
Definition of Linux List Groups
A “group” In Linux refers to a collection of user accounts with similar privileges or access rights. Groups are a way to manage and organize users on a system, allowing administrators to assign standard permissions to multiple users efficiently. User management is a critical aspect of ensuring security and controlled access. Listing groups in Linux involves querying the system for information about existing groups, their members, and associated details. It’s useful for system administrators to understand the group structure and manage user access effectively. This organizational structure simplifies granting and revoking permissions to multiple users simultaneously.
Table of Contents:
Primary and Supplementary Groups in Linux
Primary Group (Login Group): A primary group in Linux is the main group associated with a user account. Each user account is assigned one primary group, specified in the user’s entry in the “/etc/passwd” file. The primary group is the default group for file and directory ownership when the user creates new files or directories.
Supplementary Group (Secondary Group): A Supplementary Group in Linux is where a user is a member of one or more groups, called supplementary groups. Users belonging to supplementary groups have expanded permissions beyond those of the primary group. This hierarchical arrangement allows for flexible and granular control over user access.
Viewing User Information
1. Viewing the primary group information for a user
Syntax:
id <username>Example:
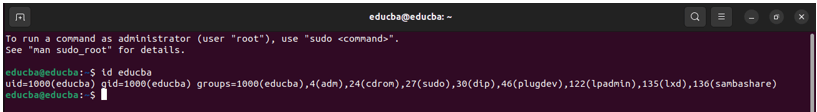
Explanation of the “id command”:
- uid=1000(educba): The user “educba” has a user ID (UID) of 1000.
- gid=1000(educba): The primary group of the user “educba” is a group with a group ID (GID) of 1000. The name of this group is also “educba.”
- groups=1000(educba),4(adm),24(cdrom),27(sudo),30(dip),46(plugdev),122(lpadmin),135(lxd),136(sambashare): This part shows the supplementary groups that the user “educba” belongs to. Each group is identified by its GID and name in parentheses.
- adm: Group ID 4 – Used for system log access.
- cdrom: Group ID 24 – Associated with CD-ROM access.
- sudo: Group ID 27 – Members of this group have sudo (superuser) privileges.
- dip: Group ID 30 – Used for dial-up access.
- plugdev: Group ID 46 – Used for controlling access to removable storage devices.
- lpadmin: Group ID 122 – Associated with printer administration.
- lxd: Group ID 135 – Associated with Linux Containers (LXD) access.
- sambashare: Group ID 136 – Used for Samba (Windows file-sharing) access.
2. Usermod Command
We can use the usermod command to change the primary group of a user:
Example:
“sudo usermod -g new_primary_group username”Replace “new_primary_group” with the desired primary group and “username” with the actual username.
2. To add a user to a supplementary group, you can execute the usermod command with the -aG option:
Example: sudo usermod -aG supplementary_group username
Replace “supplementary_group” with the desired supplementary group and “username” with the actual username. The -aG options append the user to the specified supplementary group without affecting their primary group.
3. List of groups a user belongs to
We use the ”groups” command to see the list of groups a user belongs to.
Example:
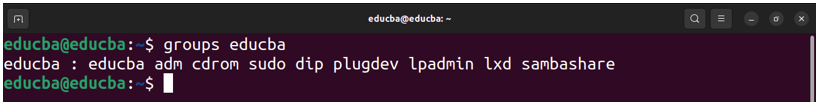
Explanation of groups command:
- educba: This is the primary group for the user “educba.” It is also the name of the group.
- adm: Group membership in the “adm” group (Group ID 4). This group is typically associated with system log access.
- cdrom: Group membership in the “cdrom” group (Group ID 24). This group is often associated with CD-ROM access.
- sudo: Group membership in the “sudo” group (Group ID 27). Members of this group typically have sudo (superuser) privileges.
- dip: Group membership in the “dip” group (Group ID 30). This group serves as the dial-up access.
- plugdev: Group membership in the “plugdev” group (Group ID 46). This group often controls access to removable storage devices.
- lpadmin: Group membership in the “lpadmin” group (Group ID 122). This group is typically associated with printer administration.
- lxd: Group membership in the “lxd” group (Group ID 135). This group is associated with Linux Containers (LXD) access.
- sambashare: Group membership in the “sambashare” group (Group ID 136). This group serves for Samba (Windows file-sharing) access.
