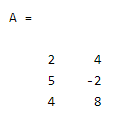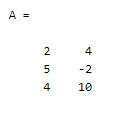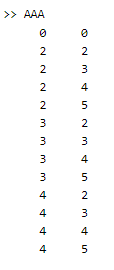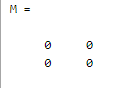Updated March 6, 2023
Definition of Matlab 2D Array
Matlab provides the functionality to implement the array, in which we can implement multidimensional arrays such as 2D arrays. With the help of a 2D array, we can manipulate the matrix, the structure of the matrix contains the rows and columns and each value from the matrix contains the row index and column index. By using 2D arrays we are able to perform different operations on matrices such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division when we have a multidimensional matrix as per the user requirement. We can also access the different element or value through the 2D array by using the row index and column index.
Syntax:
variable name = size(Array)
variable_name=size(A,size of array)
Explanation: In the above syntax, we use different parameters as follows.
- variable_name: It is a user-defined name we can assign any name that we want.
- size: Size is a function with help of size we can return the row vector that length corresponding to the size of Array.
- Same variable we used in the second syntax as shown. Here we just added the size of the array. It helps us to return the length of the array with positive integer scalar. So by using this syntax we create 1-dimensional array, two-dimensional arrays, and three-dimensional arrays, and so on.
How to Declare 2D Array in Matlab?
Now let’s see how we can declare the 2D array in Matlab as follows. The declaration of the array is very simple in Matlab. We can easily declare the 2D array in Matlab as follows.
m_array = zeros (value 1, value 2)
Explanation: This is the first way to declare the 2D array in Matlab, here we use the zeros () function and inside the zeros () function we need to pass the value 1 and value 2 as shown in the above statement. Another way to declare the 2D array is that we pass the single value inside the zeros () function as shown in the below statement as follows.
m_array = zeros (value)
Let’s see an example for better understanding of the declaration of a 2D array as follows.
m_array = zeros (3);
Explanation: See here we use zeros () function to draw the 2D array in Matlab. Here we pass the value to the zeros () function that is 3. That means we need to draw the 3 by 3 array. So similarly we can pass the different values inside the zeros () function as per our requirement.
How to Initialize 2D Array in Matlab?
Now let’s see the initialization of the 2D array in Matlab as follows. For initialization of 2D arrays we can use the same function that zeros () function.
A = matrix (value1, value2)
This is a very simple syntax of array initialization in Matlab. Here matrix means zeros () function and inside that function we need to pass the value as per the requirement.
Now let’s see the example for more details as follows.
M = [1 2; 4 -8; 5 8]
By using the above statement we created a 2 by 2 array that 2D array. So in this way we can initialize the array.
How 2D Array Work in Matlab?
Now let’s see how 2D arrays work in Matlab as follows.
Basically in Matlab we have different ways to create the 2D array, so for that reason we need to pass the different input arguments to Matlab as follows.
- First size of 2D array or we can say that size of matrix: The size of a 2D array is always an integer value, suppose size of array is less than or equal to zero then we can say that the matrix is empty and if size of array is negative then it is considered as zero.
- After that we need to specify the size of each dimension: Size of dimension should be integer if value is 0 then matrix is empty and if value is negative then it is considered as zero.
- Size of row vector: It also uses the same properties that if the value is less than zero then the matrix is empty and if the value is negative then it is treated as zero.
Now let’s see the output argument
The output argument of a 2D array is that matrix or we can say that matrix. Basically the output argument depends on the input argument. In another way we say that the output argument shows the actual result that we want.
Example of Matlab 2D Array
Now let’s see the different examples of 2D arrays in Matlab for better understanding as follows.
Let’s see the very basic example of a 2D array as follows.
A = [2 4; 5 -2; 4 8]
Explanation: Suppose we need to create a 2D array that is size 2 by 2. At that time we can use the above statement to create the 2D array. In the above example we use A as a variable name that is used to store the matrix values in form of row and column,, actually that array is the array value as shown above statement. Inside the array we can declare the positive as well as negative value. In this example we need to create 3 rows and 2 columns where a semicolon is used to indicate the next row. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see another way to implement the 2D array as follows.
A = [2 4
5 -2
4 10]
Explanation: In the above example we avoid the use of semicolons and see how we can write the rows on the command line window. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the screenshot as follows.
Let’s see another example of a 2D array using a loop as follows.
M =[0 0];
for j=2:4
for k=2:5
M=[M;j k];
end
end
disp(M)
Explanation: By using a for loop we try to implement the 2D array. Here we use two for loops: inner and outer for loop as shown in above example. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see how we can create the 2D array by using zeros () function as follows.
M = zeros(2)
Explanation: In the above example we use zeros () function to create a 2D array, by using the above statement we can create the 2 by 2 empty array. The final output of the above statement we illustrated by using the screenshot as follows.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn Matlab 2D arrays. From the above article we have learned the basic syntax of 2D arrays and we also see different examples of 2D arrays. From this article we learned how and when we use Matlab 2D arrays.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab 2D Array. Here we also discuss the definition and how to declare 2D array in Matlab? along with examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –