Updated April 20, 2023

Introduction to Linux Directory Permissions
In the Linux operating system, directory permission is used to grant the access used to access the specific directory. The permission level of the directory is a bit similar to the file. In the directory permission, we need to take care of read permission, write permission and execute permission. In the Linux ecosystem, we are getting the multi-user environment i.e. multiple users can access the Linux environment as well as access the directory structure. To avoid any data loss or any untrusted user access. It is mandatory to keep the proper permission directory on the respective directory.
Syntax of Directory Permission
Given below is the syntax of Directory Permission:
ll [ Directory Name ]
chmod [ OPTION ] [ Access Type ] [ Directory Name/Path ]
chown [ OPTION ] [ Owner/Group ] [ Directory Name/Path ]- ll: The “ll” command is useful to print the directory permission information of the specific directory.
- chmod: We can use the chmod keyword in the syntax or command. It will take the two arguments as access permission and the directory name or path. As per the provided arguments, it will change the directory permission of the specified directory.
- chown: The “chown” keyword is similar to “chmod”. But here, we are using chown for changing the directory owner and group.
- OPTION: We can provide the different flags as options that are compatible with the “chmod” and “chown” command.
- Access Type: We can provide the different flags of access permission that are compatible with the “chmod” command.
- Directory Name/Path: As per the requirement, we can provide the name or path of the directory to change the permission.
How does Linux Directory Permission work?
The directory permission works on the basis of below two points:
- Permission/Access Type
- Access group or user
As per the above two points, we can set or define the directory permissions on the directory.
1. Permission/Access Type: In the Linux environment, the permission type will be read, write and execute.
2. Access group or user: We can define or grant access to a specific group or the users. Accordingly, the directory permission the specific group or user can access the directory.
Below are the lists of directory permission options available:
| Sr. No | Option | Description |
| 1 | -4, –read | We can use the integer value as “4” to grant the read access on the directory. |
| 2 | -2, –write | We can use the integer value as “2” to grant the write access on the directory. |
| 3 | -1, –execute | We can use the integer value as “1” to grant the execute access on the directory. |
Examples of Linux Directory Permissions
Given below are the examples mentioned :
Example #1
Directory Permission
It is a very simple and common way to check the directory permission in a Linux environment. It will print the current information of directory permission on the Linux terminal.
Code:
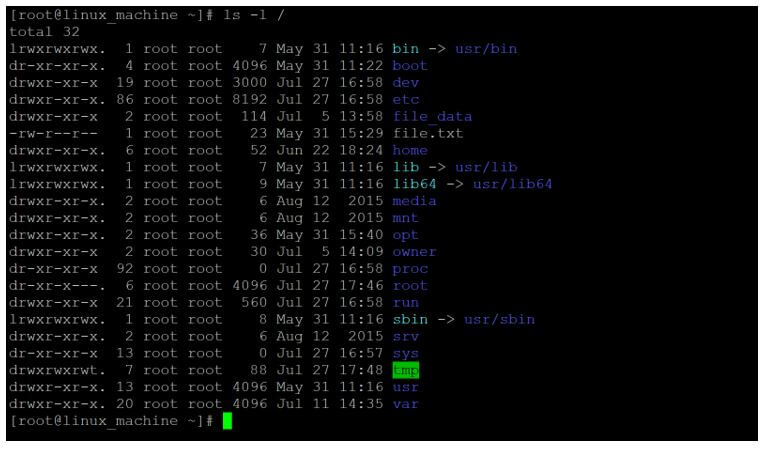
ls -l /Explanation:
- As per the below screenshot, we are able to get the different directory access type information. The entire directory having “root” owner and “root” group access.
Output:
Example #2
Directory Permission – Change to “read” Permission
By default, when any directory will create then the directory owner having full permission. The group and others will have the read and execute permission. But we can change the directory permission to read-only.
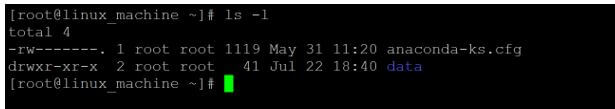
Code:
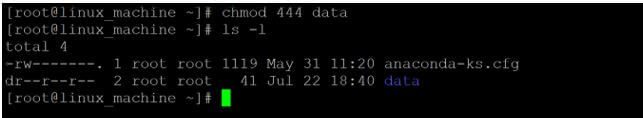
chmod 444 dataExplanation:
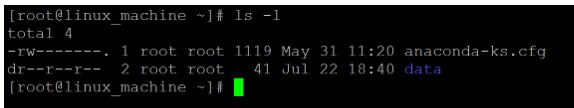
- We are changing the access type of the “data” directory from 755 (-rwx rx rx) to 444 (- r r r). On “data” directory, the owner, group and other only are having the read access.
