Updated June 15, 2023

Introduction to Macros in C
In the C programming language, the compilation process involves sending the C program to the compiler, which translates the program into machine language. Prior to compilation, the C preprocessor, also known as a macro preprocessor, performs certain tasks. The sign “#” denotes macros, and the compiler processes the statements associated with this symbol.
Examples of Macros in C
As discussed above, there are two types of macros. They are:
1. Object-Like Macro
In the C programming language, a macro is a pointer variable, identifier, or variable generated with the #define directive.
Example:
#define MAX 100In this case, we can use the macro name “MAX” with the value 100, which will be substituted with “MAX.”
2. Function-Like Macro
This macro is similar to a function call in the C programming language.
Example:
#define ADD (p, q) (p) + (q)Before using macro in C programming, we should note the following points:
- When we use the #define statement to define a constant with a macro name, it remains constant throughout the program. Example:
#include<stdio.h>
#define PI 3.14
intmain()
{
printf("The value of Pi is %f", PI);
return 0;
}Output:
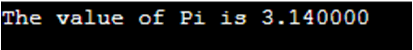
Similarly, in the C program, “#include” is used to include the header files. For example, we saw in the above code “#include<stdio.h>” in this “stdio.h” is a header file; we use this header file because to read and print the values, we use “printf” and “scanf” are within this “stdio.h” header file.
- It’s worth noting that when the argument is supplied to the function-like macro, it accepts any datatype. Let us consider an example below:
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
#define INCREMENT(n) ++n
intmain()
{
char *p = "Educba";
int a = 20;
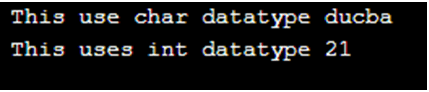
printf(" This use char datatype %s ", INCREMENT(p));
printf("\n This uses int datatype %d", INCREMENT(a));
return 0;
}Output:
- The macro can alternatively be written in numerous lines, beginning each statement with “” and ending with “”. Let us see an example of this:
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
#define MACRO(n, limit) while (n < limit) \
{ \
printf("Educba "); \
n++; \
}
intmain()
{
int n = 0;
MACRO(n, 5);
return 0;
}Output:

- When defining macros in C that are used for conditional compilation, conditional statements such as if-else directives can be used within the macro. Let us consider an example:
Example:
intmain()
{
#if VERBOSE >= 2
printf("Message");
#endif
}No Output:
- If a function-like macro is used with arguments passed to it, the arguments are not evaluated before the macro expansion occurs. Let us see the example:
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
#define DIV(a, b) a/b
intmain()
{
printf("%d", DIV(5+3, 3+2));
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
Here the above macro is expanded as 2 +3 /3 + 5 = 2 + 1 + 5 =8, which is confusing, so you can resolve by the below-modified macro.
#include <stdio.h>
//here, instead of writing a*a we write (a)*(b)
#define DIV(a, b) (a) / (b)
intmain()
{
printf("%d", DIV(5+3, 3+2));
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
The macro expands to (2 + 3) * (3 + 5), which simplifies to 5 * 8, resulting in 40.
- Let us see an example:
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
#define concate(p, q) p##q
intmain()
{
printf("%d ", concate(56, 78));
}Output:
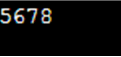
The given code defines a function-like macro that takes a token and concatenates it with the values “p” and “q”.
- Let us see an example:
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
#define get_string(n) #n
intmain()
{
printf("%s", get_string(Educba));
}Output:

Conclusion
In C programming language, the macro is not less than similar to functions, but macro has built-in macro also. The macro uses the “#define” directive to define the macro in the C programming language. This is very useful to save time and have less code writing.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Macros in C” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


