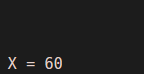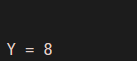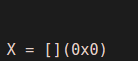Updated March 3, 2023
Introduction to Matlab Global Variables
In MATLAB if various functions declare the name of a variable as global, in that case, these functions will utilize a single instance of the variable called global. If we make any change in the value of that variable, by changing it in any of the function, the change will be applicable to all the other functions using it as a global variable.
Functions have their variables called local variables. The scope of these variables is limited only to the scope of the function itself whereas the scope of the global variables extends to all the functions that call the global variable.
Syntax:
- global v1, v2, v3 ….vn is used to declare any variable as a global variable.
- As it is evident from the syntax, we can set multiple variables as global in a single declaration.
- If we need to clear a global variable, we can use the syntax “clear all” to clear all the global variables defined
How set a Variable as Global in Matlab?
Let us now understand how to set a variable as global in MATLAB:
Example #1
In the first example, we will declare a global variable in the beginning and then will use it inside a function. The steps to be followed for this example are:
- Declare a variable as global
- Create a function
- Call the global variable inside the function
- Call the function to get the output and verify if the global variable is working as expected
Code:
global x
[Declaring the global variable ‘x’]
x = 10;
[Assigning a value to the global variable]
Next, we will create a function that performs the multiplication of 2 integers. One of the inputs will be the global variable declared above.
function A()
global x
X = 6 * x;
X
end
Now if we call the function ‘A’, then the output must be 6 * 10 = 60.
This is how our input and output will look like in the MATLAB command window:
Input 1:
Declaring the global variable:
Input 2:
Creating the function and calling the global variable declared in the above step:
Input 3:
Calling the function ‘A’:
Output:
As we can see in the Output, we have obtained products of 10 & 6 which is 60. Here, we have utilized our global variable defined outside the body of the function as one of the inputs.
Next, we will create another function and will utilize the same global variable ‘x’ created by us in the beginning.
Example #2
In this example, we will create a new function but will utilize the same global variable as we created for our first example. Here, we will not declare a global variable but will simply call it inside the body of our new function. This is a valid approach because we have already declared the variable ‘x’ as global at the beginning of our workspace. The steps to be followed for this example are:
- Create a function
- Call the global variable inside the function
- Call the function to get the output and verify if the global variable is working as expected
Code:
We will create a function that performs a division of 2 integers and will directly use the global variable declared in the first example as one of the inputs.
function B()
global x
Y = 80 / x;
Y
end
Now if we call the function ‘B’, then the output must be 80 / 10 = 8.
This is how our input and output will look like in the MATLAB command window:
Input 1:
Creating the function ‘B’ and using the global variable declared in the beginning of the workspace:
Input 2:
Calling the function ‘B’:
Output:
As we can see in the OUTPUT, we have obtained the division of 80 & 10 which is 8. Here, we have utilized our global variable defined at the beginning of the workspace as one of the inputs.
Next, we will learn how to clear the global variables. For this, we will use the syntax “clear all”. Please keep in mind that, if we use the “clear all” syntax. we will no longer be able to use the global variable ‘x’ defined above in our functions.
Example #3
In this example, we will clear the global variable created by us. The steps to be followed for this example are:
- Use “clear all” syntax
- Call the global variable inside the function
- Call the function to get the output and verify if the global variable is working as expected (it should not give any output, as we have cleared the global variable from our workspace)
Code:
clear all
We will use the same function A created by us in the first example, that performs multiplication of 2 integers
function A()
global x
X = 6 * x;
X
end
Now if we call the function ‘A’, then there must not be any output.
This is how our input and output will look like in the MATLAB command window:
Input 1:
Clearing the global variable created:
Input 2:
Calling the function ‘A’:
Output:
As we can see, we are not getting any value as the output. This is because we do not have any value now for the global variable ‘x’.
Conclusion
- If a function is declared as global, its single instance can be used across various functions.
- “global” is the syntax used to declare any function as global.
- “clear all” can be used if we want to clear the global variables created.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab Global Variables. Here we discuss the introduction, Syntax, How set a Variable as Global in Matlab? and examples with code implementation respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –