Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to Metadata in SQL
Metadata in simple words describe as data about data. Usually, the metadata returns the information about the database, db objects, db files, etc., in the SQL server. In relational databases metadata is said to be consisting the information regarding the schema, storage, etc., Metadata in databases for schema consists of information regarding tables, columns, constraints, foreign keys, indexes, and sequences. It also consists of information regarding the views, procedures, functions, and triggers. Access to this metadata is provided in the form of a set of tables or views called system catalog or data dictionary.
Syntax:
To find ID of a schema object below syntax format is used:
SELECT OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.tablename');Example:
SELECT OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.staging_employee');To find the information about all the columns in db we use the below syntax: –
SELECT nameas "TABLE COLUMN NAMES",column_id AS " COLUMN ID"
FROM sys.columns/* - - - Predefined columns- - - */
WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N’dbo.tablename');Example:
SELECT name as " TABLE COLUMN NAMES",column_id AS " COLUMN ID"
FROM sys.columns/* - - - Predefined columns - - - */
WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.staging_employee');To find the information related to the table we use the below syntax:
SELECT name AS "COLUMN NAME",max_column_id_used "MAX COLUMN ID USED"
FROM sys.tablesTo find the information related to the schema we use the below syntax:
SELECT name AS "SCHEMA NAME",schema_id AS "SCHEMA ID"
FROM sys.schemas /* - - - Predefined Schema - - - */
WHERE principal_id = DATABASE_PRINCIPAL_ID(N'DATABASENAME');Example:
SELECT name AS "SCHEMA NAME",schema_id AS "SCHEMA ID"
FROM sys.schemas/* - - - Predefined Schema - - - */
WHERE principal_id=DATABASE_PRINCIPAL_ID(N'dbo');How does Metadata Work in SQL?
Metadata related result set operations are used in our daily application. For example, we have data types of a column the data type related information can be found in the metadata. We can also get the information related to the length of the column and how much space storage has been taken.
The main usage of metadata is especially in ad hoc queries; we won’t know the metadata of the result set. To get those metadata we need to use the functions SQLNumResultCols, SQLDescribeCol, and SQLColAttribute.
To retrieve result set metadata, we use SQLDescribeCol and SQLColAttribute. SQLDescribeCol always returns the same five pieces of information (a column’s name, data type, precision, scale, and null ability. A single piece of information is returned by the SQLCOLAttribute. However, SQLColAttribute can return a sophisticated selection of metadata, including the information of the column’s case-sensitivity, display size, updatability, and search ability.
Most of the applications that require only the metadata returned by SQLDescribeCol. SQLDescribeCol is faster than the SQLColAttribute because the information is returned in a single call. Rest of the application use SQLColAttribute to require additional metadata and use both the functions.
Metadata is often very expensive to get it from the data source. Because of this reason, we need drivers to cache any metadata. This driver will retrieve it from the server and hold it. It would be easier for the application to request only the metadata that is absolutely needed.
