Updated June 3, 2023
Introduction to MySQL DESCRIBE table
Often, we forget the contents, names, and attributes assigned to the columns of the tables. In this case, we need to get the details of the table structure. MySQL provides the functionality to describe the table using the DESCRIBE statement. Many alternative statements are available in MySQL for describing the table, such as desc, which is the short name of the describe, and show columns internally used by the describe query itself.
Syntax:
The syntax of the describe statement is simple, as shown below:
DESCRIBE name_of_table;Or
DESC name_of_table;Where name_of_table is the table name that you want to describe.
Example of MySQL DESCRIBE table
Let us consider one example: a table named developers inside the educba named database. Now, we want to describe that table.
Code:
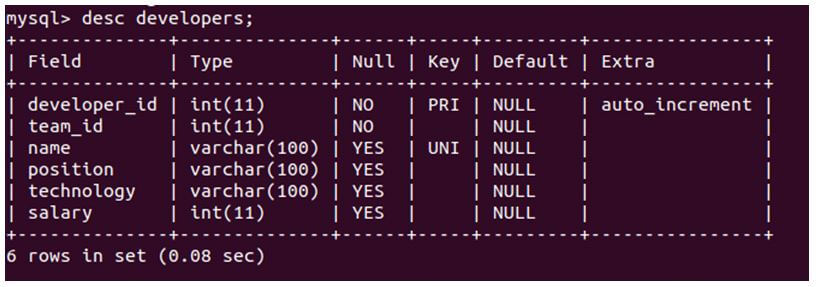
desc developers;Output:
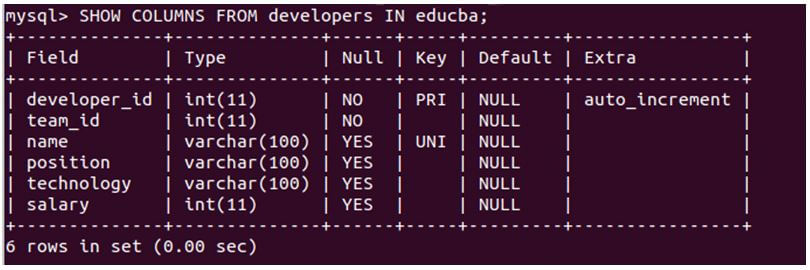
We can see in the output that we get different details for each table column. The field stands for the name o the column; the type is the column’s data type. Null stands for whether the column allows the NULL value in it or not. If the value of the Null is YES, then it will enable a NULL value, while in the case of NO, a NULL value is restricted for storing in that column. The key indicates that the column is being indexed. This can be either primary key indexing, foreign key indexing, or unique index. The default value of a column specifies the value that will be assigned to the column if no explicit value is provided during insertion. The Extra attribute provides additional information about the column and is set to “auto_increment” if the column has the AUTO_INCREMENT option enabled during table creation rather than being left blank.
The above output reveals that the developer’s table consists of six columns, with the names of the columns specified in the Field column of the output. The developer_id column serves as the primary key and has the auto_increment option enabled. The name column has a unique index assigned to it, ensuring that duplicate values cannot be stored in this column of the developer’s table. The developer_id and team_id columns enforce a NOT NULL constraint, ensuring these columns cannot contain NULL values. On the other hand, the remaining columns allow NULL values to be stored in them.
Let us use the alternative of the DESC statement to describe the developer’s table using the following statement.
Code:
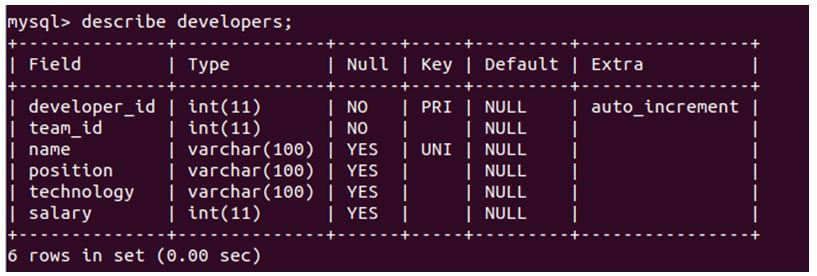
describe developers;Output:
We can see that both of the queries give the same output.
