What is Marketing Mix Modeling?
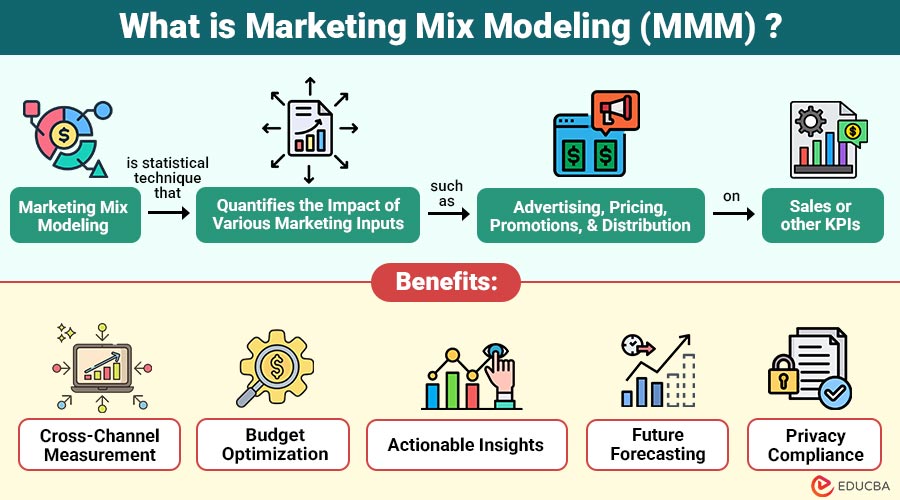
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) is statistical technique that quantifies the impact of various marketing inputs—such as advertising, pricing, promotions, and distribution—on sales or other KPIs. It evaluates historical data to identify which factors most strongly influence performance and how adjusting the marketing mix can improve future results.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Marketing mix modeling quantifies marketing channel contributions, enabling data-driven decisions for budget allocation and performance optimization.
- It integrates offline and online channels, offering a holistic view of marketing effectiveness and ROI.
- Historical data analysis and modeling help forecast future outcomes, improving accuracy in marketing investment decisions.
- Marketing mix modeling ensures privacy compliance, measures impact without user-level tracking, and efficiently guides strategic marketing initiatives.
Why is Marketing Mix Modeling Important?
Here are some key reasons why marketing mix modeling is important:
1. Privacy-safe Measurement
Provides privacy-safe measurement by relying on aggregated data rather than individual-user-level tracking across platforms.
2. Holistic Channel View
Delivers a holistic view by integrating performance insights across online and offline marketing channels seamlessly.
3. Marginal ROI Measurement
Quantifies marginal ROI to clearly understand the incremental impact and efficiency of each marketing channel investment decision.
4. Budget Optimization
Helps optimize future budget allocation by reallocating spending toward channels that consistently deliver higher returns over time.
5. Improved forecasting
Improves forecasting accuracy by modeling how marketing investments influence future business outcomes with higher confidence.
How does Marketing Mix Modeling Work?
MMM relies on analyzing multi-year historical data to identify relationships between marketing inputs and sales outputs.
The MMM process typically follows these steps:
Step 1: Data Collection
Historical data is gathered across marketing channels, business outcomes, and external variables over a consistent time period.
Step 2: Data Preparation
Data is cleaned, normalized, and aligned to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Step 3: Model Building
Statistical techniques, such as multiple regression or Bayesian modeling, are used to estimate channel contributions.
Step 4: Validation and Calibration
Models are tested for accuracy, stability, and business logic before being finalized.
Step 5: Insights and Optimization
Results are translated into actionable insights, including ROI, contribution percentages, and budget recommendations.
Key Components of Marketing Mix Modeling
Here are the key components of marketing mix modeling:
1. Base Sales
The portion of sales occurring without marketing influence, driven by brand strength and trends.
2. Incremental Sales
Additional sales generated directly by marketing efforts, showing the tangible impact of campaigns.
3. Adstock Effect
Represents the lingering influence of advertising, continuing to affect sales even after campaigns end.
