Updated June 2, 2023
Introduction of MySQL Drop Database
We can delete the database and all the contents of the database when they are no more helpful by using the DROP DATABASE command. This deletes the contents and all the schema-related information stored about the database entirely from your MySQL database server. You will find no trace of the dropped database. Hence, it is necessary to be extra careful while using this command, as restoration of the database is impossible if you do not have any backup, as the DROP DATABASE command permanently deletes the contents. In this article, we will learn the syntax of the DROP DATABASE command and its usage with the help of examples.
Syntax:
DROP DATABASE [IF EXISTS] name_of_database;Where name_of_database helps specify the database name you wish to delete entirely, including its contents like tables, stored procedures, triggers, etc.
To convert to active, you must follow the specific instructions for your program or system. You may need to log in to the system and navigate to your account settings or preferences. Look for an option to switch your status to active and follow any prompts or confirmation steps. If you encounter any issues or errors during the process, check for troubleshooting resources or contact customer support for assistance.
Examples of MySQL Drop Database
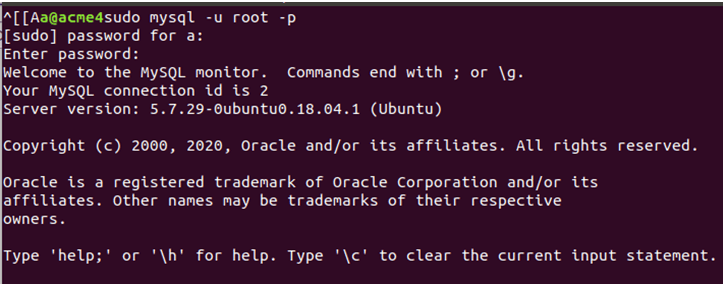
Firstly we will have to open the MySQL connection using the command:
mysql -u root -pIf you attempt to log in with the username “root,” the system will prompt for a password if a password has been set.
Executing the above command will give you the following output:
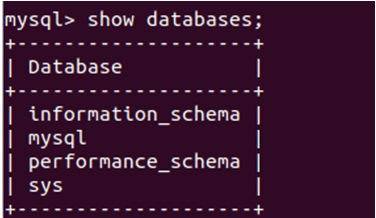
Then you must execute the following command to list all the databases in your MySQL database server.
SHOW DATABASES;That gives the following output in my case:
Now, let us try to delete the database that is not present on our database server and see the outputs –
DROP DATABASE educba;Executing the above command gives the following output:
We observe that the system throws an error with error code 1008, indicating that the ‘educba’ database cannot be dropped because it does not exist.
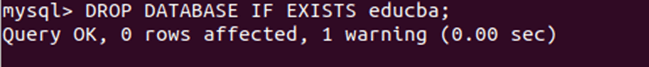
Now, let us study the output after adding the IF EXISTS clause in our query statement –
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS educba;The output of the execution of the above query is as shown below:
The output indicates that the query was executed successfully and without any errors, even though the “educba” database does not exist in our database. This indicates that the query did not have any impact on the rows. Additionally, the output shows the presence of one warning.
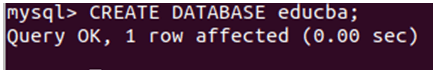
Now, let us create one database named educba using CREATE DATABASE command –
CREATE DATABASE educba;that gives the following output:
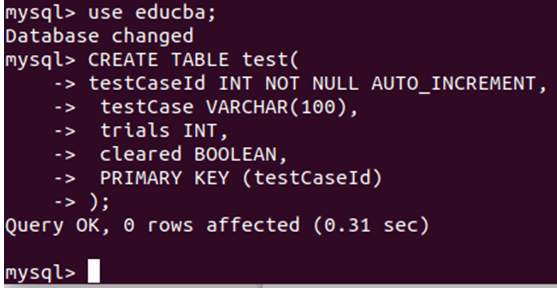
Now let us create two tables named to test and development
CREATE TABLE test(
testCaseId INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
testCase VARCHAR(100),
trials INT,
cleared BOOLEAN,
PRIMARY KEY (testCaseId)
);That gives the following output:
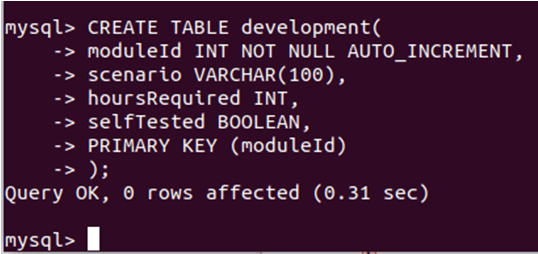
And one more create table query for development that is as follows –
CREATE TABLE development(
moduleId INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
scenario VARCHAR(100),
hoursRequired INT,
selfTested BOOLEAN,
PRIMARY KEY (moduleId)
);Execution of the above query gives the following output:
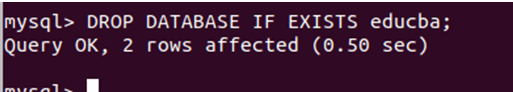
Now, let us drop the educba database using the drop database command –
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS educba;That now gives the following output:
It can be concluded that the query executed successfully without any errors or warnings and returned two affected rows. The DROP DATABASE command gives the return value as the number of the tables that were present in that database and got deleted when dropping the database.
An alternative to DROP DATABASE –
In MySQL, the database and schema are used interchangeably, meaning both are the same thing and synonyms. Hence, we can make the use of
DROP SCHEMA [IF EXISTS] name_of_database;This functions in the same manner as that of the DROP DATABASE command.
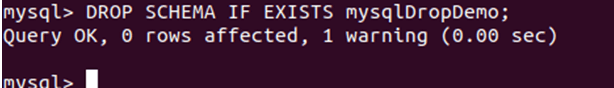
Let us try to delete the database named mysqlDropDemo using the following query statement –
DROP SCHEMA mysqlDropDemo;The output of the above query execution is as follows:
It throws an error saying no database named mysqlDropDemo exists in my database server. Now, let us execute the same query with the IF EXISTS clause in it –
DROP SCHEMA IF EXISTS mysqlDropDemo;That gives the following output:
It can be seen that one warning is raised.
Let us create the database named mysqlDropDemo using the following query –
CREATE DATABASE mysqlDropDemo;that gives the following output:
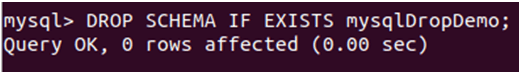
Now if you execute the same query of DROP SCHEMA, then the output will be different. We will be executing the following query statement –
DROP SCHEMA IF EXISTS mysqlDropDemo;That now results in the following output:
We can observe the successful dropping of the database as no rows are returned or affected. This is due to the absence of any tables in the mysqlDropDemo database.
You can also confirm the presence and dropping of databases at each stage while performing this task by using the SHOW DATABASES; command that gives the list of all the databases present on your database server at that particular moment when this command is executed.
Conclusion
We can drop the database using the SQL command DROP DATABASE, which entirely and permanently deletes the database and all the contents of that database. Hence, we should be careful while using this command, as it is impossible to restore the dropped database if you don’t have any backup. DROP SCHEMA is an alternative command to delete a database existing on the database server. We treat schemas and databases similarly, considering them as synonyms. To avoid raising an error when the DROP query specifies a database name that does not exist, we can use the IF EXISTS clause in both DROP DATABASE and DROP SCHEMA commands.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MySQL Drop Database. Here we also discuss the introduction and syntax, along with different examples and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –