Updated May 15, 2023
Definition of Linux WC
The Command WC (word count) in Linux OS allows one to find the word count, newline count, and the count of bytes or characters in a file mentioned by the file arguments. The output from the word count command will give you the count of lines in a file or the number of words or characters in a file.
Syntax:
The Syntax of WC Command is given as:
wc [options].. [file]..Here options include:
- wc -l: To print the number of lines in a file.
- wc -c: To print the count of bytes in a file.
- wc -w: To print the number of words in a file.
- wc -m: To print the count of characters in a file.
- wc -L: To print the length of the longest line in a file.
Advantages of Wc Command
WC Command in Linux helps to find out the following points:
- Allows to find out the word count, newline count, and the count of bytes or characters in a file mentioned by the file arguments.
- The output produced is the four-columnar by default.
- The four columnar output arguments are: the first column gives the line that is in the file, the second column will provide you with the count of words in the file, the third column will provide you with the count of characters that is present in the file and the last column is the file name in the argument.
How does WC Command Work in Linux?
We can use –the help command in Linux to find out how WC Command works in Linux.
Syntax:
wc --helpUsage:
wc [OPTION]… [FILE]…
wc [OPTION]… –files0-from=F
We can print Word, newline, and count the number of bytes for each FILE in the system, and also, we can count the total number of lines if there is more than one FILE mentioned in the arguments. A word in the file is a non-zero-length of chars that might be delimited with white space. When there is no FILE, or if FILE is -, we should read the standard input.
The options that are mentioned below might be used for selecting the counts that are printed and the ones that are always in the following order – newline, Word, character, byte, and the maximum length of the line.
Let us take an example file and perform wc command on it. Here we can list the data that is present in fruits.txt file by using the cat command.
cat fruits.txt
wc fruits.txtOutput:

When we perform the WC command on the above file, we can see that the output displayed is in a four-columnar manner. Here the first column gives the line that is in the file that is 5; the second column will provide you with the count of words in the file that is 5, and the third column will give you the count of characters that is present in the file which is 38 and the last column is the file name in the argument that is fruits.txt.
Examples of WC Command in Linux
Below are examples of options that can be used in the WC command with their syntax and examples for better understanding.
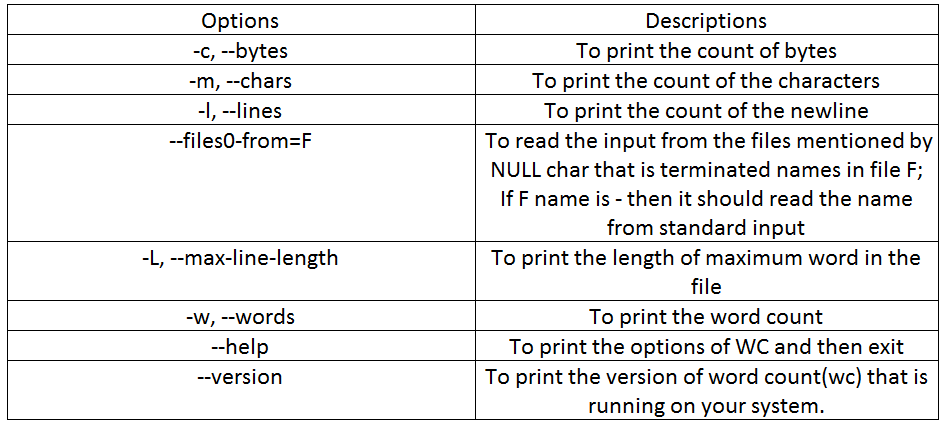
1. Option -l
To print only the number of lines in the file, we can use the option ‘l.’ The output generated will be two columnar in which the first is the count of a number of lines and the second is the file’s name.
Syntax:
wc -l filenameExample:
wc -l fruits.txtOutput:
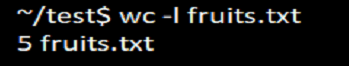
2. Option -w
To print only the number of words in the file, we can use the option ‘w.’ The output generated will be two columnar in which the first is the count of a number of words and the second is the file’s name.
Syntax:
wc -w filenameExample:
wc -w fruits.txtOutput:
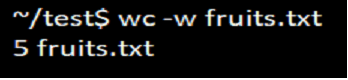
3. Option -c
To print only the number of bytes in the file, we can use the option ‘c.’ The output generated will be two columnar, in which the first is the count of a number of bytes and the second is the file’s name.
Syntax:
wc -c filenameExample:
wc -c fruits.txtOutput:
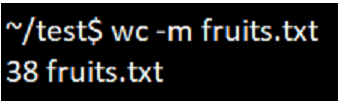
4. Option -m
To print only the number of characters in the file, we can use the option ‘m. The output generated will be two columnar, in which the first is the count of a number of characters and the second is the file’s name.
Syntax:
wc -c filenameExample:
wc -m fruits.txtOutput:
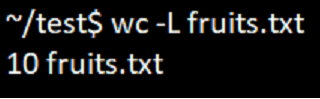
5. Option -L
The option ‘L’ will help to find out the longest (in terms of long characters) line in the file. A character in the file will be considered that will include space, newline, or tab.
Syntax:
wc -L filename
Example:
wc -L fruits.txtOutput:
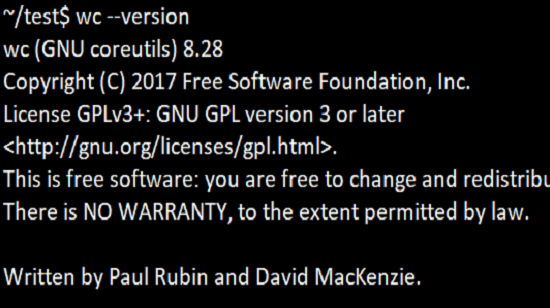
6. Option –version
The option of ‘version’ will help you to print the version of word count(wc) that is running on your system.
Syntax:
wc --versionExample:
wc --versionOutput:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Linux WC” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


