Updated April 18, 2023
Introduction to Linux Directory Structure
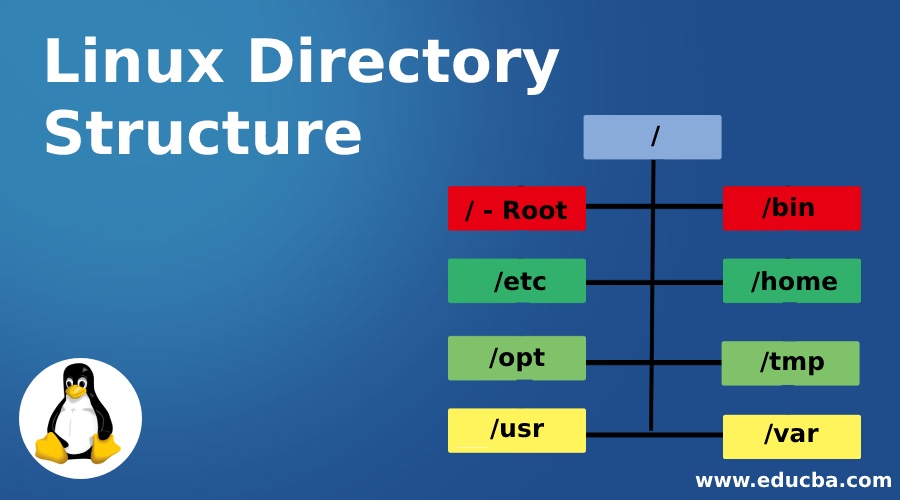
The structure of the Linux directory looks like a tree. This is very much different from that of the windows file system. Linux directory will look like /bin, /lib, etc. File Hierarchy System (FHS) is maintained by Linux Foundation. The FHS defines the structure and purpose of a particular Linux directory. Courtesy of this FHS we will find the same directory structure in most Linux distributions. In this, we will discuss the important and basic Linux directories.
Linux Directory
Below are the important and basic Linux directories:
1) / – Root
The base of Linux directory is the root. This is the starting point of FHS. Every directory arises from the root directory. It is represented by a forward slash (/). If someone says to look into the slash directory then they referring to the root directory.
2) /bin
This directory contains all the binary or executable program files. All the source code that we write is in a human-readable form. This source is converted into a machine-readable code. The binary file is nothing but strings of zeroes and ones. Another important thing is that applications, programs, and commands that we use are sometimes located in the /bin directory.
Example: ps, ls, ping, grep, cp.
3) /etc
The core configuration files are stored in /etc directory. It controls the behavior of an operating system or application. This directory also contains startup and shutdown program scripts that are used to start or stop individual programs.
Example: /etc/logrotate.conf, /etc/resolv.conf.
4) /home
The user’s home directory is stored under /home directory. Linux system often contains multiple user accounts. The home directory allows the users to separate their data from other users in the Linux Operating System. For example, if the user name of the account is john then the home directory will be /home/john. Here the john directory is known as a subdirectory. A subdirectory is nothing but a directory that resides inside another directory.
5) /opt
The opt directory is used for installing the application software from third-party vendors that are not available in the Linux distribution. Usually, the software code is stored in the opt directory and the binary code is linked to the bin directory so that all users can run that software. For example, Google Earth application doesn’t come under Linux distribution and it is installed in the /opt/google/earth directory.
6) /tmp
All the temporary files created by the system and the user are stored under this directory. A user can also store files under this directory. But remember that the contents of this directory are deleted whenever the system reboot or restarts. So do not store files in this directory that you want to store for a long time.
7) /usr
This is called a user directory. This directory contains libraries, source code, binaries and documentation required for second-level programs. The binary files of a user is stored in /usr/bin and the binary files of the system are stored in /usr/sbin. The system libraries are stored in /usr/lib.
Example: useradd, atd, cron, userdel.
8) /var
The variable data files such as log files are located in the /var directory. File contents which tend to grow are located in this directory. This includes
- /var/log: System log files generated by OS and other applications.
- /var/lib: Contains database and packages files.
- /var/mail: Contains Emails.
- /var/tmp: Contains Temporary files needed for reboot.
Listing Directories in Linux
The files and directories in the Linux Operating System can be listed using the ls command. Let us see how to use ls command to list files and directories.