4. What is the “/etc/passwd” and the “/etc/group” file
The /etc/passwd and /etc/group files are essential components for managing user and group information.
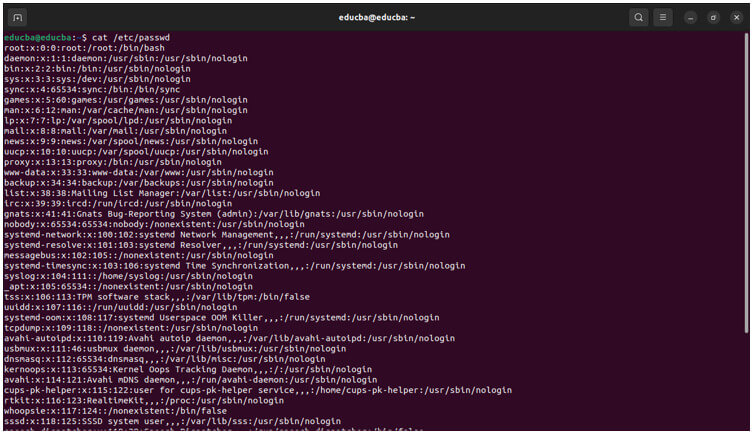
/etc/passwd File: The /etc/passwd file is a system file that stores user account information. Each line in the file represents a user and contains several fields separated by colons (:).
Output:
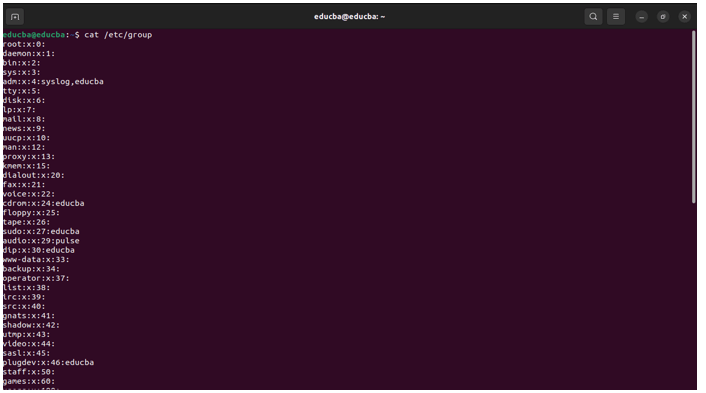
/etc/group: The /etc/group file contains information about user groups on the system. Each line represents a group and consists of fields separated by colons.
Output:
Getent Command
The getent in Linux retrieves entries from various system databases, including passwd (user information), group (group information), hosts (hostname/IP address mapping), services (network services), protocols (network protocols), and more. The name “getent” stands for “get entries.” It retrieves information from databases configured in the /etc/nsswitch.conf file, which determines the order and sources of databases used for name service switches.
1. getent passwd <username>
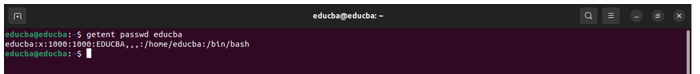
Explanation:
Username: educba
User ID (UID): 1000
Group ID (GID): 1000
User Info: EDUCBA,,,
Home Directory: /home/educba
Login Shell: /bin/bash
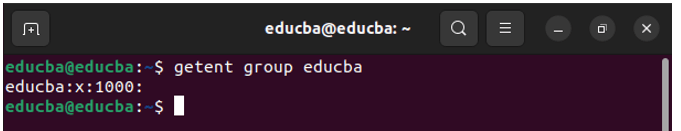
2. getent group <groupname>
This command retrieves information about a specific group.
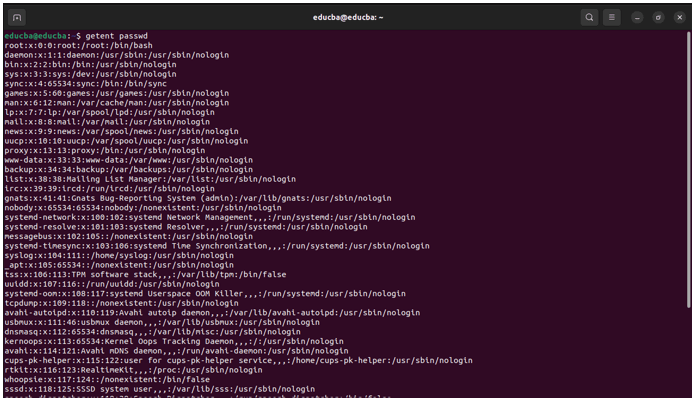
3. getent passwd
This command lists information about all users on the system.
