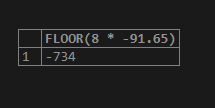
Let us consider one more example of a negative value. But in this example, we will use an expression that will evaluate the value that is of numeric type. Consider the expression 8 * -91.65, whose actual value is −733.2, and use this expression in the FLOOR() function to retrieve the maximum integral value less than the passed value using the following query statement –
SELECT FLOOR(8 * -91.65);The output of the above query statement execution is as follows –
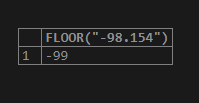
Now, we will consider a negative number wrapped as a string and use it as a FLOOR() function parameter. For example, consider the “-98.154” value that is used in the following manner –
SELECT FLOOR("-98.154");The output of the above query statement execution is as follows –
3. Using the FLOOR() function with values in the table
Let us see how we can use the FLOOR() function in the query statements on the values of the columns. We will create one table named workers using the following query statement –
CREATE TABLE 'workers' (
'developer_id' int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
'team_id' int(11) NOT NULL,
'name' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
'position' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
'technology' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
'salary' int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ('developer_id'),
UNIQUE KEY 'name' ('name')
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=28 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;Now, we will insert some records in the worker’s table using the following query statements –
INSERT INTO `workers` VALUES
(1,1,'Payal','Developer','Angular',30000),
(2,1,'Heena','Developer','Angular',10000),
(3,3,'Vishnu','Manager','Maven',25000),
(4,3,'Rahul','Support','Digital Marketing',15000),
(5,3,'Siddhesh','Tester','Maven',20000),
(6,7,'Siddharth','Manager','Java',25000),
(7,4,'Brahma','Developer','Digital Marketing',30000),
(8,1,'Arjun','Tester','Angular',19000),
(9,2,'Nitin','Developer','MySQL',20000),
(10,2,'Ramesh','Administrator','MySQL',30000),
(11,2,'Rohan','Admin',NULL,20000),
(12,2,'Raj','Designer',NULL,30000);
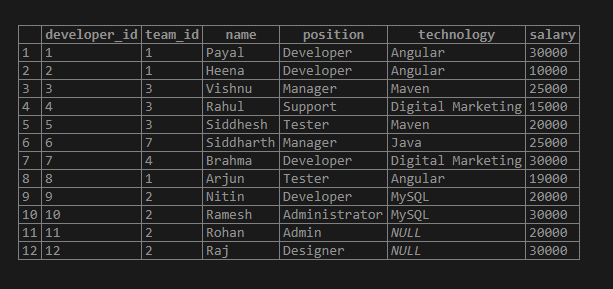
Select * from `workers`;that gives the following output after the execution of the query –
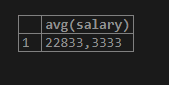
Now we will calculate the average salary using the following query statement –
SELECT avg(salary) from workers;The execution of the above query statement gives the following output –
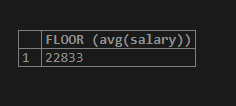
If we want to retrieve the average salary in integer format with the greatest value that is less than or equivalent to the average value using the FLOOR() function using the following query statement –
SELECT FLOOR (avg(salary)) from workers;The execution of the above query statement gives the following output
Conclusion – MySQL floor
MySQL 4.0 and all the above versions of MySQL support the mathematical function FLOOR(). We can retrieve the maximum value in integer format that is less or equivalent to the passed numeric number or expression whose results can be either the floating value of an integer or decimal value.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL floor” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.