Updated March 24, 2023
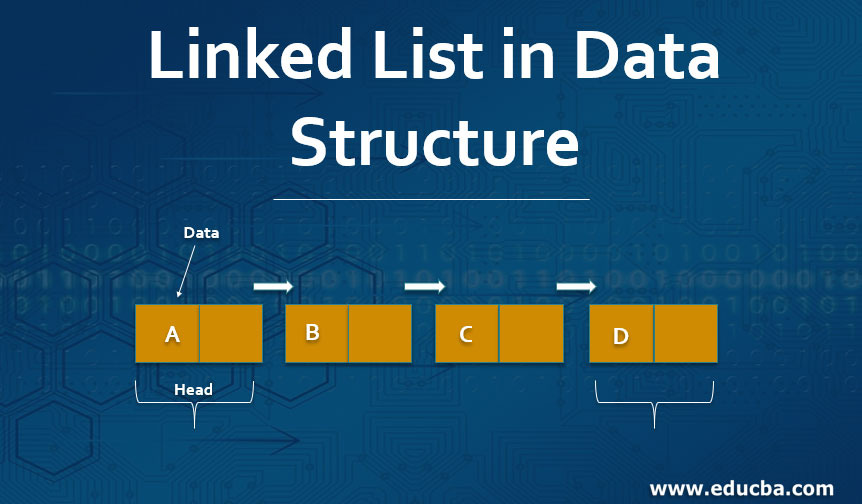
Introduction to Linked List in Data Structure
A linked list is a type of data structure that stores data in the form of a list of nodes. Each node has two parts. The first part stores the data element and the second part stores the reference to the next node. A linked list is a compelling data structure and helps in effective and efficient memory management.
How to Perform Operations on Linked List?
Operations like insertion and deletion can be efficiently performed for a linked list. Both insertions, as well as deletion, can be done from the beginning as well as the ending. We shall see how insertion and deletion happen for both cases through programs. Let’s go through the following programming code implemented in C language to understand linked list insertion and deletion operations.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int d;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *start = NULL;
void insertbegin(int);
void insertend(int);
void display_list();
void delete_begin();
void delete_end();
int c = 0;
void main ()
{
int i, d;
for (;;) {
printf("\n1. Beginning Insert.\n");
printf("\n2. End Insert.\n");
printf("\n3. Display linked list.\n");
printf("\n4. Beginning Delete.\n");
printf("\n5. End Delete.\n");
printf("\n6. Exit\n");
scanf("%d", &i);
if (i == 1)
{
printf("\nEnter an element for beginning insertion: ");
scanf("%d", &d);
insert_begin(d);
}
else if (i == 2)
{
printf("\nEnter an element for ending insertion: ");
scanf("%d", &d);
insert_end(d);
}
else if (i == 3)
display_list();
else if (i == 4)
delete_begin();
else if (i == 5)
delete_end();
else if (i == 6)
break;
else
printf("\nInvalid input.");
}
getch();
}
void insert_begin(int x)
{
struct node *t;
t = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
t -> d = x;
c++;
if (start == NULL) {
start = t;
start -> next = NULL;
return;
}
t -> next = start;
start = t;
}
void insert_end(int x)
{
struct node *t, *temp;
t = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
t -> d = x;
c++;
if (start == NULL)
{
start = t;
start -> next = NULL;
return;
}
temp = start;
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
temp -> next = t;
t -> next = NULL;
}
void display_list()
{
struct node *t;
t = start;
if (t == NULL)
{
printf("There is no element in the linked list.\n");
return;
}
printf("There are %d elements in linked list.\n", c);
while (t->next != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", t->d);
t = t->next;
}
printf("%d ", t->d);
}
void delete_begin()
{
struct node *t;
int k;
if (start == NULL)
{
printf("There's no element in the list.\n");
return;
}
k = start -> d;
t = start -> next;
free(start);
start = t;
c--;
printf("%d deleted from the beginning of the linked list.\n", k);
}
void delete_end()
{
struct node *t, *v;
int k;
if (start == NULL)
{
printf("Linked list is empty.\n");
return;
}
c--;
if (start->next == NULL)
{
k = start->d;
free(start);
start = NULL;
printf("%d deleted from the end of the linked list.\n", k);
return;
}
t = start;
while (t->next != NULL) {
v = t;
t = t->next;
}
k = t -> d;
v -> next = NULL;
free(t);
printf("%d deleted from end successfully.\n", k);
}
When we execute the program, we get options, as shown in the screenshot below. We have to enter the requisite option number for performing that operation.