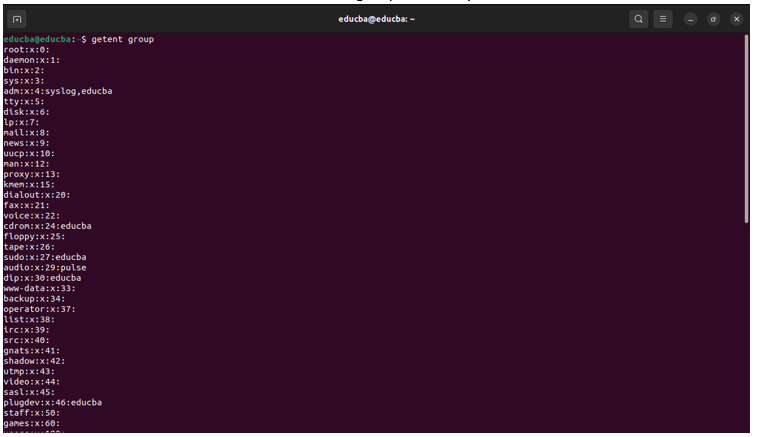
4. getent group
This command lists information about all groups on the system.
Cut and Sort Command
We use the cut and sort command to extract and organize information.
1. Cut Command
Using cut to Extract Relevant Information: The /etc/group file has colon-separated fields. You can use cut to extract specific fields, like the group name, GID (Group ID), and members.
Command:
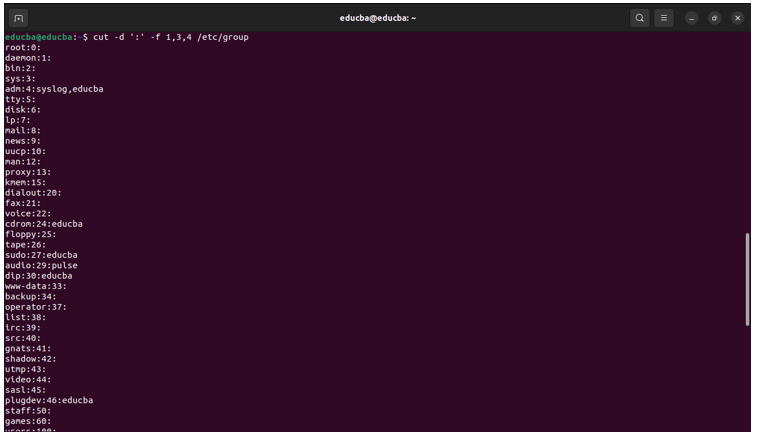
cut -d ':' -f 1,3,4 /etc/groupThis command will extract the group name, GID, and members from the /etc/group file.
Original Output:
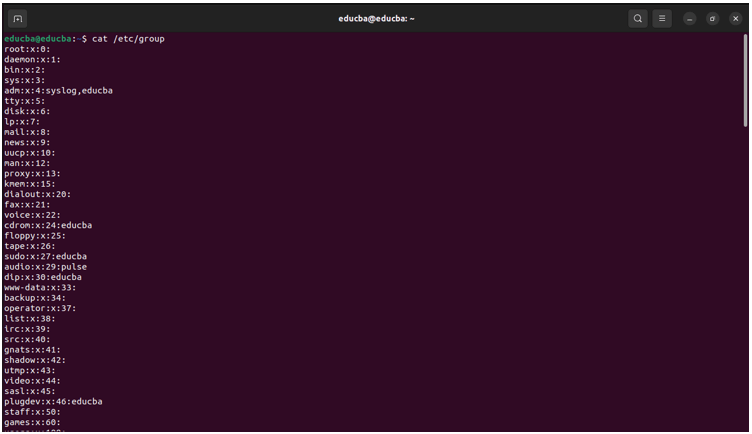
Output after using the cut command:
2. Sort Command
The Sort command will Sort the groups based on a specific field, such as the GID.