LS COMMANDS
Syntax:
$ ls [options] [directory/file]When ls command is used without any options or arguments it simply displays all the files and directories that is present in the current directory that the user is working in.
Command:
$ lsOutput:
![]()
If you want to list files in a particular directory use the directory name as the argument and pass it to the ls command.
Command:
$ ls /etcOutput:
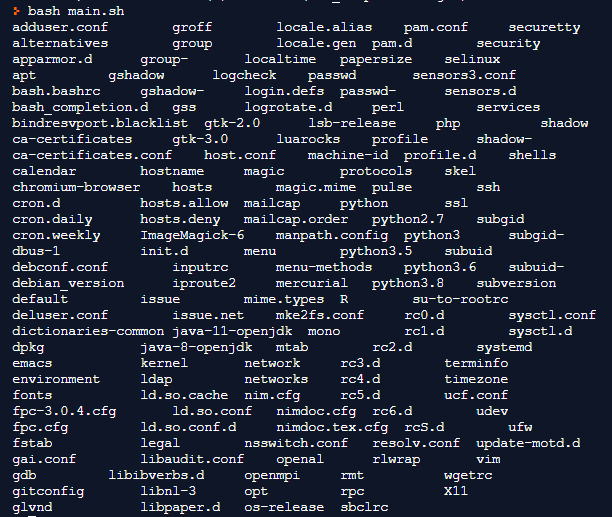
We can likewise pass different directories to the command ls isolated by space.
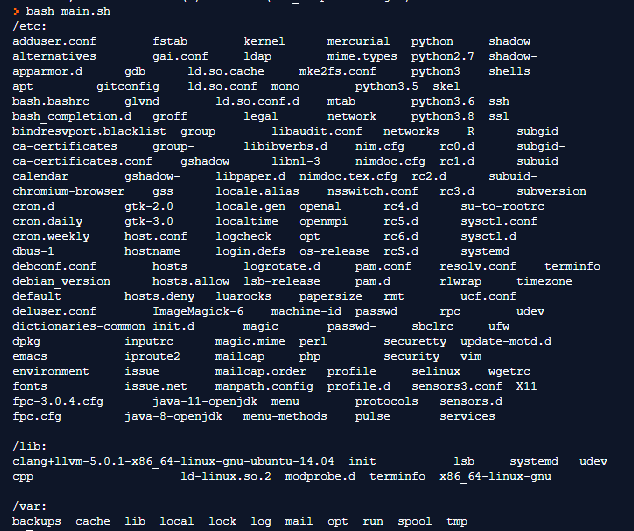
Command:
$ ls /etc /lib /varOutput:
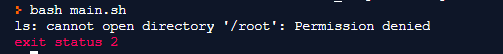
If the user doesn’t have read permission to a particular directory then the output will produce a message saying permission denied.
Command:
$ ls /rootOutput:
There are numerous options in ls. Let us discuss about few basic options.
Long Listing Format
By default ls command displays only the name of the file and directory. The -l option makes the ls command to display files in a long listing format. Using the -l option prints the following information.
- file type
- file permission
- number of hard links present in the file
- file owner
- file group
- file size
- date and time
- file name
Take a look at the following example
Command:
$ ls -l /etc/hostsOutput:
![]()
Here the – indicates a regular file.
- r: permission for reading file.
- w: permission for writing.
- x: permission for executing the particular file.
- s: setgid bit.
- t: sticky bit.
The next couple of fields which is root, root indicates the owner and name of the group. 337 is the size of the file in bytes. The next field indicates the date and time when the file is last modified. The last column indicates the name of the file.
How to Display Hidden Files?
In Linux distribution a hidden file starts with dot (.). In order to display a file which is hidden use the command shown below.
$ ls -la ~/Output:
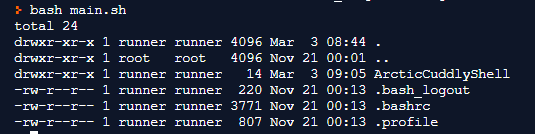
$ ls -a![]()
$ ls -al
Sorting the Output:
To sort the output file by size use.
$ ls -STo sort the file by date and time.
$ ls -tTo sort the file by extension name.
$ ls -XTo List Sub-directories Recursively.
$ ls –RIf we want to display the output in reverse order.
$ ls -ltr /var
The above command will sort the files by last edited time in var directory and displays it in reverse order.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Linux Directory Structure” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


