Updated May 23, 2023
Introduction to MySQL DATE_FORMAT()
MySQL DATE_FORMAT() function is a valuable tool in MySQL to design a Date according to the indicated format provided in the query statement to retrieve the date value as output. , the MySQL DATE_FORMAT() function presents the Date value to a given layout or design that it accepts as arguments while executing. Here, the format is a type of string arrangement that includes predefined specifiers in MySQL, where % is a required character to be placed before each specifier. Also, the resultant of MySQL DATE_FORMAT() function is a string, but its character set and collation are based on the settings of the client’s connection.
Syntax of MySQL DATE_FORMAT()
The succeeding syntax specifies the structure to write a query for MySQL DATE_FORMAT() function:
DATE_FORMAT(Date_Value, Format);In addition to this syntax, we use the SELECT keyword with this MySQL function to execute a query statement like this:
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(Date_Value, Format);Hence, the MySQL DATE_FORMAT() function takes two parameters as inputs to provide the required date format structure. Date_Value is the argument that denotes the valid date value that needs to be formatted, and format is the required parameter to define the arrangement or format to be used for the Date_Value.
The format is constructed using predefined specifiers, which results in a string type.
So, we can illustrate the format having one or multiple grouping of the below values:
|
Format |
Explanation |
| %a | Everyday name in the Shortened form [Sun–Sat]. |
| %b | Month name in the Shortened form [Jan – Dec]. |
| %c | Name of Month in numbers [0 – 12]. |
| %D | Daytime of the month is numeric, trailed by suffixes [like 1st, 2nd, …]. |
| %d | Daytime of the month as a numeric form[01 – 31]. |
| %e | Daytime of the month as a numeric form [0 – 31]. |
| %f | Denotes Microseconds within the range [000000 – 999999]. |
| %H | Denotes Hour within range[00 – 23]. |
| %h | Denotes Hour within the range [00 – 12]. |
| %I | Denotes Hour within the range [00 – 12]. |
| %i | Numeric Minutes range [00 – 59]. |
| %j | Daytime of the year [001 – 366]. |
| %k | Denotes Hour within the range [0 – 23]. |
| %l | Denotes Hour within the range [1 – 12]. |
| %M | Full name of the month [January – December]. |
| %m | Numeric name of Month [00 – 12]. |
| %p | Either AM or PM. |
| %r | Denotes Time in 12-hour AM or PM format [hh:mm:ss AM/PM]. |
| %S | Denotes Seconds ranging [00 – 59]. |
| %s | Denotes Seconds ranging [00 – 59]. |
| %T | 24-hour format of Time [hh:mm:ss]. |
| %U | Denotes Week, where the Sun is the initial day of the week [00 – 53]. |
| %u | Denotes Week, where Mon is the initial day of the week [00 – 53]. |
| %V | Denotes Week, where Sun is the initial day of the week [01 – 53] and is also used with %X. |
| %v | Denotes Week where Mon is the initial day of the week [01 – 53] and also used with %X. |
| %W | Name of Weekday in full [Sunday – Saturday]. |
| %w | Daytime of the week where Sunday=0 and Saturday=6. |
| %X | Denotes Year for the week where Sun is the initial day and is used with %V. |
| %x | Denotes Year for the week where Mon is the first day and is used with %V. |
| %Y | Denotes Year as a numeric, 4-digit value. |
| %y | Denotes Year as a numeric, 2-digit value. |
| %% | Supplements percentage (%) character to the result. |
How does MySQL DATE_FORMAT() Function work?
MySQL DATE_FORMAT() function works using the following query structure:
Code:
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(Date_Value, '%a %D %b %Y') as Date_Formatted FROM TableName;In the above query, the Date_Value represents a particular value or any table column value with Date as the Data type and alias as Date_Formatted, which denotes the column title in the output. The result string will be set for the specified format as ‘%a %D %b %Y’, which includes the weekend name in abbreviated form, the name of the day of the month with English suffix, the month name in abbreviated form and four digits year value in number form.