Output:
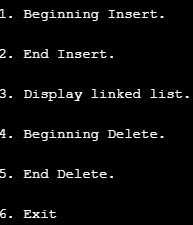
Code Explanation: We implemented the above code and executed it to check how it works. Going through the code, we can find that the program asks the user to enter one of the six choices viz. first inserting an element at the beginning of the linked list, second inserting an element at the end of the linked list, third displaying the linked list, fourth deleting an element from the beginning of the linked list, fifth deleting an element from the end of the linked list, and lastly to exit from the program. The infinite loop continues, till the user keeps passing proper input.
In case of exit the program breaks. As can be seen, the program makes heavy use of pointers which is the most important element of a linked list. We verified the above programming code and validated if it works well through a series of executions. The various inputs and the results returned are shown by the following screenshots. Let’s go through each of them,
Let’s begin by entering certain elements at the beginning of the linked list.
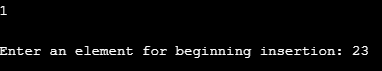
Input 1:
So, we entered 1 as the option. It refers to inserting an element at the beginning of the linked list. We passed 23 as the input which successfully got inserted in the beginning.
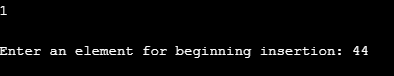
Input 2:
Likewise, we inserted another element which is 44 the beginning of the linked list as shown by the screenshot below.
Input 3:
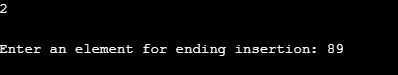
We entered option 2, which refers to inserting an element at the end of the linked list. We inserted 89 at the end of the linked list as can be seen in the below screenshot.
Input 4:
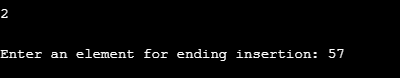
Similarly, we inserted another element, 57 at the end of the linked list as shown by the following screenshot.
Input 5:
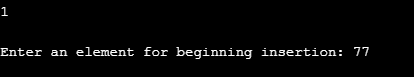
Again, we inserted another element at the beginning of the linked list. This time we inserted 77 as can be seen in the below screenshot.
Input 6:
Now, we chose option 3, which is for displaying the linked list. As can be seen below, the linked list now has five elements.
![]()
Input 7:
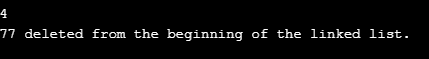
We will now delete some elements. This time option 4 was chosen and 77 stored at the beginning got deleted from the list.
Input 8:
Similarly, we deleted another element from the beginning of the linked list.
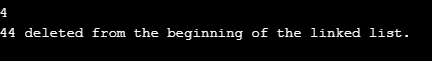
Input 9:
Now, we chose option 5 to delete an element from the end of the linked list.

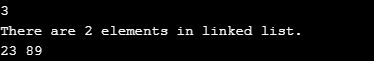
Input 10:
Finally, we displayed the linked list. As can be seen below, the list now contains only two elements.
Conclusion – Linked List in Data Structure
Linked list, as a data structure, is a very complex concept. The use of the concept happens in large-scale applications where memory usage is important. There are various ways in which the linked list can be used, and the context often governs the implementation.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Linked List in Data Structure. Here we discuss a basic concept, how to perform operations in the linked list, and insertion and deletion operation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-

