Updated March 20, 2023
Introduction to Login Page in PHP
It will be seldom found that an engaging website doesn’t propose an account creation from its customers. In order to do so, they need to have the facilities for a new user to register themselves, and later on login and interact with the website using their account. PHP exposes enough utilities to set up a functional Login Page, quickly, which can also scale later on as when required. After setting up a basic login form to request the credentials, the same PHP script can be used to process and validate the credentials, and redirect to the appropriate page on successful login. It also provides options for creating and storing cookies and sessions, to track users once they have completed the login process.
How do Login Pages Work in PHP?
PHP is a scalable stateless server-side scripting language. It allows one to capture form data by storing them in arrays $_GET or $_POST depending on whether the method used while submitting the form is GET or POST. Generally, the post method is preferred due to security reasons. Upon submission, these arrays can be indexed by the input field names to get the specific value.
For login forms, the credentials are passed and stored in these arrays, which more often than not, is just a set of usernames and passwords. Based on the requirement, either the username & password combination can be directly validated in the PHP code itself, or the valid set of username, password combinations might be stored in a database which could be looked up.
Setting up the Login Page
Let’s create a page, Login.php containing the following HTML lines:
Code:
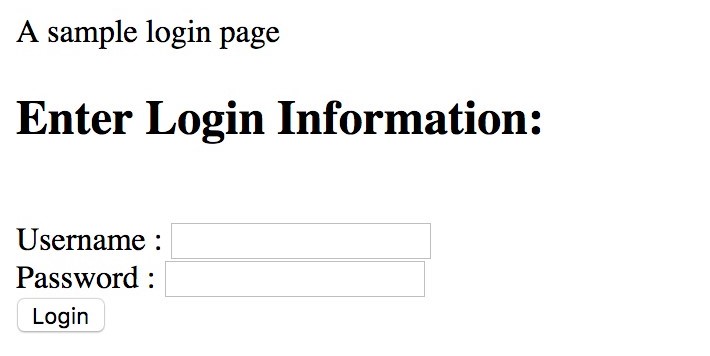
<html>
<head>A sample login page</head>
<body>
<h2>Enter Login Information:</h2><br>
<form action="" method="post">
<label>Username : </label><input type="text" name="username" /><br/>
<label>Password : </label><input type="password" name="pwd" /><br/>
<input type="submit" value="Login" />
</form>
</body>
</html>Output:
These lines create a very simple form, requiring a user to enter two fields, a username, and a password. It provides a third input, which is a submit button and causes form data, i.e. username and password, be sent to the location mentioned in the action attribute of the form tag. Since it’s empty above, it passes the form information to the same PHP page.
How to Create a Login Page in PHP?
The above page is static HTML code, without actually validating the user or login the person to internal web-pages. In order to do so, we need to process the values passed in the fields username and pwd stored in $_POST because of the method posts.
Thus the values are present can be checked using:
Code:
<?php
$error = "";
if(isset($_POST['username']) && isset($_POST['pwd'])){
// check for validity
}
?>Upon verifying at both inputs are indeed present, we can validate their values and redirect a person to the appropriate welcome page.
We can achieve this by inserting following simple piece of code within the if-statement block shown above:
Code:
$username = $_POST['username'];
$password = $_POST['pwd'];
if($username == "admin" && $password == "l0G3In"){
header('location: Home.php');
}
else {
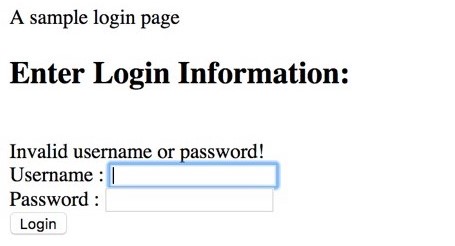
$error = "Invalid username or password!";
}With the above lines, once the user has submitted a valid set of credentials, he’s allowed access to home.php, or we store an error message which can be shown to the user.
Session
We don’t want a user to repeatedly login in upon every request. Thus we need to keep track of users who have logged in, irrespective of the page they are requesting. One way of achieving this in PHP is using sessions.
Briefly, sessions are a server-side small piece of information, temporarily stored for a client, once the page is requested. In PHP this is achieved by calling function session_start() as the first line in the script. From next time the page is accessed, session_start() doesn’t create a new session but retrieves information of the session started earlier and stores in a special array $_SESSION.
Values to be passed across pages while a session is active can be set in a similar fashion to a normal array and isset() function can be used to check if a particular value is available within the array.
Combining all the things discussed, the code will look as follows:
Code:
<?php
session_start();
if(isset($_SESSION["login"]) && $_SESSION["login"]==True){
header('location: Home.php');
}
$error = "";
if(isset($_POST['username']) && isset($_POST['pwd'])){
$username = $_POST['username'];
$password = $_POST['pwd'];
if($username == "admin" && $password == "l0G3In"){
header('location: Home.php');
}
else {
$error = "Invalid username or password!";
}
}
?>
<html>
<head>A sample login page</head>
<body>
<h2>Enter Login Information:</h2><br>
<?php echo $error;?>
<form action="" method="post"><label>Username : </label><input type="text" name="username" /><br/>
<label>Password : </label><input type="password" name="pwd" /><br/>
<input type="submit" value="Login" />
</form>
</body>
</html>Output:
Home.php
Now, any other page which requires a login just needs to check that the session key login is set. If not, the user can be redirected to the login page. Else he has access to the secret internal content.
Let’s create one for demo purposes:
Code:
<?php
session_start();
if(!isset($_SESSION["login"]) || $_SESSION["login"]!=True){
header('location: Login.php');
}
?>
<html>
<head>Welcome to User's Home Page</head>
<body>
<h2>Wishing you a good day!!</h2><br>
</body>
</html>Output:
The above code first retrieves the session details by invoking session_start(). It then validates that the session is still active for a user who had completed the login process. If not, the user is sent to the Login.php page. If the user had successfully logged in, the rest of the content is available to the user.
Conclusion
It’s extremely easy to create login pages in PHP. Here we have directly stored the credentials in the script, but ideally (and most commonly) they will be stored in some form of a database or key manager. Also, here we used sessions, which are stored on the browser side, but you can use cookies that are stored on the browser (client) side but are less reliable.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Login Page in PHP. Here we discuss how to create a login page in PHP with working and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –