Updated April 18, 2023

Introduction to Linux rm Command
In the Linux operating system, rm command is used to remove or delete the files or directories. Similarly, we can also use the “unlink” command to remove the single file only. The Linux rm command-line utility was written by Paul Rubin, David MacKenzie, Richard M. Stallman, and Jim Meyering.
Syntax of rm command
rm [ OPTION ] FILE NAME | DIRECTORY NAME- rm: Using the rm keyword in the command | syntax. It will take the two sets of arguments as an OPTION and FILE/DIRECTORY NAME and delete it subject to file/directory permission and given option.
- OPTION: We can provide the different flags as an option to the rm command.
- FILE: Input file or directory name.
How does Linux Rm Command work?
As the name suggested, rm command is useful to remove or delete the file or directory from the Linux filesystem. As per the file or directory permission, the “rm” command will delete the file. The “rm” command is accepting the two arguments as OPTION and File/Directory name then remove the File/Directory as per the OPTION and file permissions.
Examples to Implement Linux Rm Command
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1. Rm Command
With the help of rm command, we are able to delete the file from the Linux filesystem.
Code:
pwd
ls
rm file.txtExplanation: We are having a sample directory. In the same directory, we have a “file.txt” file (refer screenshot 1 (a)). With the help of the rm command, we are able to remove the file. But using the default “rm” command, it asking the file delete confirmation. If we will enter “n” (no) then only the file will not delete (refer screenshot 1 (b)). If we will press “y” (yes) then the file will delete. (refer screenshot 1 (c)).
Output:
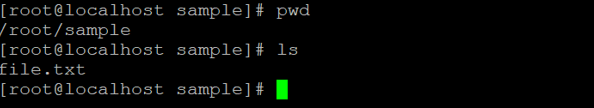
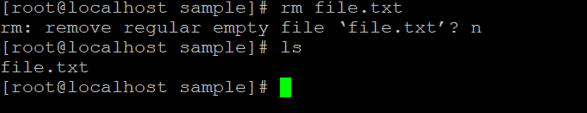
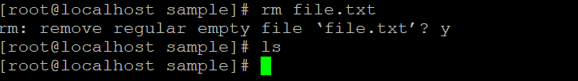
Example #2. delete empty directory
With the help of rm command, we are able to delete the different types of directory present on Linux filesystem. Here, we are deleting the empty directory. We need to use the “-d” option in the rm command.
Code:
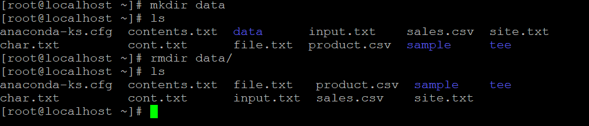
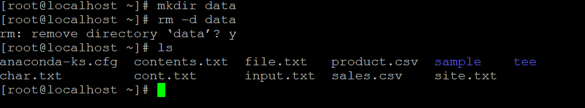
mkdir data
ll data/
rmdir data
rm -d dataExplanation: We are creating one sample directory (“data”)and no data present in it i.e. it is an empty directory (refer the screenshot 2 (a)). Now we are able to delete the empty directory in 2 different ways. In the first way, we can “rm” command with “-d” option, and second way, we can use the “rmdir” command to delete the empty directory (refer the screenshot 2 (b)).
Output :
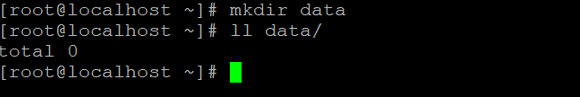
Example #3. with “-rf” option
In rm command, we are having the functionality to delete or remove the number of files forcefully and recursively in the same working directory. No need to provide the number of file names to “rm” command. We need to use the “-rf” option in the rm command.