EXPLAIN Statement to DESCRIBE Table
The EXPLAIN statement in MySQL describes complex queries, including the execution plan and the retrieval of rows from each table involved in the query. This statement applies to SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations. Additionally, it can be used to describe the structure of a table.
Let us try using EXPLAIN statement to describe the same table developers using the following query statement.
Code:
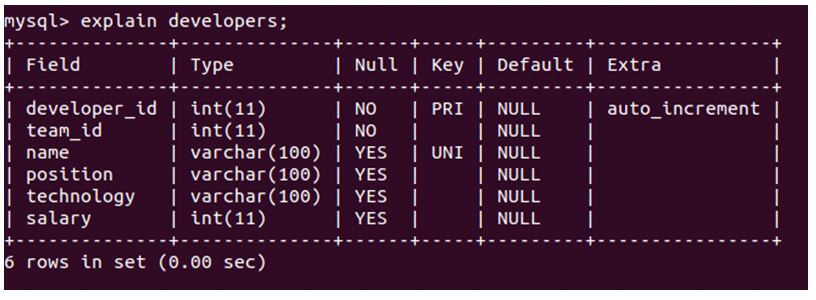
explain developers;Output:
We can observe that the EXPLAIN query gives the same output as the describe statement.
Internal Execution of DESCRIBE Statement
When we execute the described query internally, it runs the same flow as show columns from that table name statement.
Let us see the syntax of the SHOW COLUMNS statement.
Code:
SHOW COLUMNS FROM name_of_table;Where name_of_table is the table name whose column details need to be retrieved.
Let us use the show columns statement to describe the same table developers using the following query statement.
Code:
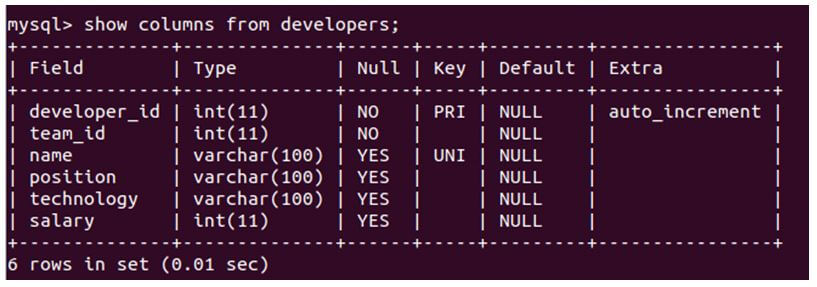
show columns from developers;Output:
We can also mention the name of the database to which the table belongs if we are not using the same database to which the table belongs, as shown in the below query statement.
Code:
SHOW COLUMNS FROM developers IN educba;Output:
If we want to retrieve additional details about the table’s columns, we can use the FULL clause in the SHOW COLUMNS statement, as used below in the query statement.
Code:
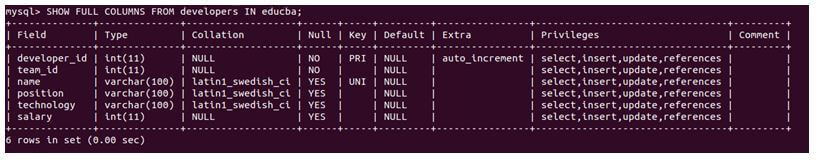
SHOW FULL COLUMNS FROM developers IN educba;Output:
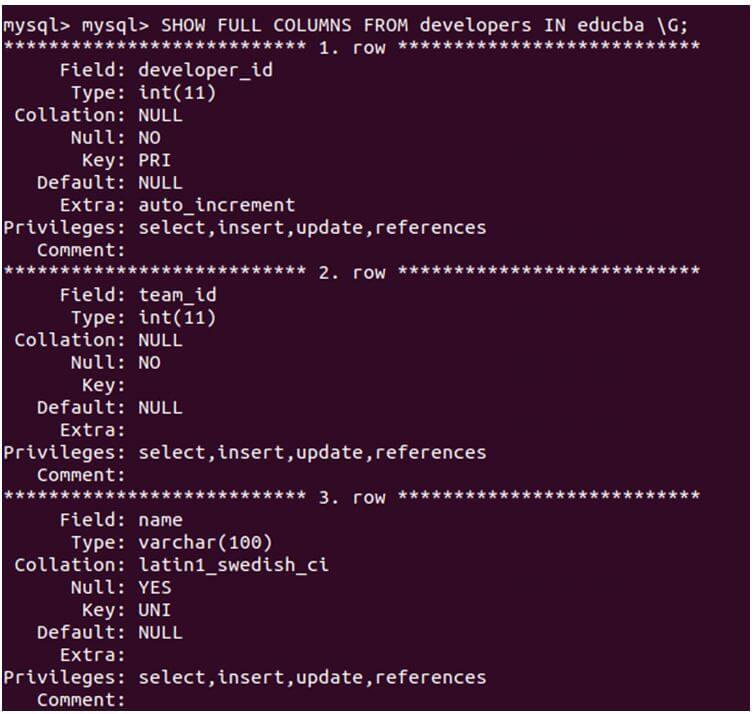
We can see the additional column details, including the collation, privileges, and comments associated with the table’s columns. Privileges encompass the operations that a user can perform on the columns. The comment stands for the comment if we have given it to the column while adding it to the table. If you want to display the description of the columns in the vertical format of the list, then you can use \G in the query.