Command:
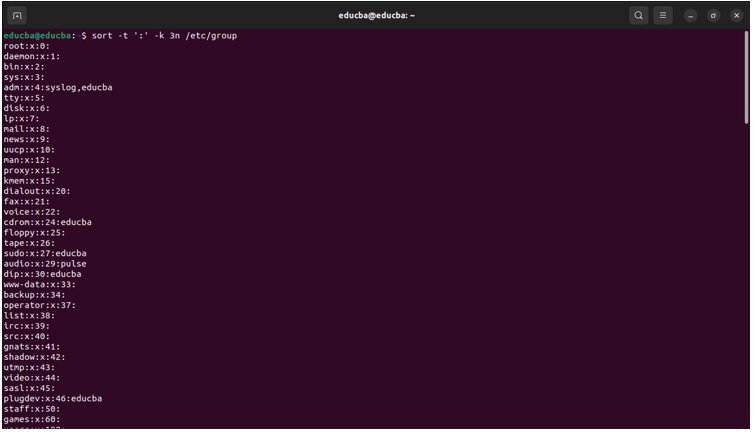
sort -t ':' -k 3n /etc/groupOutput before the Sort command:
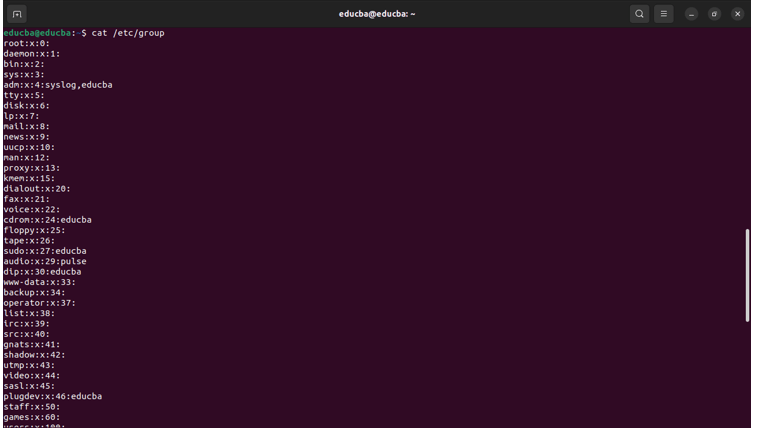
Output after the Sort command:
Example 1: Combining cut and sort for a Sorted Group List
Combining the two commands, we can create a sorted list of groups with relevant information.
Command:
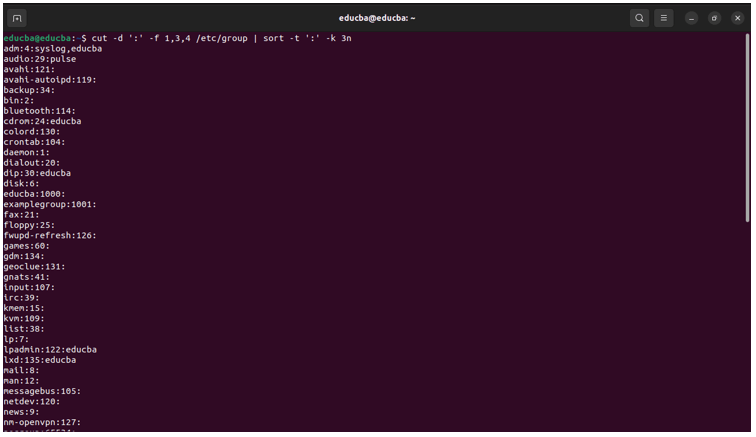
cut -d ':' -f 1,3,4 /etc/group | sort -t ':' -k 3nThis command extracts the desired fields with cut and then sorts the output based on the GID with sort.
