Updated July 1, 2023

Introduction to Loops in C++
Loop statements in C++ execute a certain block of the code or statement multiple times, mainly used to reduce the length of the code by executing the same function multiple times and reducing the code’s redundancy. C++ supports various loops like for loop, while loop, and do-while loop; each has its syntax, advantages, and usage. In the programming world, the loop is a control structure that is used when we want to execute a block of code, multiple times. It usually continues to run until and unless some end condition is fulfilled.
If we did not have loops, we would have to use the iterative method to print a repetitive block of statements, which would look something like this:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << " Good morning \n";
cout << " Good morning \n";
cout << " Good morning \n";
cout << " Good morning \n";
cout << " Good morning \n";
}Output:

In this example, we have printed “Good morning” five times by repeating the same set of lines.
A loop has a certain set of instructions. We use a counter to check the condition for loop execution in a loop. In cases when the counter has not yet attained the required number, the control returns to the first instruction in the sequence of instructions and continues to repeat the execution of the statements in the block. If the counter has reached the required number, that means the condition has been fulfilled, and control breaks out of the Loop of statements and comes outside of the loop to the remaining block of code.
Types of Loops in C++
Now that we have seen how a Loop works let us make it clearer by going through the types of Loops out there. In C++ programming, we have three types of Loops in C++ :
- For Loop
- While Loop
- Do While Loop
For Loop
Loop is an entry controlled loop, meaning that the condition specified by us is verified before entering the loop block. It is a repetition control structure. The loop written by us is run a specified number of times.
To control the loop, we use a loop variable in For loop. This variable is first initialized to some value, then we perform the check on this variable, comparing it to the counter variable, and finally, we update the loop variable.
Syntax:
for(initialization expression; test expression; update expression)
{
// statements to execute in the loop body
}Initialization Expression:
Here we initialize the loop variable to a particular value. For example, int i=1;
Test Expression:
Here, we write the test condition. If the condition is met and returns true, we execute the loop body and update the loop variable. Otherwise, we exit the For loop. An example for test expression is i <= 5;
Update Expression:
Once the body of the loop has been executed, we increment or decrement the value of the loop variable in the update expression. For example, i++;
Let us look at an example of For loop:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
{
cout << " Good morning \n";
}
return 0;
}Output:

While Loop
While the loop is also an entry controlled loop, we verify the condition specified before running the loop. The difference is that we use For loops when we know the number of times the body of the loop needs to run, whereas we use while loops in circumstances when beforehand we do not know the precise number of times the body of the loop needs to run. The execution of the loop is terminated based on the test condition.
Syntax:
initialization expression;
while (test_expression)
{
// statements to execute in the loop body
update_expression;
}The syntax of the loops differs only in the placement of the three expression statements.
Let us look at an example of while loop:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 0; // initialization expression
while (i < 5) // test expression
{
cout << "Good morning\n";
i++; // update expression
}
return 0;
}Output:

Do While Loop
Do while loop is an exit controlled loop meaning the test condition is verified after the execution of the loop, at the end of the body of the loop. Hence, the body executes at least once, regardless of the test condition, whether it is true or false. In a while loop, the condition is tested beforehand, whereas in a do loop, the condition is verified at the finish of the loop’s body.
Syntax:
initialization expression;
do
{
// statements to execute in the loop body
update_expression;
} while (test_expression);In do while loop, we end the body of the loop with a semicolon, whereas the other two loops do not have any semicolon to end the body of their loops.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 2; // initialization expression
do
{
cout << " Good morning\n";
i++; // update expression
} while (i < 1); // test expression
return 0;
}Output:
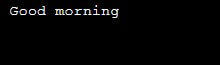
In the above-given code, the test condition says I should be less than 1 (i<1), but still, the loop executes at least onc, before checking for the condition, hence giving us the output “Good morning” one time.
Infinite Loop
An infinite loop or an endless loop is a loop that does not have a proper exit condition for the loop, making it run infinitely. This happens when the test condition is not written properly and it permanently evaluates to true. This is usually an error in the program.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int i;
for ( ; ; )
{
cout << "This loop runs indefinitely.\n";
}
}Output:
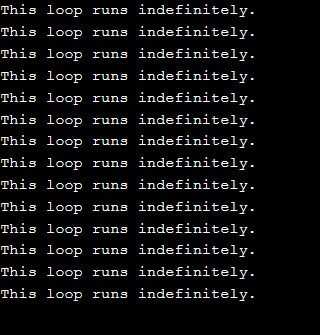
In this example, we have failed to mention any test expression and have left it blank; therefore this loop will run indefinitely until manually terminated.
Conclusion – Loops in C++
In this article, we have seen the various loops used in C++. Each of these loops has different benefits. We use loop when we know the number of times we need to run the loop, we use while loop when we know the condition for termination, but we do not know the precise number of iterations and we use do while loop when we need the code to execute at least once as in menu programs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Loops in C++. Here we have discussed different types of loops in C++ with syntax and example. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