Let us use the \G in the above command.
Code:
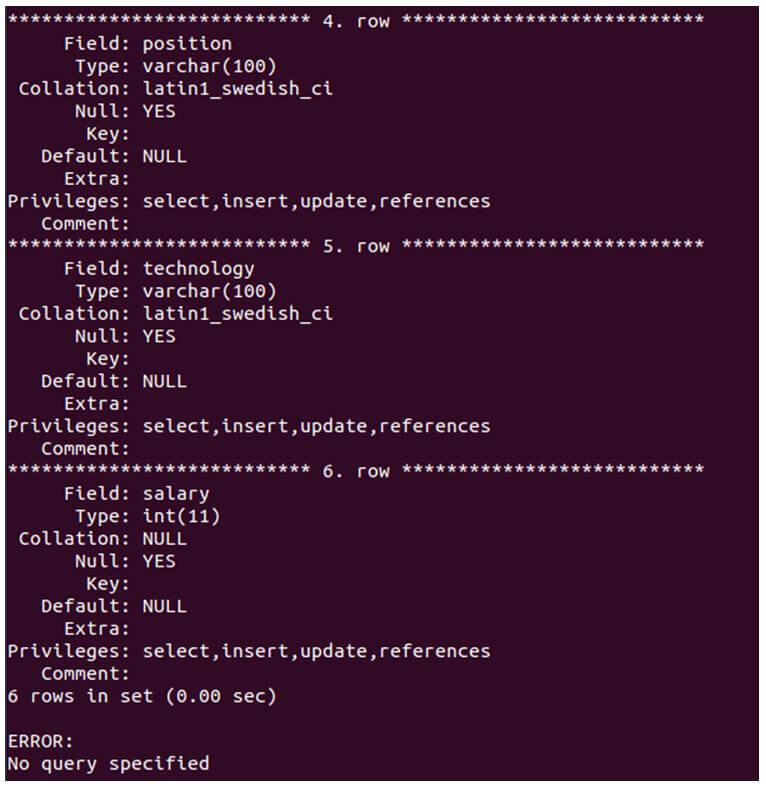
SHOW FULL COLUMNS FROM developers IN educba \G;Output:
If we want to retrieve column details of only columns beginning with t character, you can use the following query statement.
Code:
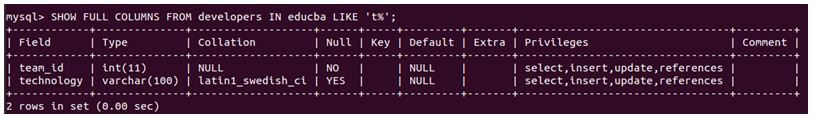
SHOW FULL COLUMNS FROM developers IN educba LIKE 't%';Output:
The output gives the column details of only team_id and technology column, as both begin with the ‘t’ character.
Conclusion
We can use DESCRIBE or DESC statement to get the details of the table’s columns. Other alternatives for describing the table’s columns are the EXPLAIN statement, which is most often used for describing the flow of complex queries. Internally, describe the statement using the SHOW COLUMNS statement to fetch the details of table columns. We can directly use this statement to get details of the table columns.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on the “MySQL DESCRIBE table” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.