Output:
Example 2: Cut and Sort
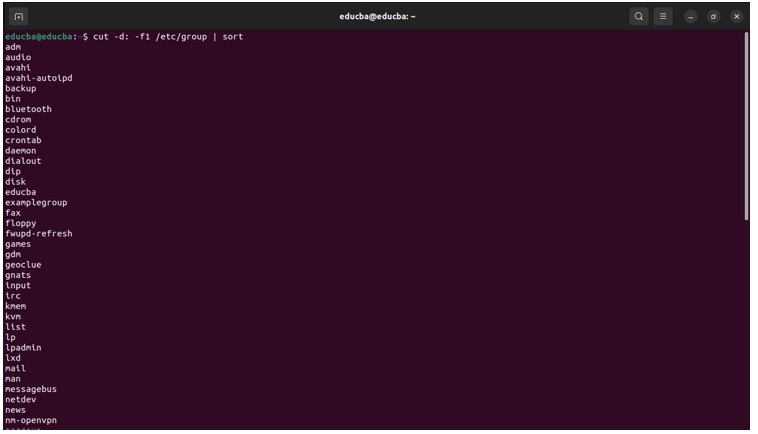
Command:
cut -d: -f1 /etc/group | sortThis command extracts the group names from the /etc/group file using the cut command and sorts them alphabetically using the sort command.
AWK Command
The awk command is a highly effective processing tool. It is beneficial for pattern scanning and processing. It takes text input, applies a program to each line, and prints the results.
The keyword “awk” comes from the initials of its designers: Alfred Aho, Peter Weinberger, and Brian Kernighan. The name “awk” is derived from the surnames of these three individuals.
Syntax for awk command:
awk 'pattern { action }' file- pattern: Specifies a pattern or condition.
- { action }: Specifies what to do with lines that match the pattern (e.g., print, modify, etc.).
- file: Specifies the input file to be processed. If not provided, awk reads from standard input (e.g., output of another command or pipeline).
A few examples using AWK:
1. Print Specific Fields from /etc/group
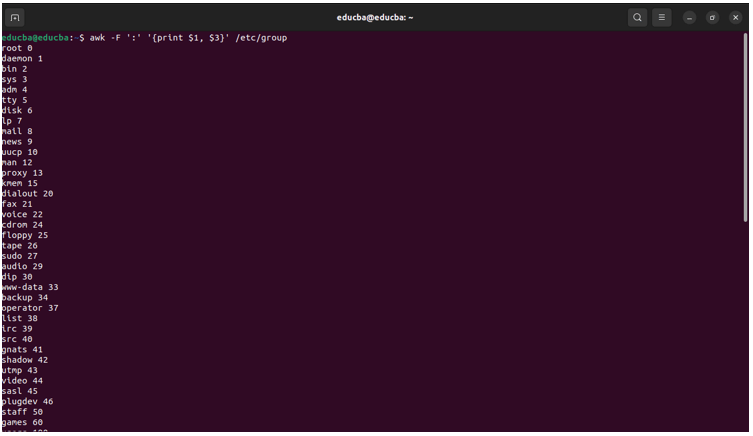
Command:
awk -F ':' '{print $1, $3}' /etc/groupOutput:
2. Filter Groups Based on a Condition (e.g., GID > 1000)
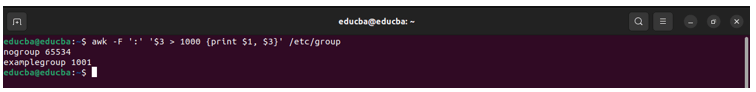
The below command print groups with GID greater than 1000
Command:
awk -F ':' '$3 > 1000 {print $1, $3}' /etc/groupOutput:
Commands to Manage a Group in Linux
1. groupadd: Used to create a new group on a Linux system
Syntax:
groupadd [options] group_nameExample:
groupadd mygroup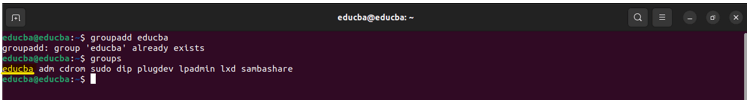
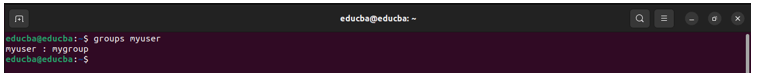
2. usermod: Modifies user account properties, such as the username, home directory, or group.
