Updated April 18, 2023

Introduction to Linux tee Command
The Linux Tee Command is using the standard streams in which it will read the standard input and writes it to both standard output and one or more files, effectively duplicating its input. Basically the tee command is useful to display the standard output of the give command or program and write the same output in the output file.
The tee command or the utility was written by Mike Parker, Richard M. Stallman, and David MacKenzie.
Syntax:
tee [ -a ] [ -i ] [ File Name ... ]- -a: –append ( Do not overwrite the files. Instead append to the given files )
- -i: –ignore-interrupts – Ignore interrupt signals.
- File Name: A file or the list of files. Each of which will get the output file.
How does Linux tee Command Work?
The Linux tee command is normally used to split the output of the input data or the program. It can be both displays and saved the output data in a file. The tee command can be used to collect the intermediate output before the data is changed by another command or program.
The tee Commands will Return the Below Exit Values:
- 0: After executing the Linux tee command, the exit value of the command is “0”. Then the command is expected correctly.
- Greater than 0: After executing the Linux tee command, the exit value of the command is greater than “0”. Then the command is not expected correctly.
The tee command reads the standard input and then writes its content to standard output. It will simultaneously copy the data into the directed or specified file or variables. The tee command syntax may differ depending on the requirement.
Examples to Implement Linux tee Command
This is the most basic usage of the tee command to display the output of the command and parallelly will write in the output file.
Example #1 – tee Command to Write Multiple File
Command:
ls -ltrh
ls -ltrh | tee tee_output.txt
cat tee_output.txtExplanation:
In the above tee command, we are getting the details information of the “/” directory with the help of “ls –ltrh” command (refer screenshot 1 (a)). The same output will provide to tee command as input (with the help of pipe). Then tee command will do both the operation of displaying the output of the command as well as write the output in output file “tee_output.txt” (refer screenshot 1 (b) & (c)).
Output:
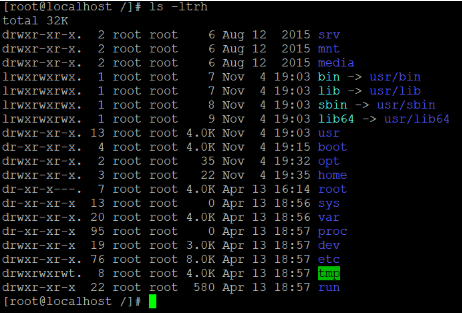
Screenshot 1 (a)
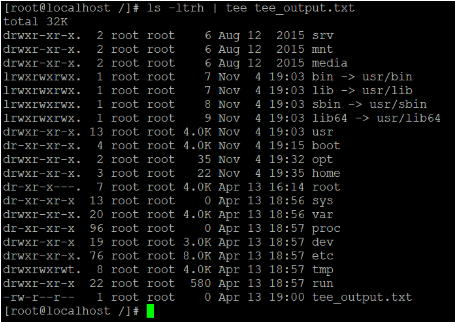
Screenshot 1 (b)
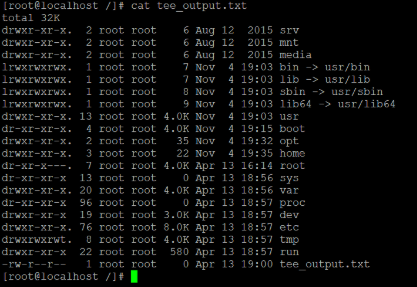
Screenshot 1 (c)
Example #2 – tee Append Command
In tee command, we are having the functionality to write the multiple output files at the same time. Just we need to pass the different files separated by space.
Command:
date
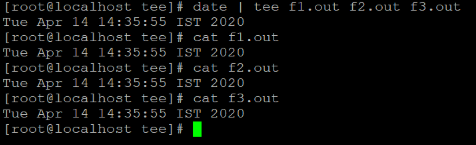
date | tee file1.out file2.out file3.out
cat f1.out
cat f2.out
cat f3.outExplanation:
As per the above command, we are using the date command to get the current system timestamp (refer screenshot 2 (a)). Now we need to display or print the output of the command as well as the same output will write in different multiples files. It will helpful for multimodal text process applications to write the output of the command in multiple files. We can perform the same operation with the help of the tee command (refer screenshot 2 (b)).
