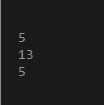Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to Matlabfprintf()
MATLAB fprintf() function is defined to write data as output either to a text file or to any result window. This function processed the data available in the real part of the matrix as well as the data given as any further matrix arguments having the flexibility of applying customization with the help of a defined format string and other name-value pair input arguments. This function can also be used to find the count for the number of bytes written. It can also be configured to throw an error message in case of invalid data operation is being called.
Syntax of Matlab fprintf
Here are the following syntax mention below
| Syntax | Description |
fprintf(file_ID,format_Spec,Arr1,...,Arrn) |
This syntax is used to apply formats specified by the argument,format_Spec, towards all elements of arrays Arr1,…Arrn in respect to the order of the columns. The data gets written to the text file pointed by file_ID. Fprintf()incorporates the encoding scheme in the call forfopen(). |
fprintf(format_Spec,Arr1,...,Arrn) |
This syntax is used to apply format on the input data and produces the results on the screen. |
nbytes = fprintf(___) |
This syntax is used to return the count for the number of bytes that is being written by the function fprintf(). |
Input Arguments
File_ID:
For the function fprintf(),fopen operation can be used to obtain the file identifier file_id in 2 forms such as:
- In the form of standard output on the screen.
- In the form of standard error.
Format_Spec:
This argument, specified with formatting operators, is used to specify formats for the output field. This also includes special characters as well as any ordinary text.
Arr1,…,Arrn:
This represents the character or numeric or arrays, can be of type a vector, scalar, matrix, or multidimensional array.
Output Arguments
nbytes:
This output argument is used to store the count for the number of bytes written byfprintf() either to the input file or as an output string that is displayed on the screen. The supported data type is a scalar and determined using the character encoding.
Examples of Matlab fprintf
Given below are the examples of Matlab fprintf:
Example #1
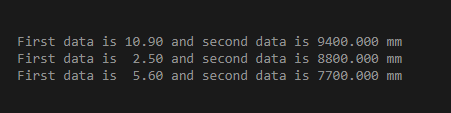
M1 = [10.9, 9400];
M2 = [2.5, 5.6 ; ...
8800, 7700];
formatSpec = 'First data is %5.2f and second data is %7.3f mm\n';
fprintf(formatSpec,M1,M2)
Output:
%5.2f in the format_Spec input customizes the first value that of each row of the output as a floating-point number having a field width of five digits, and after the decimal point, two digits are considered.
Similarly, %7.3f in the format_Spec input customizes each row’s second value as a floating-point number having a field width of seven digits. After the decimal point, three digits are considered.
\n is the control character that is used to add a new line wherever necessary.
Example #2
input = [5.04 13.34 5.26];
fprintf('%d\n',round(input));
Output:
%d in the format_Spec input caused the program to print all values defined in the vector, round(input), formatting them as signed integers.
Application of fprintf() operation
There are various use cases that are being achieved by using the function fprintf(). Such as
1. Reading tabular data from a text file
Fprintf() can be used to read the tabular data present in a text file without disturbing the tabular format. The function fopen is used to create file_ID for the text file.
File_ID = fopen('exp.txt','w');
frpintf() needs to be used twice: One to fetch the headers and the second command to fetch the data with respect to the headers.
fprintf(fileID,'%6s %12s\n','header1','header2',..);
fprintf(fileID,'%6.2f %12.8f\n',dataheader1,dataheader2,….);
2. Finding the size of the content of the file
The fprintf() function can be used to find the size of the content present in the file by fetching the count of the number of bytes being written to a new file using the fprint() function.
The function fopen is used to create file_ID for the text file.
File_ID = fopen('newfile.txt','w');
The resultant count value gets stored in the variable nbytes
nbytes = fprintf(file_ID,'%6d %5d %6d %5d\n', Input)
3. Display Hyperlinks in Command Window
The function can be used to display a hyperlink in the form of a clickable link on the screen.
The variable url is defined to hold the url address, and the site carries the display text for the address. url = ‘https://www.myurladdress.com’;
site = 'My site name';
The url needs to be configured in html format in the fprintf() call.
fprintf('<a href = "%s">%s</a>\n',url,site)
%s in the format_Spec input is used to indicate the values of the variables url and site name in printable text format.
How can formatting be applied in the case of fprintf() operation?
A formatting operator is defined as having a percent sign, %, at the beginning, and a conversion character at the end.
<image>
Different conversion characters supported by fprintf such as:
%u- Supports Integer with unsigned-Base 10
%f- Supports Fixed-point notation to use a precision operator to the digits after the decimal point.
%s-Supports string array or character vector. In this case, the output text type is the same as theformat_Spec type.
Optional Operators of Matlab fprintf
The optional identifier such as field width, subtype operators, precisions, flags, etc., further contributes to formatting operation on the output text.
Field Width can be defined as the minimum number of characters that need to be available in the given input data to print.
Subtypes operators are used to printing a floating-point value with different base values such as its decimal, octal, or hexadecimal form. The subtype operator is the immediate precedes to that of the conversion character.
Additional Note
1. Format specifiers used for the reading functions such as fscanf() and sscanf() differ from the format specifiers used for the functions exhibiting writing operations such as sprintf() and fprintf(). The reading functions specifiers do not support a precision field whereas the writing function specifiers have incorporated the feature.
2. Format_Specfprintf() also supports the inclusion of additional text preceding to a percent sign, %, or following the given conversion character.
The text can be of two forms. They are:
- Any ordinary text string to print.
- Special characters can not be used as an ordinary text and hence needs to be defined in formatSpec, following a standard form of representation.
Example:
Single quotation mark (‘)- ‘’
Backslash (\)- \\
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab fprintf. Here we discuss How formatting can be applied in the case of fprintf() operation along with the Examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –