Updated May 26, 2023

Introduction to MySQL CEIL
The MySQL CEIL() function is identical to the MySQL CEILING() function, which finds the minimum integer result value that is either larger than or equivalent to a number. MySQL CEILING() and CEIL() functions are synonyms and can be used interchangeably to take the numbers as inputs to return the respective integer value. Usually, among the Math functions in MySQL, the MySQL CEIL() function is one of the mathematical functions implemented to produce the top or identical value of the input given as an argument to the function. We can provide positive and negative numbers while applying the CEIL() function.
Syntax:
Following is the elementary simple syntax code to use the CEIL() function in MySQL:
CEIL(Numeric_Value)- In the above syntax, the numeric_value term defines the required input for CEIL function argument. This value can be an expression that weighs a number or a precise number.
- According to the type of argument number provided as input, the result number type is specified. The output type depends on the input type specified in the CEIL() query.
- Suppose we have inputted a number with type as an accurate number value or floating-point. The result value type will be exactly that of an exact number or floating-point simultaneously.
How does CEIL Function work in MySQL?
Let us see the working of MySQL CEIL() function in MySQL:
For illustration, we are writing a query using CEIL() function as follows:
Code:
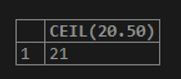
SELECT CEIL(20.50);Here, the MySQL SELECT keyword statement will be used with the math function to display the result value by calculating the number provided in the argument function with the type as a floating point.
Output:
So, it is clear that the CEIL() function will generate the smallest value that is either greater than or similar to the 20.50 input value specified in the above query as 21.
Examples of MySQL CEIL
We will demonstrate examples to show the uses of this math function in MySQL.
Example #1
We now apply the CEIL() function for a positive number in the function’s argument. For this query, we will implement the following query statement.
Code:
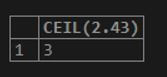
SELECT CEIL(2.43);Output:
In this above example, we know that the result produced has the smallest integer larger than or equal to the number given as input, i.e., 2.43. Thus, the CEIL() function gives three as a result.
Code:
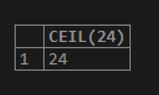
SELECT CEIL(24);Output:
Code:
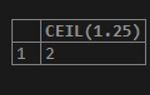
SELECT CEIL(1.25);Output:
Code:
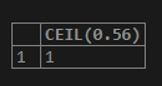
SELECT CEIL(0.56);Output:
Code:
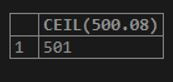
SELECT CEIL(500.08);Output:
Code:
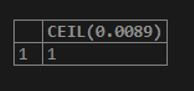
SELECT CEIL(0.0089);Output:
Code:
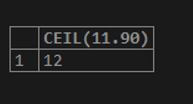
SELECT CEIL(11.90);Output:
Example #2
Let us apply the CEIL() function, providing a negative number as input to produce the output specified below.
Code:
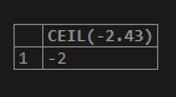
SELECT CEIL(-2.43);Output:
Code:
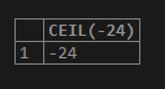
SELECT CEIL(-24);Output:
Code:
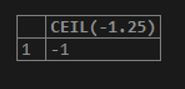
SELECT CEIL(-1.25);Output:
Code:
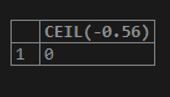
SELECT CEIL(-0.56);Output:
Code:
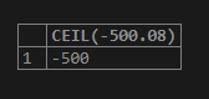
SELECT CEIL(-500.08);Output:
Code:
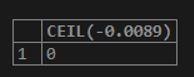
SELECT CEIL(-0.0089);Output:
Code:
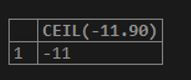
SELECT CEIL(-11.90);Output:
Here, we can see that the output gives the number as a result which is either bigger or identical to the input respectively by the MySQL CEIL() function. The CEIL() function provides the results for negative numbers as per the above observations.
Example #3
Example of MySQL CEIL() function with a query in a table.
Suppose we need a table for querying the column values against the CEIL() function and show its working in the database calculation. For this, we will create the table in the database using the query statement below.
Code:
CREATE TABLE Suppliers(Supplier_ID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, CATEGORY VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, Unit INT NOT NULL, CostEach FLOAT NOT NULL);Also, we will insert some of the demo records for further process of query.
Code:
INSERT INTO Suppliers(Supplier_ID, Category, Unit, CostEach) VALUES
('10','Snacks','10','10.87'),
('11','Drinks','25','15.025'),
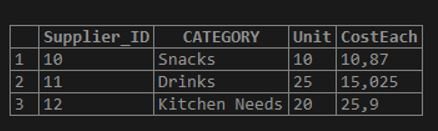
('12','Kitchen Needs','20','25.9');Again, by the following, we will display the contents of the table Suppliers using the SQL statement below.
Code:
SELECT * FROM Suppliers;Output:
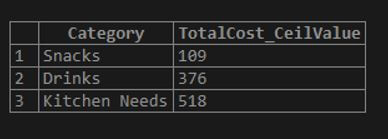
For CEIL() function query, we will illustrate the evaluation using the table column from the table created above as Suppliers. The CEIL() function query for finding the ceil values of the total cost calculated for the supplier items implementing the query code is as follows.
Code:
SELECT Category, CEIL(Unit * CostEach)TotalCost_CeilValue FROM Suppliers30 GROUP BY Category ORDER BY TotalCost_CeilValue;Output:
The above statement provides the ceil values of the cost calculated for each supplier item by multiplying the unit column values with the cost price of each item associated in the Suppliers table. Firstly, this query calculates the total cost for each supplier item. Then the resultant values are then used as inputs for the CEIL() function and then displays the smallest integer values greater than or similar to the input ones.
We should note that here in the table column named CostEach contains the float type values; therefore, the result and total cost calculated for each supplier item will be in decimal form, i.e., float type. After using the CEIL() function, these float values will be produced as result values in integer values, as you can view in the output above.
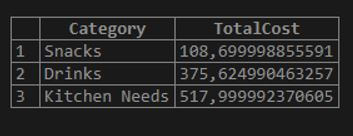
But let us see what the output will be if we do not apply the CEIL() function to the previous query.
For this, we will change the query as follows.
Code:
SELECT Category, Unit * CostEach TotalCost FROM Suppliers30 GROUP BY Category ORDER BY TotalCost;Output:
The output of the query code without the CEIL() function is as follows:
Thus, like the MySQL CEILING() function, the MySQL CEIL() function also works. So, the CEIL() function returns the least integer value but not less than the input number specified in the query function.
Conclusion
The MySQL CEIL() function performs as the mathematical technique where it rounds up the input number provided away from the zero. Actually, it generates the result integer value always up to the given argument value in the CEIL() function. MySQL CEIL() function gives the least integer value, which is not smaller than the input value. Thus, it is helpful in the database to find out the upper values of any table column values for specific conditions.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL CEIL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.