Updated May 23, 2023
Introduction to MySQL DATEDIFF
MySQL DATEDIFF is used to find the difference between the specified dates. The DATEDIFF function has two arguments; we specify the dates for which we want to find the difference. The arguments are <date1> and <date2>. The DATEDIFF function calculates only the date portion, ignoring the time portion in the column. We can use the in-built function in the DATEDIFF function as an argument, for example, CURDATE (). Here CURDATE () gets the current system date and calculates the difference with the specified second argument.
Syntax:
Given below is the syntax for DATEDIFF:
SELECT DATEDIFF (<Date argument 1>, <Date argument 2>);The above syntax is used to calculate the difference between the specified dates.
SELECT DATEDIFF (<COLUMN_NAME_1>, <COLUMN_NAME_2>) FROM TABLE_NAME;Here above syntax is used to find the difference between specified column dates.
How does MySQL DATEDIFF work?
Now let us see how the DATEDIFF works in MySQL.
Code:
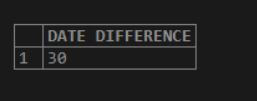
select DATEDIFF( '2020-01-31 00:00:00', '2020-01-01 11:00:00') AS "DATE DIFFERENCE";The above query calculates the difference in dates and returns 30. It considers only the date portion and excludes the time part. The screenshot is for the same.
Output:
Code:
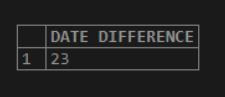
select DATEDIFF( '2020-01-31', '2020-01-01 11:00:00') AS "DATE DIFFERENCE";
/ * - - - DateDiff - - - * /Here the above query returns the date difference between them. The starting date argument doesn’t have a time portion, and the lateral argument has a time portion. It returns 30 even after we perform as the DateDiff will omit time. Here only the date portion is calculated, and the time part is omitted. The screenshot is for the same.
Output:
Code:
select DATEDIFF( '2020-01-31 12:00:78', '2020-01-01') AS "DATE DIFFERENCE";
/ * - - - DateDiff - - - * /Here the above query returns the date difference between them. The starting date argument has a time portion, and the lateral argument doesn’t have a time portion. It returns 30 even after we perform as the DateDiff will omit time. Here only the date portion is calculated, and the time part is omitted. The screenshot is for the same.
Output:
Using CURDATE() in DATEDIFF() Function
Now, let us use the CURDATE () function and try to get the date difference.
Code:
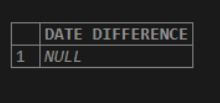
select DATEDIFF( CURDATE() , '2020-07-01 11:00:00') AS "DATE DIFFERENCE";
/ * - - - DateDiff - - - * /Here we have mentioned the in-built function in the <date1> argument, and it returns the system’s current date and calculates with the second argument <date2>, and returns the output.
Output:
Examples of MySQL DATEDIFF
Now let us see how the DATEDIFF works on the table columns.
Let us create a table as below:
Code:
CREATE TABLE DUE_CUSTOMERS
(
CUST_ID INT,
INITIATION_DATE DATETIME,
DUE_DATE datetime
);The above table consists of the data about the customers whose due date is pending. This can be calculated as CURDATE() – DUE_DATE.
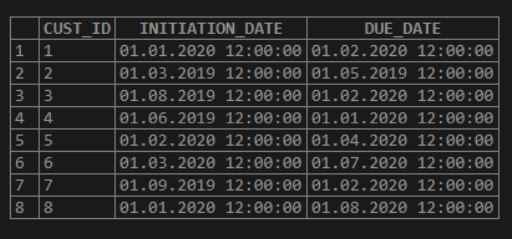
Let us insert the below rows into the above table:
Code:
INSERT INTO DUE_CUSTOMERS VALUES ( 1, '2020-01-01 12:00:00', '2020-02-01 12:00:00' );
INSERT INTO DUE_CUSTOMERS VALUES ( 2, '2019-03-01 12:00:00', '2019-05-01 12:00:00' );
INSERT INTO DUE_CUSTOMERS VALUES ( 3, '2019-08-01 12:00:00', '2020-02-01 12:00:00' );
INSERT INTO DUE_CUSTOMERS VALUES ( 4, '2019-06-01 12:00:00', '2020-01-01 12:00:00' );
INSERT INTO DUE_CUSTOMERS VALUES ( 5, '2020-02-01 12:00:00', '2020-04-01 12:00:00' );
INSERT INTO DUE_CUSTOMERS VALUES ( 6, '2020-03-01 12:00:00', '2020-07-01 12:00:00' );
INSERT INTO DUE_CUSTOMERS VALUES ( 7, '2019-09-01 12:00:00', '2020-02-01 12:00:00' );
INSERT INTO DUE_CUSTOMERS VALUES ( 8, '2020-01-01 12:00:00', '2020-08-01 12:00:00' );select * from DUE_CUSTOMERS;Output:
Now let us perform the DATEDIFF function on the mentioned table:
Example #1
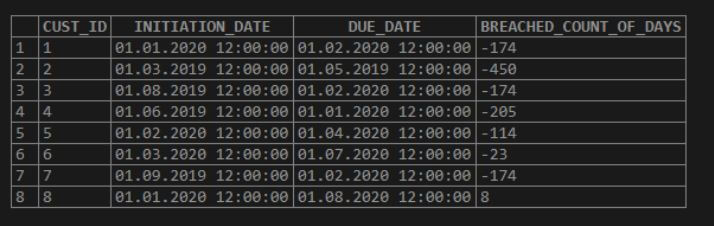
Here we are planning to get the customers who have breached the due_date. The positive values represent that the customer still has those many days to breach the due. If the values are negative, it shows that the customer has already breached the expected with the mentioned days.
Code:
SELECT *, datediff(DUE_DATE, CURDATE()) AS BREACHED_COUNT_OF_DAYS FROM DUE_CUSTOMERS; / * - - - DateDiff - - - * /Output:
Example #2
Here the negative values mean that the customer has breached the due date. The last record has a negative value, meaning the customer has not yet breached the due date.
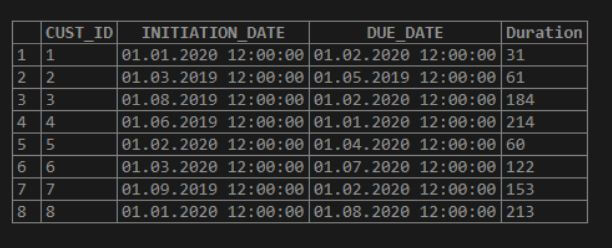
We can obtain the duration of the due time given to the customers.
Code:
SELECT *, datediff( DUE_DATE, INITIATION_DATE ) AS Duration FROM DUE_CUSTOMERS;
/ * - - - DateDiff - - - * /The above query gets the duration of time given to the customer DUE_DATE – INITIATION_DATE.
Output:
The above columns have omitted the time portion of the data, and the table has only calculated the date difference from those columns.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL DATEDIFF” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.