Syntax:
usermod [options] usernameExample:
usermod -g mygroup myuser(changes the primary group of the user)
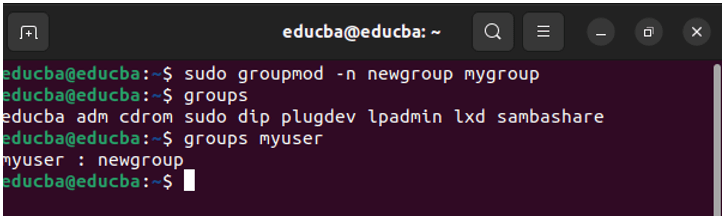
3. groupmod: Modifies group properties, such as the group name or GID (Group ID)
Syntax:
groupmod [options] group_nameExample:
groupmod -n newgroup mygroup(changes the group name)
4. groupdel: Deletes a group from the system
Syntax:
groupdel group_nameExample:
groupdel mygroup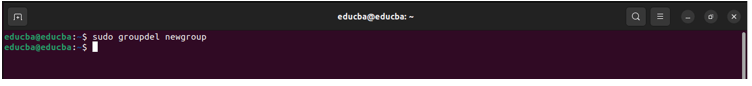
Listing the Group of a Specific User with Libuser
Note: You must first install libuser with the following command:-
‘’sudo apt install libuser''.Command:
sudo libuser-lid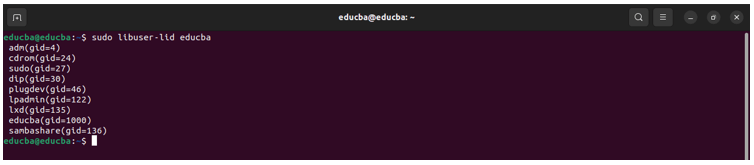
Grep Command
The grep command in Linux searches and matches patterns in text using regular expressions. It prints the matching lines.
Below is the basic syntax of the grep command:
‘’grep [options] pattern [file(s)]’’Here, pattern is the text or regular expression you want to search for, and [file(s)] are the optional file(s) in which to search. If no files are specified, grep will read from standard input.
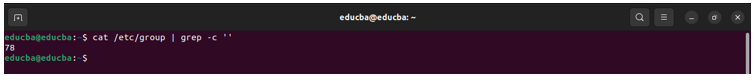
Example 1
Command:
cat /etc/group | grep -c ‘’Output:
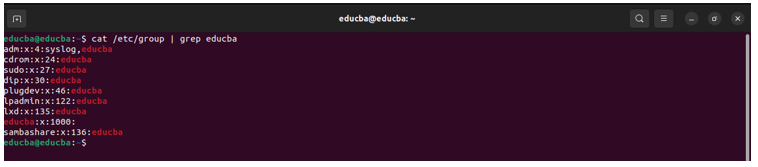
Example 2
Command:
cat /etc/group | grep educbaOutput:
Uses for Linux Listing Commands
- User Management: When managing user accounts on a Linux system, administrators often need to check which users belong to a specific group. This information is crucial for access control and permissions.
- File and Directory Permissions: Users and groups assign directory and file permissions in Linux. Listing groups can help administrators understand the current access control setup and make necessary adjustments.
- System Administration: System administrators may use group information when configuring services or applications that require specific group memberships for access or functionality.
- Troubleshooting: When troubleshooting permission issues or access problems, listing groups can provide insights into which groups a user belongs to and help identify potential issues.
- Security Auditing: Security audits often involve reviewing user and group memberships to ensure proper access controls and identify any security vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Understanding how to list groups and manage their memberships not only enhances system administration skills but also contributes to creating a more organized and secure computing environment. It also provides valuable insights into the collaborative and security aspects of operating systems. We have seen that /etc/group file, and getent commands will give you complete information on the group lists in Linux. We have also used cut, sort, and count options to modify the output for better understanding.
FAQ’s
1. What is the significance of the /etc/group file in Linux group management?
Answer: The /etc/group file contains information about groups on the system, including group names, group ID (GID), and a list of group members.
2. What are default groups in Linux, and how are they created?
Answer: During user creation, default groups are often created and specified in the /etc/default/useradd configuration file. They include the user’s primary group and other groups specified for that user.
3. Can I create a group with a specific GID in Linux?
Answer: Yes, you can use the groupadd command with the -g option to specify a specific GID. For example: ’’sudo groupadd -g 1001 new_group”.
4. Are there any graphical tools available for managing groups in Linux?
Answer: Yes, several graphical tools, such as “Users and Groups” or “gnome-system-tools,” provide a user-friendly interface for managing users and groups in Linux.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Linux List Groups” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


