Updated March 23, 2023

Introduction to Logical Operators in C
Logical operators are part of binary operators. These operators are specifically used when we are going to combine two or more requirements together. These can be used in many conditional and relational expressions. On evaluating these conditions, these are the Boolean expressions which give an output of either 1/0 for True/False respectively. Let us below learn about different logical operators in the C programming language.
Different Logical Operators in C
The three main logical operators are ‘&&’, ‘||’ and ‘!’. The truth tables can be understood by:
|
a |
b | a && b |
a || b |
|
0 |
0 | 0 | 0 |
|
0 |
1 | 0 |
1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
And for NOT operator:
|
a |
!a |
|
1 |
0 |
| 0 |
1 |
The output ‘1’ and ‘0’ denotes the True and False respectively. Through these, the conditional operations that are being performed can be very well understood.
Examples to Implement Logical Operators in C
Types of logical operators with their examples and implementation are explained below.
1. AND Operator
This operator is symbolized by ‘&&’. This operator gives the true as the output if all the conditions.
Example #1
Let us see a simple example using the AND operator given below.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter a digit between 1 to 10: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
if((n>0) && (n<=10))
{
printf(" Given number is in between 0 and 10");
}
else if((n>10) && (n<=20))
{
printf("Given number is in between 10 and 20");
}
else
{
printf("Please enter a number in the given range");
}
return 0;
}This above example has our and condition which has many conditions and all the conditions must be satisfied.
Output:
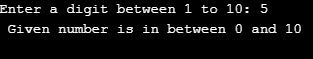
Example #2
In a similar way, we can write another example using AND operator.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b;
a=855;
b=1300;
if((a>=500) && (b<1000))
{
printf(" This is the first condition");
}
else
{
printf(" This is the second condition");
}
}Output:
![]()
So, this is how we are going to have the AND condition.
2. OR Operator
This is the condition where any one of the given scenario can be true.
Example #1
Let us check this operator with a small example given below.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter a digit between 1 to 20: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
if((n%2==0) || (n%5==0))
{
printf(" Number given is divisible by either 2 or 5");
}
else{
printf(" Number is not divisible by 2 or 5");
}
return 0;
}Output:
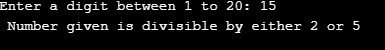
So, if the given number is either divisible by 2 or 5, then the condition is executed.
Example #2
Now let us see what happens if the same condition is executed with ‘and’ condition.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter a digit between 1 to 20: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
if((n%2==0) && (n%5==0))
{
printf(" Number given is divisible by 2 and 5");
}
else{
printf(" Number is not divisible by 2 and 5");
}
return 0;
}Output:

After comparing the two examples we can understand the main difference between ‘AND’ and ‘OR’ logical operators. As the output for these logical operators is a Boolean expression, True/False which is the outcome executes the code inside those conditional statements.
3. NOT Operator
This logical operator is usually defined by symbol ‘!’. This operator is equal to “not equal to”.
Example #1
Let us see a small example of this below.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n %2 != 0)
{
printf(" This is an odd number");
}
else
{
printf(" This is an even number");
}
return 0;
}Output:

Example #2
In a similar way, we can write another example using Not operator.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b;
printf("Enter a number : ");
scanf("%d",&a);
printf("Enter b number: ");
scanf("%d",&b);
if(a!=b)
{
printf(" A and B values given are different");
}
else
{
printf(" A and B values given are same");
}
return 0;
}Output:
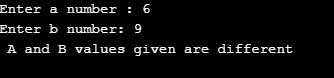
So, these are the three logical operators defined through the C programming language.
Example #3
Here let us see one more example where all three of them can be used together.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x,y,z;
printf("Enter first number : ");
scanf("%d",&x);
printf("Enter second number: ");
scanf("%d",&y);
printf("Enter third number: ");
scanf("%d",&z);
if((x>=y) && (y>=z))
{
printf(" X is the highest number");
}
else if((x>=y) || (x>=z) )
{
printf(" X is either greater than y or z");
}
else if((x>=y) || (x>=z) && (y>=z))
{
printf(" Both 'and' and 'or' are used and X is definitely larger ");
}
else if( x!=y)
{
printf(" Checking for a condition that X is not equal to Y");
}
else
{
printf("Finally");
}
return 0;
}Output:
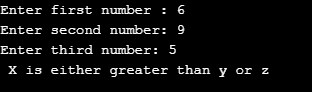
This is just an example of using all these logical operators in one program.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Logical Operators in C. Here we discuss the basic concept, different logical operators in C along with examples and code implementation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


