Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Multiple Inheritance in C++
Inheritance is an object-oriented property concept where a class can access the properties and methods of the other class. The class which attains the qualities of the other class is called the derived/child class. The class which gives the right to give its properties to other classes is called base/parent class.
In the concept of Multiple Inheritance, there are multiple base classes and a child class. The derived class can attain its qualities from all the base classes. Let us move further in understanding the concept of Multiple Inheritance in C++ programming language.
Diagram and Syntax of Multiple Inheritance
The diagram for this is:
Diagram:
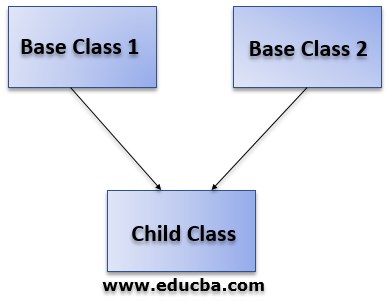
As per the above diagram, we can clearly state that in the case of the concept of multiple inheritances, a derived class can get its properties from both base classes.
Syntax:
class A
{
//code
}
class B
{
//code
}
class c: public A, public B (access_modifier class_name)
{
//code
}How it Works in C++?
Below, let us see the example pertaining to the concept of multiple inheritance in C++ programming language.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base_class_1
{
public:
void show_1()
{
cout<<" This is show function of first base class"<<endl;
}
};
class Base_class_2
{
public:
void show_2()
{
cout<<" This is show function of second base class"<<endl;
}
};
class derived_class: public Base_class_1,public Base_class_2
{
public:
void show_3()
{
cout<<" This is show function of the derived class"<< endl;
}
};
int main()
{
derived_class d;
d.show_1();
d.show_2();
d.show_3();
}Output:

Here, according to the code:
- There are two base classes written and each one had its own method.
- Then we had written a derived class that inherits the properties of both classes. This is done by adding a colon and providing both the base class names.
- In the main class, we had only created an object for the derived class. And access all the methods of all the classes.
- In this way, the inheritance can be done and all the base class properties/variables/methods can be successfully accessed in the derived classes.
In multiple inheritance there can be any number of base classes that should be only greater than 2.
Examples of multiple inheritance in C++
Let us check a few examples for the concept of multiple inheritance.
Example #1
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Value_1
{
public:
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
};
class Value_2
{
public:
int c = 30;
int d = 40;
};
class Value_3
{
public:
int e = 50;
int f = 60;
int g = 70;
};
class Value_4: public Value_1,public Value_2,public Value_3
{
public:
void sum()
{
int result;
result= a+b+c+d+e+f+g;
cout<<" Sum of all the values is: "<<result<< endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Value_4 v;
v.sum();
}Output:
![]()
Now, if we try to exclude the class Value_3 from the inherited classes list. The output would be as below.
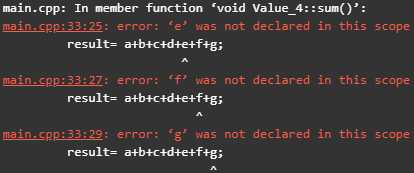
The sum method of the class Value_4 would not find the values of the variables ‘e, f and g’ as the class Value_3 is not being inherited by the class Value_4. So, the output for that program is the compilation error where the values of the variables are not being declared.
Example #2
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Sum
{
public:
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
void sum()
{
cout<<" Result of sum is: "<<a+b<<endl;
}
};
class Mul
{
public:
int c = 30;
int d = 40;
void mul()
{
cout<<" Result of multiplication is: "<<c*d<<endl;
}
};
class Div
{
public:
int e = 50;
int f = 60;
void divi()
{
cout<<" Result of division is: "<< f/e<<endl;
}
};
class Mod
{
public:
int g = 70;
int h = 20;
void mod()
{
cout<<" Result of Modulo Division is: "<< g%h<<endl;
}
};
class Sub: public Sum,public Mul,public Div,public Mod
{
public:
int i = 80;
int j = 90;
void sub()
{
sum();
mul();
divi();
mod();
cout<<" Result of subtraction is: "<<i-j<< endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Sub s;
s.sub();
}Output:
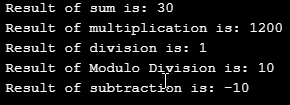
Here, as observed in the derived class method, we have called all the methods of the base classes. And in the main method, we had created an object and called the method only for the derived class, which gave us the perfect output of all the methods.
Example #3
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class First
{
public:
void display_1( int a, int b)
{
cout<< "Values of a and b are: "<<a <<" and "<<b<<endl;
}
};
class Second
{
public:
void display_2()
{
cout<< "This is just an empty method for displaying"<<endl;
}
};
class Third: public First,public Second
{
public:
void display_3(float f1, float f2)
{
cout<< "Values of a and b are: "<<f1 <<" and "<<f2<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
int a;
int b;
cout<<" Enter value for a: "<<endl;
cin>>a;
cout<<" Enter value for b: "<<endl;
cin>>b;
float f1;
float f2;
cout<<" Enter value for float f1: "<<endl;
cin >>f1;
cout<<" Enter value for float f2: "<<endl;
cin>>f2;
Third t;
t.display_1(a,b);
t.display_2();
t.display_3(f1,f2);
}Output:
In this way we can even call the parameterised methods between derived and base classes. In the same way, we can even manipulate the data of the base class in the derived class.
As an exercise, try making few changes to the variables in the methods of derived classes and check how it works.
Conclusion
Here, we have seen the concept of multiple inheritance which can take place through the concept of variables and methods using the C++ programming language. We even displayed the error output in case of accessing the property of the base class without being inherited by the derived class. Keep practicing with different access modifies (public, private and protected) and understand the workflow for the same.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Multiple Inheritance in C++. Here we discuss the introduction and syntax of Multiple Inheritance in C++ along with examples and code implementation. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


