Updated July 19, 2023
Introduction to Lessor
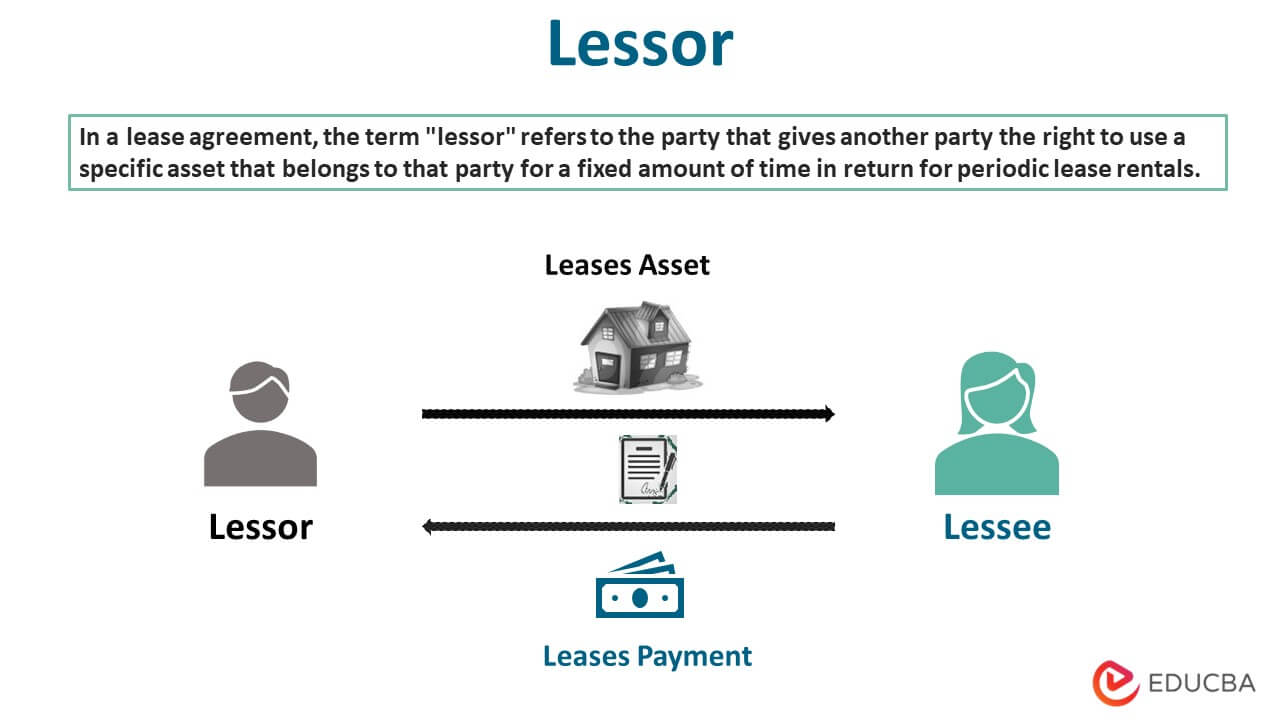
Lessor refers to the party that grants a right to use a particular asset owned by such party to another party for a certain period against the periodic lease rentals under a lease agreement.
The person to whom such right to use the asset is given is the lessee. The arrangement is a leasing arrangement that allows the lessee to use an asset for a particular period.
Explanation
A leasing arrangement involves a party granting a right to the other party to use an asset for a defined term against the periodic rentals. The party that owns the asset and grants the right to the other party is known as the lessor. There can be different assets that can be provided on lease by the lessor. These involve property, machinery, equipment, and so on. The lease rentals can be monthly, or the lessee can make a lump-sum payment. The agreement only confers a right to use the asset to the lessee,, and it is important to note that the lessor remains the asset’s owner.
Role of Lessor
- There shall not be any disruption in the enjoyment of the lease rights during the lease term.
- If there is any defect in the underlying asset, it shall disclose the same before entering into the lease arrangement. There can be two types of defects: latent and apparent.
- Latent defects are defects that cannot be identified through regular inspections. In contrast, apparent flaws can be easily detected through routine examinations.
- The lessor is responsible for reimbursing the lessee for any expenses incurred in preserving the leased asset. However, the lessee will meet the regular maintenance and operating expenses.