Examples of Metadata in SQL
1. To find ID of a schema object below syntax format is used.
SELECT OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.tablename');Example for the above:
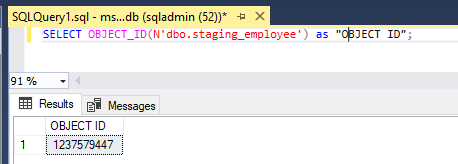
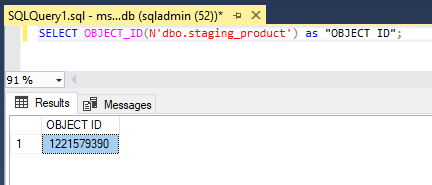
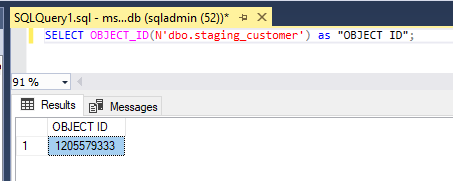
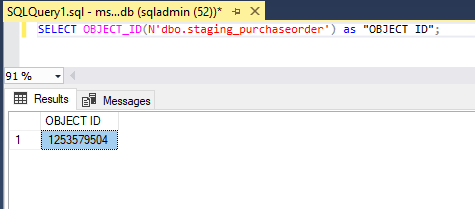
SELECT OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.staging_employee')as "OBJECT ID";SELECT OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.staging_product')as "OBJECT ID";SELECT OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.staging_customer')as "OBJECT ID";SELECT OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.staging_purchaseorder')as "OBJECT ID";2. To find the information about all the columns in db we use the below syntax:
SELECT name as "TABLE COLUMN NAMES",column_id AS " COLUMN ID"
FROM sys.columns
WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.tablename');Example for the above:
SELECT name as "TABLE COLUMN NAMES",column_id AS " COLUMN ID"
FROM sys.columns /* - - - Predefined column table - - - */
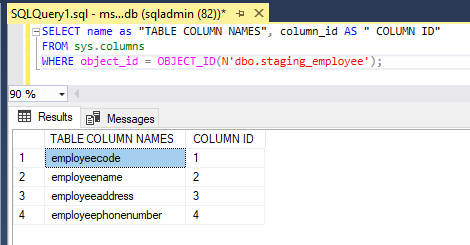
WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.staging_employee');SELECT name as "TABLE COLUMN NAMES",column_id AS " COLUMN ID"
FROM sys.columns /* - - - Predefined column table - - - */
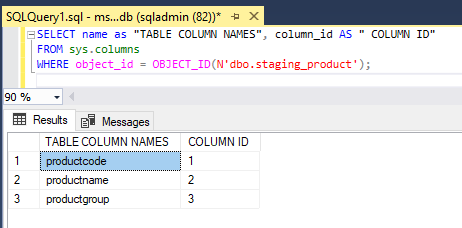
WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.staging_product');SELECT name as "TABLE COLUMN NAMES",column_id AS " COLUMN ID"
FROM sys.columns /* - - - Predefined column table - - - */
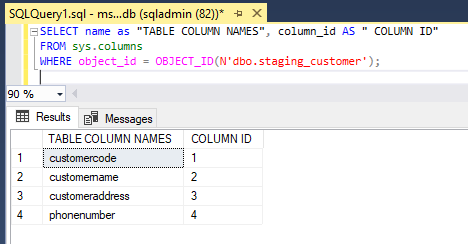
WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.staging_customer');SELECT name as "TABLE COLUMN NAMES",column_id AS " COLUMN ID"
FROM sys.columns
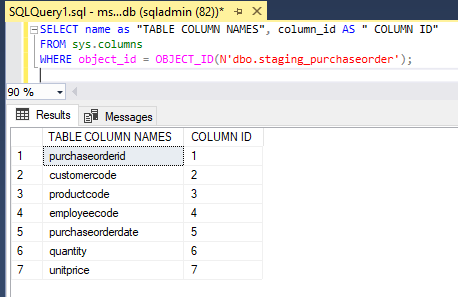
WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.staging_purchaseorder');3. To find the information related to the table we use the below syntax:
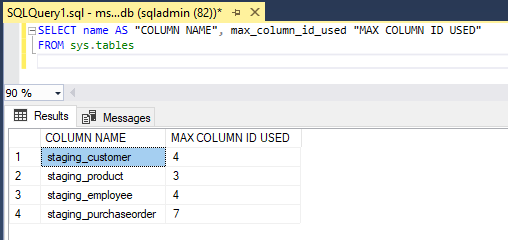
SELECT name AS "COLUMN NAME",max_column_id_used "MAX COLUMN ID USED"
FROM sys.tables4. To find the information related to the schema we use the below syntax:
SELECT name AS "SCHEMA NAME",schema_id AS "SCHEMA ID"
FROM sys.schemas
WHERE principal_id = DATABASE_PRINCIPAL_ID(N'DATABASENAME');Example for the above:
SELECT name AS "SCHEMA NAME",schema_id AS "SCHEMA ID"
FROM sys.schemas
WHERE principal_id = DATABASE_PRINCIPAL_ID(N'dbo');Conclusion
Metadata in simple words describe as data about data. Usually, the metadata returns the information about the database, db objects, db files, etc., in the SQL server. In relational databases metadata is said to be consisting the information regarding the schema, storage, etc., Metadata in databases for schema consists of information regarding tables, columns, constraints, foreign keys, indexes, and sequences.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Metadata in SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.