Output:
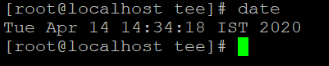
Screenshot 2 (a)
Screenshot 2 (b)
Example #3 – tee Command to Hide Output
In tee command, we can overwrite the specific output files. We can append the command output to a specific file or output file. We can use the “-a” option to append the command output to specific output files.
Command:
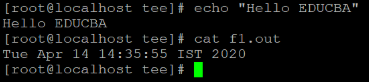
echo "Hello EDUCBA"
cat f1.out
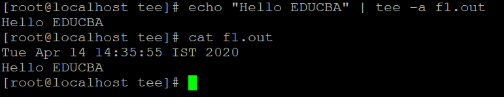
echo "Hello EDUCBA" | tee -a f1.out
cat f1.outExplanation:
In the above tee command, we are using the echo command to display the written text (refer screenshot 3 (a)). The file “f1.out” having some data in it. Now with the help of tee command, we will write the echo command output to “f1.out” file with appending the command output data with existing file data (refer screenshot 3 (b)).
Output:
Screenshot 3 (a)
Screenshot 3 (b)
Example #4 – tee Command with SUDO
In tee command, we can hide the output of the command via redirecting the command output to “null”.
Command:
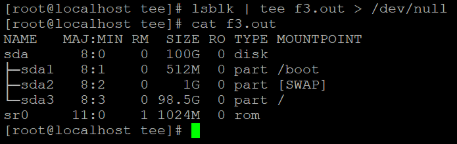
lsblk | tee f3.out > /dev/null
cat f3.outExplanation:
In the above tee command, we are using “lsblk” command to get the information of the storage drive to our machine. But in general, if we are using the tee command we are displaying the output of the command. But in some cases, we do not want to display the output just need to redirect it. In the above tee command, we are using “lsblk” command but it is not displaying the output of it (refer the output screenshot.)
Output:
Example #5
In the tee, we can evaluate the sudo permissions while working with tee commands. While using the redirection operators it will identify or understand the sudo permission available in the command.
Command:
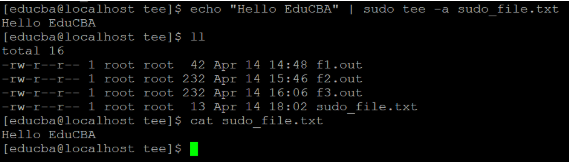
echo "Hello EduCBA" > sudo_file.txt
echo "Hello EduCBA" | sudo tee -a sudo_file.txt
cat sudo_file.txtExplanation:
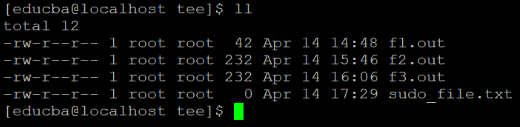
In tee directory, we are having the 4 different files in it (refer screenshot 4 (a)). Let consider “sudo_file.txt”. The permission or access is the only reserve for root user only. The “educba” user having sudo access but while writing the “sudo_file.txt” file. It is getting the permission denied error (refer screenshot 4 (b)). Because the redirection of the output command is not supporting by sudo.
To overcome this condition, we can use the sudo in tee command. The tee command having the capability to understand or evaluate the sudo permissions and write to the output file (refer screenshot 4 (c)).
Output:
Screenshot 4 (a)

Screenshot 4 (b)
Screenshot 4 (c)
Conclusion
We have seen the uncut concept of “Linux Tee Command” with the proper example, explanation, and command with different outputs. The tee command is a command-line interpreter. It is using the concept of the standard stream to reads standard input and writes the standard output to single or multiple files parallelly. For evaluating the number of command and command output results, the tee command is useful.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Linux tee Command” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