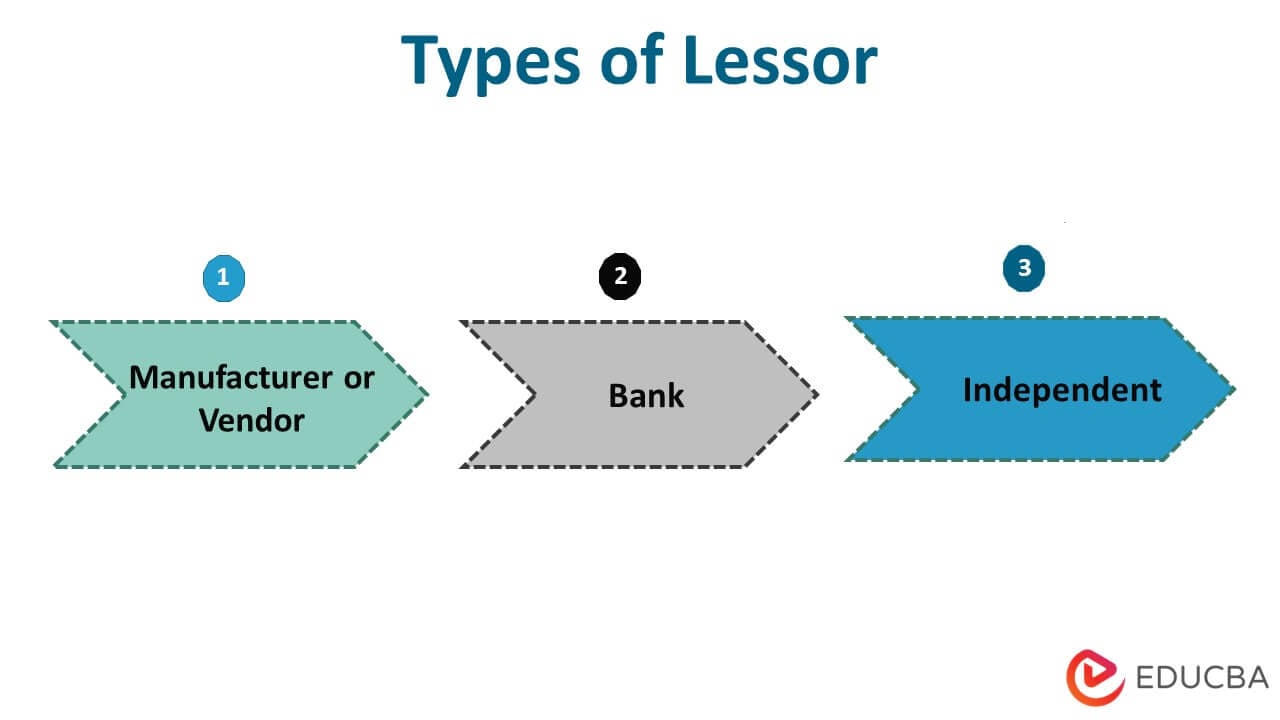
Types of Lessors
There are typically three kinds of lessors as follows:
- Manufacturer or Vendor: The lessor either manufactures the assets that it leases or is a vendor who has an agreement with the leasing company to provide competitive rates.
- Bank: Banks sometimes own leasing companies and extend leasing offers to their existing customers.
- Independent: These are the lessors that are purely into leasing. They might deal with specific industries or asset classes or may deal generally, too.
Examples of Lessors
Suppose a company named RE Properties owns various real estate properties, including commercial and residential properties. The company enters into 5 agreements as follows:
|
Property Type |
Lease Term |
Monthly Rentals |
| Residential- 2 agreements | 5 years | $5,000 |
| Commercial- 3 agreements | 10 years | $12,000 |
Here, RE Properties is the lessor that has entered into lease agreements for the properties.
Lessor vs Lessee
In a leasing arrangement, there are two parties, the lessor and the lessee. A lessor is a party that owns the asset and gives a right to use the asset to the lessee. The lessor retains the ownership rights during the lease term and receives periodic lease rentals as agreed with the lessee. At the end of the lease term, the possession of the asset is given back to the lessor unless the lessee exercises the option to purchase the asset against the transfer price.
Lessee is the party that obtains the right to use the asset for a defined period. The lessee must make periodic payments to the lessor through lease rentals. The asset remains in the lessee’s possession during the lease term, although the lessee doesn’t acquire ownership of the asset under the lease.
Advantages
- It gets periodic lease rentals through which not only can it recover the cost of the asset but can earn profits.
- It can claim tax benefits for expenses such as depreciation on assets, maintenance incurred, etc.
- Ownership lies with the lessor, and if the lessee defaults in payments, it can take back the possession of the asset. Thus, this arrangement is less risky for the lessor.
- Lease rentals are typically higher than the installments paid to the asset financer, which creates a profitable project for the lessor.
Disadvantages
- The lessor bears the risk of the asset becoming obsolete.
- The lessor can’t charge increased lease rentals in a situation where the market value of the asset increases.
- It takes a substantial time to recover the initial cost of the asset.
- Unusual market fluctuations can impact cash flows, and the lessor may face difficulties in managing cash flows within leasing projects.
Conclusion
Organizations often prefer leasing arrangements as the same gives them a right to use the asset for a certain period. It is especially preferred when the cost of an asset is high, and the acquisition of the asset requires high cash outflow.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Lessor” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.