Updated June 5, 2023
Introduction to Lua for loop
In Lua script for loop is one of the features. It is one of the conditional loop structures for initializing or declaring the values to the variables, which depends upon both user or customized and predefined variables; check the conditions by using some conditional operators, increment or decrement the variables with satisfy the boolean conditions if the loop is satisfied their conditions it will execute the other statements that is if a boolean condition is true else if the condition is false it will terminate the loop so that the for loop is the repetition loop control structure which depends upon the user condition mentioned in the loop statement.
Syntax:
Lua script has some basic functionality for each keyword, variable, and method for user or custom items. Here for loop is one of the conditional loop structures, and it is used for iterating the values with different time intervals. Based on the initialization, the values will be validated and increment.
For initializing a variable with a value, maximum/ minimum conditional value, increment/ decrement, the values
do
----some lua script code logics depends upon the requirement----
EndThe above codes are the basic syntax for utilizing the for loop to iterate the values. We also use the do keyword for starting or performing the loop operations; once evaluated the conditions the loop will end by using the end keyword.
Flowchart
The Lua script has separate workflows for every conditional statement and method. We have a flowchart to know the workflow of the Lua script-based application.
<image>
The above diagram is the flowchart and workflow for the for loop structure.
How for loop work in Lua?
Generally, for loop is one of the features and conditional statements for executing the application. Due to the declaration and initialization of datas, they can be populated and structured in the application in a more sophisticated. Whenever we initialize the variable, it must be the first and most priority thing for any loops in the script for controlling the variables. In the next step, we can check and evaluate the variables with some conditions like maximum or minimum values to execute the statements with further steps. Once completed in the second step, it goes to the third and final step of the for loop; we can increment/decrement the variables.
Based on the user requirement, we can increase or decrease the variable values; this statement is only for updating the loop variables with control structures. If the above steps are evaluated successfully, the boolean condition is assigned as true, or it goes to the false statement. Also, it terminates the loop automatically in the script. The “for” loop is an efficient repetition control structure that allows the processing or operation of user data for multiple iterations based on the user’s requirements.
Example #1
Code:
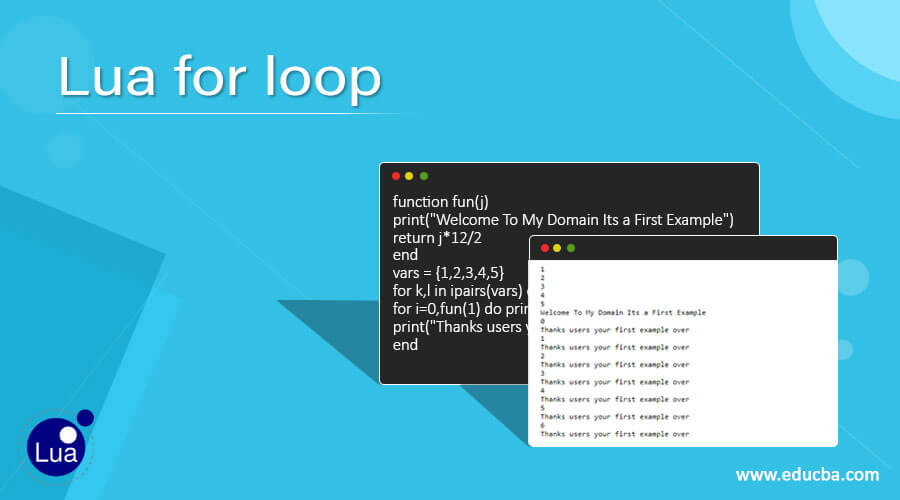
function fun(j)
print("Welcome To My Domain Its a First Example")
return j*12/2
end
vars = {1,2,3,4,5}
for k,l in ipairs(vars) do print(l) end
for i=0,fun(1) do print(i)
print("Thanks users your first example over")
endOutput:
The above example we used for loops in different formats. Here we can use one function, passing the parameters as func(j). By using this variable, we can perform some mathematical operations like j*12/2; with the help of this formula, we can calculate user input values with the help of for loop the values are repeating and iterating the input values and printed on the output console. We used the recursion concept to calculate the output with the user inputs mentioned.
Example #2
Code:
a="123 456 789 12354 643 -6313 4652 2156435 62134 1275 127536 21756 217564 21753 2175 1275 2156 21756 1275 7215"
b=loadstring("return {"..a:gsub("%s+",",").."}")()
for i,j in ipairs(b) do print(i,j) end
str = "Welcome To My Domain Its a second example"
for k in string.gmatch(str, "%a+") do
print(k)
end
if(str == 'Welcome') then
print("Your input is validated")
else
print("Thanks for giving the inputs to the screen and it will not get the exact match \n so Please provide your inputs it will helpful for validating the code")
endOutput:
In the second example, we utilized a variable containing string-type values, which included integer inputs enclosed in double quotes (“”). The input values were separated and split using the loadstring() method. At the same time, we use for loop to iterate and match the exact inputs to the number formats. Here string.gmatch() method will evaluate and match the same user inputs to the other type like string or integer. We can also validate the given input strings in the if loop; it is one of the condition loop statements for validating user datas. After iterating and matching the user input string to an integer type, we can validate the values in the if statement.
Example #3
Code:
vars=string.format
vars1 = {"one two three four five"}
vars1[0]="zero"
vars1[1] = "one"
vars1[2] = "two"
print("\nWelcome To My Domain its third example")
local t=0
for t= 1, #vars1 do
print(vars("t=%s, u=%s", tostring(t), tostring(vars1[t])))
end
print("\n Thanks for giving the inputs to the screen and will get the exact match outputs")
for t=2, table.maxn(vars1) do
print(vars("t=%s, u=%s", tostring(t), tostring(vars1[t])))
endOutput:
In the final example, we used for loops to iterate the values and the tostring() method to map the exact number to string type values. Each value will have stored as separate rows and columns in the table structure. Here table keywords will help to create and store the data in the table format.
Conclusion
In conclusion, part Lua script is one of the system-level programming languages, and the client side validates these scripts. Like for loop is one of the basic conditional statements, and using these loop, n number of values will be iterated and printed. The Lua script supports all types of browsers and operating systems.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Lua for loop” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.