Examples of MySQL DATE_FORMAT()
Given below are the examples of MySQL DATE_FORMAT():
Example #1
Some simple examples using DATE_FORMAT() function.
Some DATE_FORMAT() function examples are written with the following SQL statements:
Code:
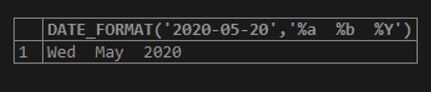
SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2020-05-20','%a %b %Y');This results in the day and month with year as specified in the date provided in the DATE_FORMAT() function.
Output:
Code:
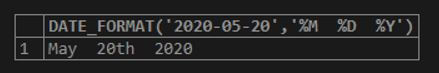
SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2020-05-20','%M %D %Y');Output:
Code:
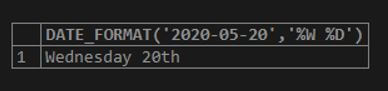
SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2020-05-20','%W %D');Output:
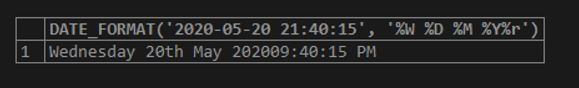
The following query includes a date with a time value also:
Code:
SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2020-05-20 21:40:15', '%W %D %M %Y%r');Output:
The resultant format of the above query displays the time value extracted from the given date value in the argument of the function above.
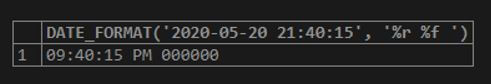
Code:
SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2020-05-20 21:40:15', '%r %f ');Output:
Here, the output has a date format in Seconds.
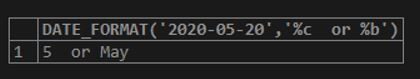
SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2020-05-20','%c or %b');Output:
The result consists of both numeric month names and shortened month names.
Example #2
Example of DATE_FORMAT() function with MySQL NOW() function.
You can also use MySQL NOW() function with the MySQL DATE_FORMAT() to access the present date/time values. This can be defined using the following commands with specifiers.
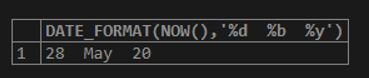
Code:
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(NOW(),'%d %b %y');Output:
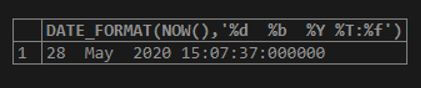
Code:
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(NOW(),'%d %b %Y %T:%f');Output:
Code:
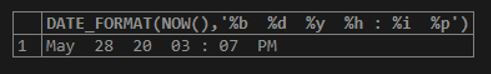
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(NOW(),'%b %d %y %h : %i %p');Output:
Code:
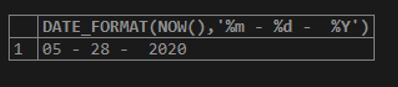
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(NOW(),'%m - %d - %Y');Output:
Example #3
Example of DATE_FORMAT() function with Table Column Value.
Suppose we have a table in the database named Persons; then we will apply the MySQL DATE_FORMAT() function to one of the columns having Date as a data type.
Code:
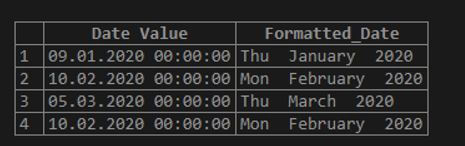
SELECT JoinDate AS 'Date Value', DATE_FORMAT(JoinDate,'%a %M %Y') AS 'Formatted_Date' FROM Persons;Output:
From the above query, we learned that the JoinDate is a column in the table Persons, and using the DATE_FORMAT() function, we display the date values in a specified format.
Conclusion
The MySQL DATE_FORMAT() function defines the arrangement to display the Date/Time value in several formats defined by the specifiers in MySQL. Thus, the MySQL DATE_FORMAT() function provides a date value from 2020-05-27 to Tuesday, May 2020. We can define the required formats using other specifiers with combinations to make the date layout proper.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL DATE_FORMAT()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.