Updated April 18, 2023

Introduction to Linux uniq
Linux uniq command-line utility is helpful to filter out the repeated or duplicate records in the file. In other words, it will detect the adjacent duplicate lines and omit/delete the duplicate lines from the inputs data or file.
This utility was written by Richard M. Stallman and David MacKenzie.
Syntax:
uniq [ OPTION ] ... [ INPUT [ OUTPUT ] ]The uniq syntax is simple. As per the above syntax, the “INPUT” refers to the input data or input file. It will contain the repeated lines of duplicate data that needs to be filtered out. If the “INPUT” keyword does not specify, then “uniq” will read the standard input. The “OUTPUT” refers to the output file in which we can store the filtered output data generated by the “uniq” command.
How does Linux uniq Command work?
The Linux uniq command is like a filter program, and it will use after the sort. The uniq command will get the repeated or duplicate input data or input file. With the help of different filter actions or keywords available in the uniq. We will filter out the adjacent data or duplicate data from the input file and process the end result to the output file.
Examples to Implement Linux uniq Command
Examples to implement the Linux uniq command are given below:
1. Uniq Command
The uniq command will help to remove the duplicate data or records from the input file.
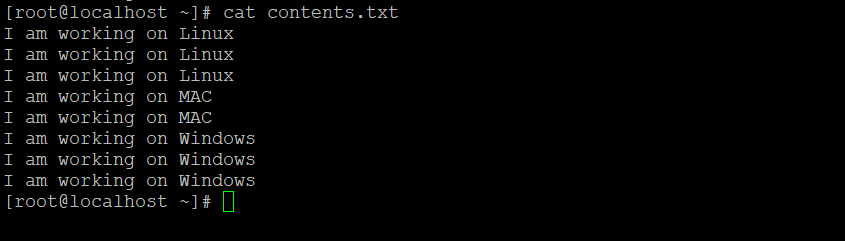
uniq contents.txtExplanation: We have the sample text file “contents.txt”. It has some data in the same file (refer to screenshot 1 . Now we are using the uniq command to filter out the duplicate data (refer to screenshot 1 ).
Output:
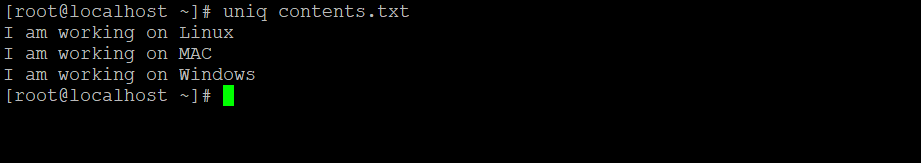
2. Uniq Count Command
In the uniq count command, we will identify how many times the line was repeated in the input file or data with prefix value. To count the number of duplicate records in the input file, we can use the “-c” option with the uniq command.
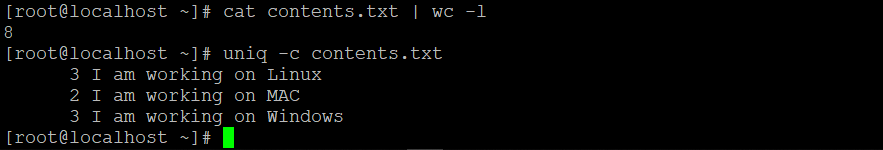
uniq -c contents.txtExplanation: In the contents.txt file, there are a total of 8 records in it. The non-duplicate records are three. With the help of the “-c” option, we will get the number of duplicate count record information.
Output:
3. Uniq Repeated Command
It will display or print the unique records from the input file. No repeated or duplicate records will display. For repeated records, we can use the “-d” option with the uniq command.
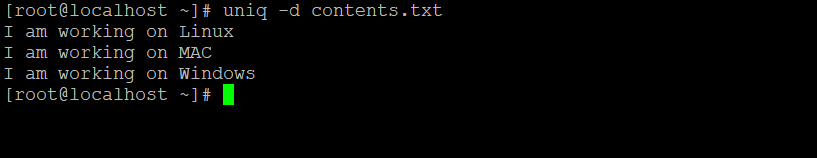
uniq -d contents.txtExplanation: From the input file (contents.txt), we will only identify the repeated unique records.
Output:
4. Uniq all-repeated
With the help of all-repeated commands, we will be able to get all the records from the input file. For all-repeated records, we can use the “-D” option with the uniq command.
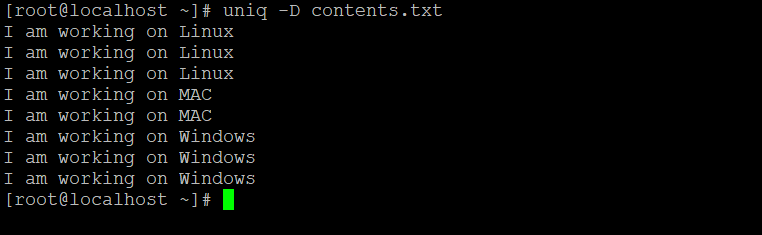
uniq -D contents.txtExplanation: From the input file “contents.txt”, we can print all the records with the help of all-repeated functionality in uniq.
Output:
5. Uniq Unique Command
The unique command will help to identify the unique records or data from the input file. For unique records, we can use the “-u” option with the uniq command.