Code:
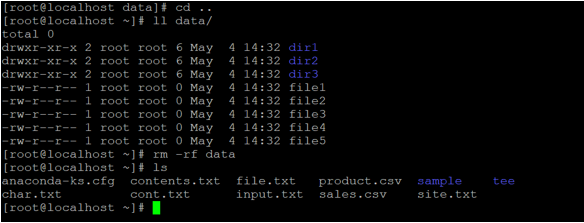
rm -rfdataExplanation: In the above command, we are able to delete the number of files and sub-directory from the working directory. To delete the number of files forcefully, we need to use “-rf” option with “rm” command. In the data directory, we are having 3 different files and three sub-directories. We are deleting all the items for it.
Output:
Example #4. with user interactive “-ri” option
In rm command, we are having the functionality to delete the files as per the user inputs. If the user provides the inputs as “y” (yes) then only the file will delete otherwise not. We need to use the “-ri” option in the rm command.
Code:
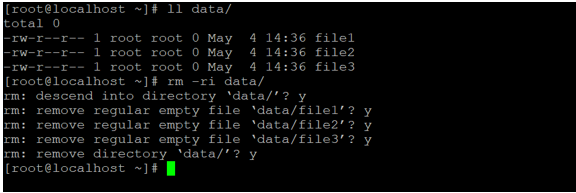
rm -ri data/Explanation: As per the above command, we are recursively deleting all the files from the directory with user inputs. In the “data” directory, we are having three files and deleting the files as per the user inputs.
Output :
Example #5. Prompt Option before delete
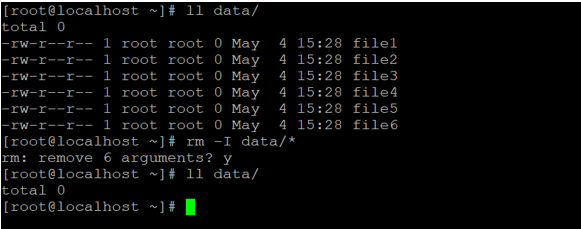
In the Linux rm command, there is the facility to prompt the number of files that are present in the directory. If we will pass the user input as “y”(yes) then in the next instance all the files will remove. We need to use the “-I” option in the rm command.
Code:
rm -I data/*Explanation: As per the above command, we have 6 files in the “data” directory. With the help of the “I” option, we are getting the prompt before deleting the number of files form the current working directory. If we will pass the user input as “n” (no) then the files would not be deleted, if we pass the input as “y” (yes) then all the files would be deleting.
Output:
Example #6. with Regular Expression Option
In the Linux rm command, we can use the regular expression to delete the files from the filesystem. We need to use the “-f” option in the rm command.
Code:
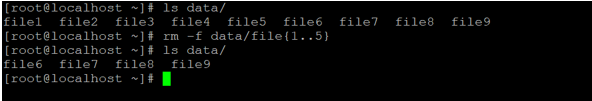
rm -f data/file{1..5}
ls data/Explanation: As per the above rm command, we have used the regular expression to delete the 5 files from the “data” directory. In the data directory, there are a total of 9 files. We have deleted initial 5 files and remaining files are present in the directory.
Output:
Example #7 – Delete Large Number of Files
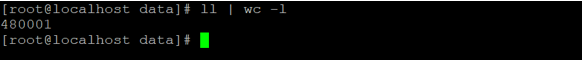
In a Linux or UNIX operating system, there are a huge amount of files in the directory. It would be difficult to delete all the files in the traditional way. We need to use the different way to delete those files in single rm command.
Code:
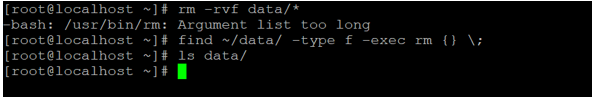
find ~/data/ -type f -exec rm {} \;
ls data/Explanation: As per the above command, we are deleting the huge number of files in single rm command. With the help of find command, we are finding the files and pass the argument (array) to the rm command. Accordingly, the rm command will delete the number of files.
Output:
Conclusion
We have seen the uncut concept of “Linux Rm Command” with the proper example, explanation and command with different outputs. The default rm command is used to delete the number of files or directory recursively. But we need to use the rm command very carefully.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Linux rm Command” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