Output:
Example #2
Directory Permission – Change to “write” Permission
In the directory permission concept, we are able to change the permission from the current state to write permission. We need to use the “2” (write) integer value with the chmod command.
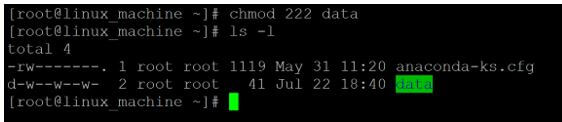
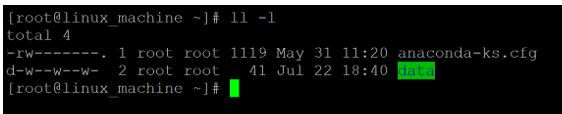
Code:
chmod 222 dataExplanation:
- We are changing the access type of the “data” directory from 444 (-r r r) to 222 (- w w w). On “data” directory, the owner, group, and others only is having them write access.
Output:
Example #3
Directory Permission – Change to “execute” Permission
In the Linux environment, we are able to change the permission from the current state to execute permission. We need to use the “1” (execute) integer value with the chmod command.
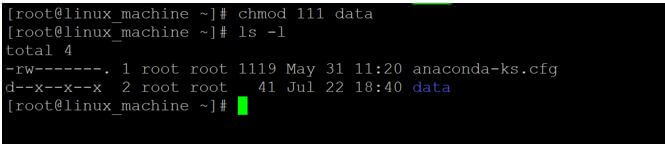
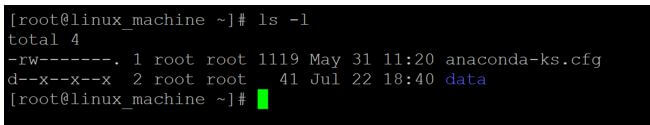
Code:
chmod 111 dataExplanation:
- We are changing the access type of the “data” directory from 222 (-w w w) to 111 (- e e e). On “data” directory, the owner, group, and others only are having the execute access.
Output:
Example #4
Directory Permission – Change the Directory “Owner”
In the Linux ecosystem, we are having the functionality to change the directory owner from the current owner to requested user.
Code:
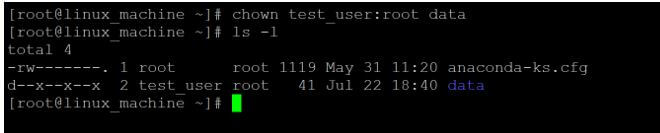
chown test_user:root dataExplanation:
- As per the above command, we are able to change the “data” directory owner from “root” user to “test_user” user.
Output:
Example #5
Directory Permission – Change the Directory “Group”
As per the directory owner change, we can also change the access directory group as well.
Code:
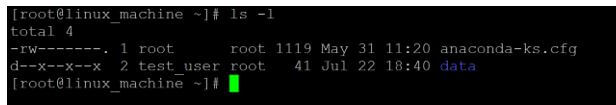
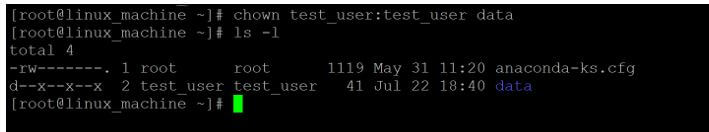
chown test_user: test_user dataExplanation:
- As per the above command, we are able to change the “data” directory group from the “root” group to “test_user” group.
Output:
Example #6
Directory Permission – With Option “-R”
In the Linux environment, we are having a huge amount of files as well as the sub-directories. It is not possible to change the directory permission one by one. To overcome this problem, we are having the “-R” option. With the help of this option, we can set the directory permission recursively.
Code:
chmod -R 777 data/
chown -R test_user: test_user data/Explanation:
- As per the above two commands, we are able to reclusively change the “data” directory access type from 755 (-rw r r) to 777 (-rwerwerwe) and the owner and group from “root” to “test_user”.
Output:

Conclusion
We have seen the uncut concept of “Linux Directory Permission” with the proper example, explanation, and command with different outputs. The directory permission is very important in terms of security point of view. We are able to change the access type of the directory as well as the directory owner and group.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Linux Directory Permissions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


