Updated March 14, 2023
Introduction to MongoDB URI
MongoDB provides different types of functionality to the user; the MongoDB URI is one of MongoDB’s functionalities. Basically, URI is used to create the instance of the MongoDB client. In another word, we can say that it is a connection string URI format; by using URI connection string format, we can establish the connection between MongoDB instances and different applications. For connection, we require the different drivers, or we can say that libraries such as nodes.js, java, and python, etc. So we can use any one library as per our requirement. It is also used to establish the connection with the MongoDB deployment.
Syntax of MongoDB URI
Given below is the syntax mentioned:
mongodb://[specified user name: specified password@]host 1[:specified port number 1][,….. host N][:specified port number N] [/[specified database name]][?options]
Explanation:
- mongodb: This is a mandatory prefix to indicate which string has a standard format.
In the above syntax, we used different parameters as follows.
- Specified user name: specified user name means the actual user name, and when we provide the user name, then the password is an optional part of this syntax.
- Specified host and port number: The mongod instance (or mongos instance for a sharded cluster) is operating on this host (and optional port number). A hostname, IP address, or UNIX domain socket can all be specified. Specify as many hosts as your deployment topology requires, and it is used to specify the port number that we need to connect with MongoDB. So we can connect the multiple port number and host numbers as per our requirement. Also, we need to provide the database name that we need to share with different hosts.
How URI Works in MongoDB?
Given below shows how URI works in MongoDB:
Basically, MongoDB URI used different components as follows:
- Specified database name: This is an optional part of URI, but we must authenticate the database using a username and password.
- Option: This is also an optional part of URI, and it provides different connection options to the user, such as a replica set and TLS option.
Connection string option as follows:
- Replica set option: If the mongod is a member of a replica set, this specifies the name of the replica set. It’s critical to provide a seed list of at least two mongod instances when connecting to a replica set. This is because the client will make a solo connection if you just supply the connection point of a single mongod instance and leave off the replicaSet.
- ssl:
true: Establish a secure connection using TLS/SSL.
false: Establish a connection without using TLS/SSL.
False is the default setting. - connectTimeoutMS: The amount of time it takes to attempt a connection before it times out in milliseconds. Although various drivers may vary, the default is never to timeout.
- socketTimeoutMS: The amount of time it takes to send or receive data on a socket before it runs out in milliseconds. Although various drivers may vary, the default is never to timeout.
Pool connection options are as follows:
Some drivers need the connection pool handling for implementation, and some do not support the pool connection.
In the pool, the connection provides the different connection options as follows:
- maxPoolSize: It is used to define the maximum number of connections, and the default size is 100.
- minPoolSize: It is used to define the minimum number of connections, and the default size is 0.
- maxIdleTimeMS: It is used to determine how many milliseconds are required to remain connected.
Write concern options as follows:
Compose concern portrays the sort of confirmations that the mongod and the driver give to the application in regards to the achievement and solidness of the composing activity. For full clarification of compose concern and compose activities, as a rule, see Write Concern.
- W: Relates to the compose concern w Option. The w choice solicits affirmation that the compose activity has spread to a predefined number of mongod occurrences or to mongod cases with indicated labels.
- wtimeoutMS: It is used to determine the time limit of write concern.
Read Concern option as follows:
It is used to provide the isolation level to read the replica set.
- readConcernLevel: It is an isolation level, and it accepts either local or majority level. In the same way, we have another option to establish the connection, such as authentication options, read preference options and server-level selection, etc.
Example of MongoDB URI
Given below is the example of MongoDB URI:
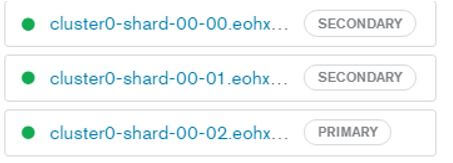
First, we created a cluster by using cloud MongoDB, as shown in the below screenshot as follows.
The above screenshot shows three different clusters one is primary and the other two is a secondary cluster.
Now we need to connect these clusters; then we need to follow the following steps as follows:
- First, we need to click on the connect button.
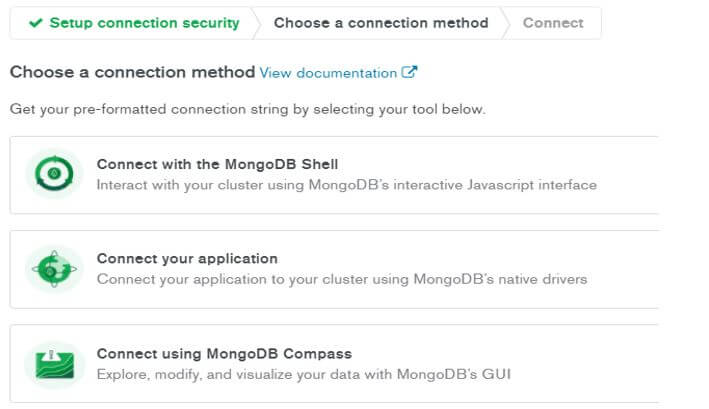
- Then, in a second step, we need to select the connection method as per our requirement.
- For example, suppose we need to connect the clusters by using MongoDB compass, so click on MongoDB compass.
The following screenshot shows the connection method as follows.
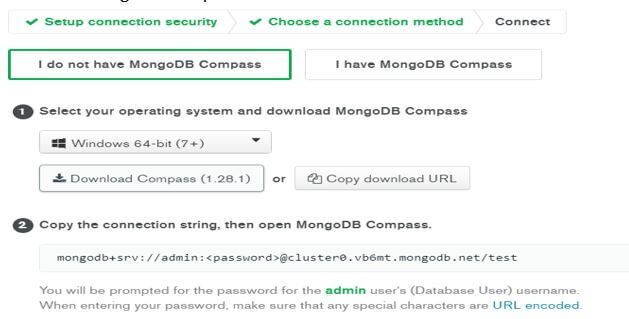
After clicking on the compass button, we need to select the operating system as per our requirement and select the compass version for download. If you have a compass, then you just need to click on I have a compass. In the next step, we need to copy the connection string and paste it into your compass application.
The selection of the operating system and MongoDB compass version is shown in the below screenshot as follows.
mongodb+srv://johan:<password>@cluster0.vb6mt.mongodb.net/test
Explanation:
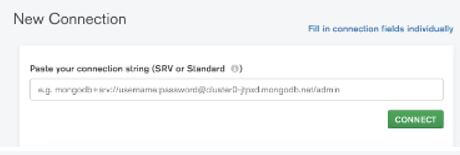
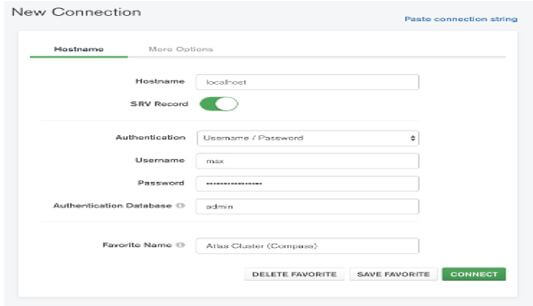
- Above the connection string, we need to paste it into the compass application and click on connect button.
- Cluster connection with compass application as shown in below screenshot as follows.
Conclusion
From the above article, we have seen the basic syntax of the URI, and we also saw different examples of the URI. From this article, we saw how and when we use MongoDB URI.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MongoDB URI. Here we discuss the introduction, how URI works in MongoDB? and examples for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –