Updated July 1, 2023

Introduction to Linux Xargs
In the Linux operating system, we are having multiple utilities to work on the streaming or live data. Xargs is one of the utilities. It is used to capture the stream data from the standard input. After that, it will generate and perform the execution on arguments commands. In other words, we can say that it will get the previous command output as input to the next command. The output result will be useful for the next arguments command.
As for GNU packages, we are getting the xargs version 4.2.X. The default behavior of the xargs tool or utilizes is not to have the logical end of the file marker.
Syntax
Linux Command [ OPTIONS ] [ FILE/DIRECTORY PATH ] | [ xargs ] [ OPTIONS ] [ LINUX COMMAND ]- xargs: We can use the “xargs” keyword in the syntax or command. It will take different arguments like options, Linux commands, etc. As per the provided arguments, it will pass the output data to the next command (as an input).
- OPTIONS: We can provide the different flags as the option that is compatible with the “xargs” command.
How Linux Xargs Works?
The xargs are basically working on the input and output arguments. While working with the xargs utility, it will grab the previous command output and pass the same output as in input to the next command. As per the shared input to the next command, it will perform the execution of the command.
Below are the lists of options that are compatible with the xargs command.
| Sr No | Option | Description |
| 1 | -0, –null | Instead of by whitespace, the input items will terminate by a null character. With the help of this option, the quotes and backslash are not special. |
| 2 | -a file, –arg-file=file | Instead of the standard input option, it will read items from the file. If we will use the same option, then the stdin remains unchanged when the commands are running in the state. |
| 3 | -E eof-str | It will help to set the end of the file string to eof-str. The rest of the input may ignore. If the end of the file string occurs as a line of input. |
| 4 | -e [eof-str], –eof[=eof-str] | The same option is a synonym for the -E option. It is POSIX compliant, while this option is not. There is no end of file string if eof-str will omit. |
| 5 | -i [replace-str], –replace[=replace-str] | The same option is a synonym for -Ireplace-str. If the argument is missing, then the effect is the same as -I{}. But the option is deprecated; we need to use the option -I. |
| 6 | -L max-lines | We must use the same option while most max lines are nonblank input lines (as per the command line). The trailing blanks may cause an input line to be logically continued on the next input line. |
| 7 | -l [max-lines], –max-lines[=max-lines] | The -l option is deprecated. IF we need to use the same option, we need to use the “-L” Synonym. Unlike -L, the max-lines argument is optional. |
| 8 | -p, –interactive | It will prompt the user-level command whether to run each command line and read a line from the terminal. It will run in the verbose format. It will only run the input command if the user shares the response as “y” i.e. “yes.” |
| 9 | –process-slot-var=name | It will help to set the environment variable value or name (the value will be unique) in each running process. Once the child process will exit, we can reuse the same value. |
| 10 | -r, –no-run-if-empty | It will not run the command if the standard input does not contain any nonblank. When there is no input, then the command is run once. This option comes under the GNU extension. |
Examples to Implement Linux Xargs
1. Linux Xargs Command
In the Linux environment, we are able to use the xargs command with different operators.
Command :
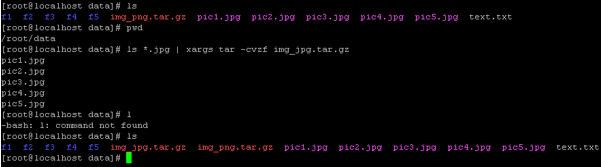
ls *.jpg | xargs tar -cvzf img_jpg.tar.gzExplanation :
As per the above command, we list the number of jpg images from the “/root/data” directory. Here, we combine multiple commands like ls, xargs, and tar. With the help of the xargs command, we are taking the list of files from the “ls” command and providing the same output files as an input to the tar command. Once the tar command will get the file, it will create the “img_jpg.tar.gz” tar file.
Output :
2. Linux Xargs Command – Listing Lines/Words/Characters
In the xargs command, we can list out the selected files in terms of lines, words, and characters.
Command :
ls *.jpg | xargs wcExplanation :
As per the above command, we list the number of jpg files and get the information of number lines, words, and characters of sorted files.
Output :

3. Linux Xargs Command: Remove Selected Files
In the Linux environment, we are able to use the xargs command to delete a specific set of files.
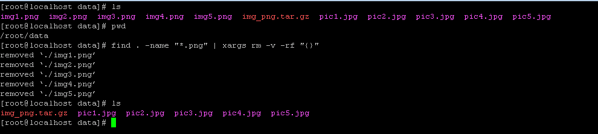
Command :
find. -name "*.png" | xargs rm -v -rf "{}"Explanation :
As per the above command, we list the number of png images and create a tar file with the help xargs utility.
Output :
4. Linux Xargs Command – Read Input File
In the xargs command, we are having the functionality to read the file.
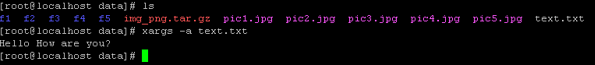
Command :
xargs -a text.txtExplanation :
As per the above command, we are a list of files in the “/root/data” directory. With the help of the xargs command, we are able to read the “text.txt” file. We need to use the “-a” option with the “xargs” command to read the file.
Output :
Conclusion
We have seen the uncut concept of “Linux Xargs” with the proper example, explanation, and command with different outputs. The xargs utility is used to get the outputs from the previous command and send the same output as an input to the next command. The xargs command or utility is majorly used in the shell/bash or application-level jobs.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Linux Xargs” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