4. Diminishing Returns Curve
Illustrates that beyond a certain investment level, additional marketing spend yields minimal incremental sales uplift.
5. ROI and Contribution
Measures each marketing channel’s return on investment and its share of overall revenue growth.
6. Optimization Scenarios
Uses predictive models to simulate different budget allocations and forecast potential future marketing outcomes.
Benefits of Marketing Mix Modeling
Here are the key benefits of marketing mix modeling:
1. Cross-Channel Measurement
Provides a comprehensive, unified view of marketing effectiveness across offline and online channels.
2. Budget Optimization
Helps allocate marketing budgets efficiently, ensuring maximum return on investment across all channels.
3. Actionable Insights
Identifies high-performing channels and areas needing improvement, enabling informed, strategic marketing decisions.
4. Future Forecasting
Accurately predicts potential sales outcomes across different budget allocations and marketing scenarios.
5. Privacy Compliance
Measures marketing impact without relying on cookies, user-level identifiers, or personal data, ensuring regulatory adherence.
Challenges in Marketing Mix Modeling
Here are some common challenges in marketing mix modeling:
1. Long Data Requirements
Accurate MMM models require 24 to 36 months of comprehensive historical marketing and sales data.
2. Slow to Adapt
MMM is not suitable for real-time decision-making due to modeling and analysis timelines.
3. Data Quality Issues
Poor-quality or incomplete input data directly leads to unreliable and inaccurate modeling results.
4. Complex to Build
Building MMM requires skilled statisticians, data engineers, and analysts for proper implementation.
5. Difficulty in Capturing External Shocks
Unexpected events such as pandemics, economic crises, or sudden shifts in consumer behavior can distort models.
Use Cases of Marketing Mix Modeling
Here are some common use cases of marketing mix modeling:
1. Consumer Goods
Analyze the impact of TV, in-store promotions, pricing strategies, and distribution on sales performance.
2. E-commerce
Measure the effectiveness of digital channels, including influencers, SEO, paid advertising, and remarketing campaigns on conversions.
3. Retail
Assess the influence of promotions, loyalty programs, and offline advertising on customer engagement and sales.
4. Automotive
Understand how media campaigns, test drives, and dealership events contribute to overall vehicle sales outcomes.
5. Telecom
Measure the effect of marketing campaigns, bundling offers, and pricing changes on subscriber growth and revenue.
Real-World Examples
Here are some real-world examples of marketing mix modeling in action:
1. Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) Companies
Large consumer goods companies use MMM to understand the impact of TV ads, in-store promotions, and digital campaigns on product sales. This allows them to optimize media budgets across channels.
2. Retail Brands
Retailers analyze how seasonal discounts, social media campaigns, and email marketing drive footfall and online conversions. MMM identifies the most profitable channels for each product category.
3. Automotive Industry
Car manufacturers use MMM to evaluate how dealership promotions, TV commercials, and sponsorships affect sales, enabling more precise allocation of marketing funds.
4. E-commerce Businesses
Online marketplaces use MMM to evaluate digital ads, influencer marketing, and retargeting campaigns, optimizing spending to maximize conversions.
Final Thoughts
Marketing mix modeling provides brands with data-driven insights into sales drivers and helps optimize budgets across channels. In today’s complex, privacy-regulated marketing environment, MMM provides a future-proof framework that does not rely on personal data. Analyzing past performance, forecasting outcomes, and guiding smarter investments enable organizations to make strategic, profitable decisions while maximizing ROI in competitive markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is marketing mix modeling used for?
Answer: MMM measures the impact of marketing efforts and helps optimize budgets and forecast future results.
Q2. How much data is required for MMM?
Answer: Typically, 24–36 months of historical data improves accuracy.
Q3. Does MMM replace digital attribution?
Answer: No. MMM complements attribution by providing a holistic view across online and offline channels.
Q4. How often should MMM be updated?
Answer: Quarterly or semi-annually for best accuracy.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Marketing Mix Modeling” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.