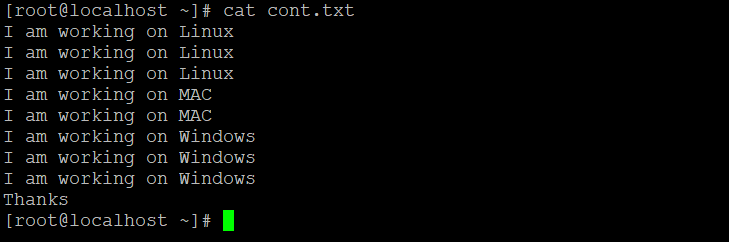
uniq -u cont.txtExplanation: In the input file “cont.txt”, we have only one unique word in the file, i.e. “thanks”. With the help of the “-u” unique option, we are able to identify from the input data or file.
Output:
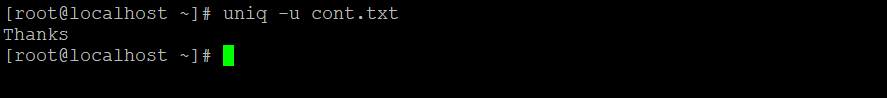
6. Uniq Using –f N Command
This uniq command, it will allow the “N” fields to be skipped while comparing the uniqueness of the lines.
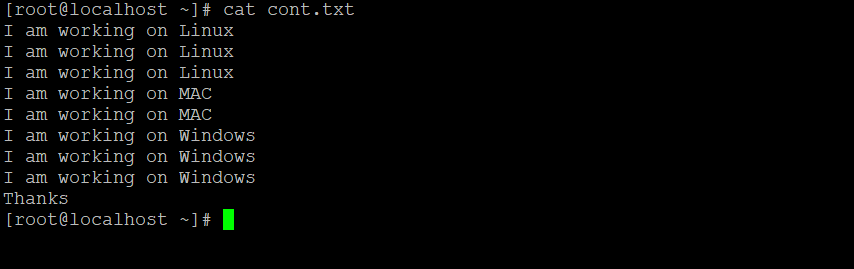
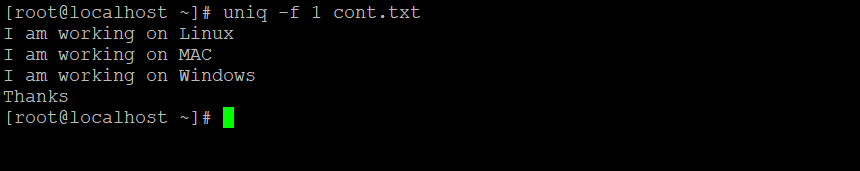
uniq -f 3 cont.txtExplanation: In cont.txt input file having the number of input records (refer the screenshot 3 (a)). We are able to print the unique records with the interval of “1” (“N”) [the “N” value is depending on the client requirement]
Output:
7. Uniq Using –s N Command
The uniq –s N command is similar to the -f N option. But it will skip the “N” characters but not skip the “N” fields.
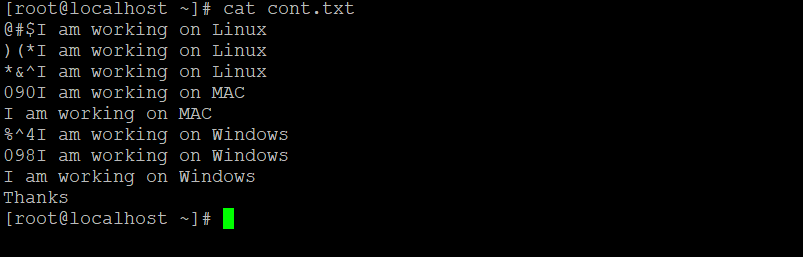
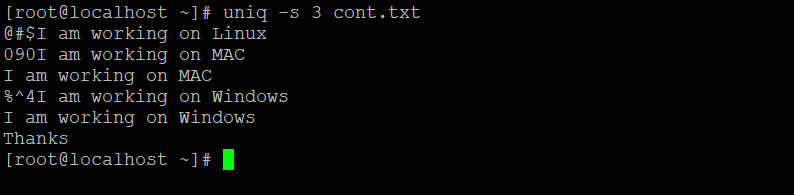
uniq -s 3 cont.txtExplanation: In the cont.txt input file, we are having multiple lines with special characters and numbers in it (refer to screenshot 1). With the help of the “-s” option, you will skip the special characters or numbers from the input file. The “N” denotes the number value. The same number of values will help to skip the special character from the input file.
Output:
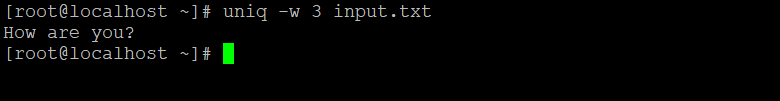
8. Uniq Using –w N Command
The uniq –w N command is similar to skipping the characters. With the help of the uniq command, we can limit the comparison to the set number of characters (“N” value).
uniq -w 3 input.txtExplanation: In the input.txt file, we are having 3 records starting to form 3 letter words, i.e. “How” (refer to Screenshot 1). With the help of the “-w” option and “N” value (3), we will skip the initial 3 characters of the input file and having a character sequence (refer to Screenshot 2).
Output:
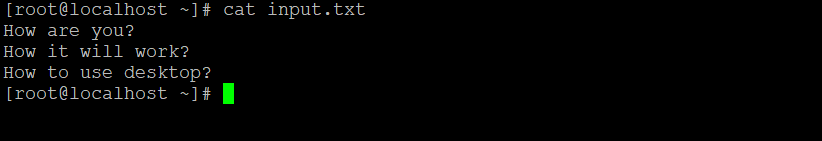
Conclusion
We have seen the uncut concept of “Linux uniq” with the proper example, explanation, and command with different outputs. The uniq command is like a filter program. It will filter out the data as per user requirements. The filter data or output data will further use of shell jobs and other application development tasks.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Linux uniq” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


