Updated June 16, 2023

Introduction to Leap Year Program in C
Generally, as we already know, a year has 365 days, but a leap year consists of 366 days. This one day is added in the month of February. This month, which generally has 28 days and is also known as the shortest month in a year, would get added with an extra day, giving us 29 days in that month. It is based on the Georgian calendar. Here, let us see how to write a program to check out whether a given year is a leap year in the C programming language.
Logic:
- Any year divisible by 4 and divisible by 100 and 400 is a leap year.
- The year which is divisible by 4 and not divisible by 100 then that year would be a leap year.
- And obviously, if the year is divisible by 4 and 100 but not divisible by 400, then that year would not be called a leap year.
Pseudo-code/Algorithm
Let us have the above-written logic in the form of a pseudo-code in an algorithmic written format:
- Suppose the year is divisible by 400 alone. Then it is a leap year. If not, then it is a non-leap year.
- Else if the year given is only divisible by 100, then it is a non-leap year.
- Else if the same year is a leap year if the given year is completely divisible by 4.
Flowchart
Below, let us see the programming of leap year through a small flowchart:

The main condition lies with the year value of divisibility with 4 and 100, and the other condition is 400.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int r;
printf("Enter any year value: ");
scanf("%d",&r);
if( ( (r%4 == 0) && (r%100 !=0) ) || (r%400 == 0))
{
printf("This year is definitely a leap year");
}
else
{
printf("This year is not at all leap year");
}
}Output:
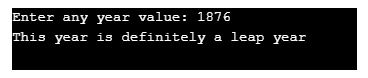
We can have an output for the non-leap year too:
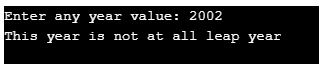
Above here, we have all the conditions for the year values in a single if statement by using ‘and’ and ‘or’ statements.
Examples of Leap Program in C
Let us see the example below:
Example #1
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int year=2020;
if(year % 4 == 0)
{
if(year % 100 == 0)
{
if(year % 400 == 0)
{
printf("The given year 2020 is a leap year");
}
else
{
printf("The given year 2020 is not a leap year");
}
}
else
{
printf("The given year 2020 is a leap year");
}
}
else
{
printf("The given year 2020 is not a leap year");
}
}Output:
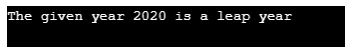
- Here, the main and first tests would be whether the year given is divisible by 4 or not.
- There is an if-else condition for the divisibility test for 4.
- If the condition gives the output true, then there would be next ‘if statements’ are true or not.
- If the divisibility test for 100 condition is true, we proceed to perform the test for 400.
- If that divisibility test is passed for 100, then the divisibility test for 400 should be done successfully too.
- Else, that year would not be considered a leap year.
- And obviously, if the first step of divisibility by 4 has to be successful at that point, we can consider that as a non-leap year condition.
Example #2
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int y;
printf("Enter any year: ");
scanf("%d", &y);
if(y % 4 == 0)
{
if(y % 100 == 0)
{
if(y % 400 == 0)
{
printf("The year given is a leap year");
}
else
{
printf("The year given is not a leap year");
}
}
else
{
printf("This year given is a leap year");
}
}
else
{
printf("This year is not a leap year");
}
}Output:
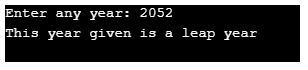
Another set of output can be as below:
Conclusion
So, this is how we can know whether any year is a leap year or not. We have our conditions of the divisibility test for 4, 100, and 400. We have analyzed, and our coding uses a single ‘if condition’ or multiple ‘if and else’ conditions. Either way, the same output can be obtained. This way, we can complete the leap year programming in C programming language.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Leap Year Program in C. Here we discuss the introduction, Pseudo-code/Algorithm, flowchart, and examples of the leap year program in c. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


