Updated April 13, 2023
Introduction to Lambda in Python
Anonymous functions are tagged as lambda functions. It is not something very newly introduced in python alone; lambdas are a part of other languages like Java, C#, and C++. lambda abstractions are the other name of these lambda functions
These lambda functions evolved from lambda calculus; lambda calculus is a computation model. The key idea behind this calculus is abstraction. Turing machines and lambda calculus, both of them can be interpreted into each other. functional languages like Erlang and lisp directly adopted the concept of lambda calculus. The Turing Machine led to essential programming elements found in languages like Fortran, C, or Python.
Key characteristics of Lambda functions
- The number of expressions a lambda function can hold is one, whereas these anonymous functions can withhold more than one argument.
- It can be used to return objects for function
Elements of Lambda functions
The key elements of lambda construction are listed below,
Syntax :
lambda argument(s): expressionSample: lambda x: x
- keyword: lambda
- A bound variable: x
- A body: x
Example:
lambda z: z + 5Here a lambda expression is declared. this function can be injected with an argument through encapsulating parenthesis around both the lambda expression and the argument significance, and since lambda is an expression, it can be named. The number of expressions a lambda function can hold is one, whereas these anonymous functions can withhold more than one argument. It can be used to return objects for function.
a = (lambda z: z+5)(2)
print(a)Output:
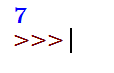
Variable_A = lambda z: z+5
print(Variable_A(2))Output:
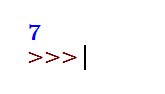
An example of converting a normal function into a lambda function is given below,
Normal function declaration and usage in python
def add_function(x, y):
return x + y
# function call
print(add_function(2, 3))Output:
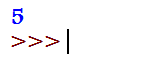
Converting the same into a lambda oriented function
Anonymous_add_function = lambda x, y : x + y
print(Anonymous_add_function(2, 3))Output:
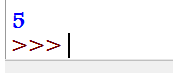
When to use the lambda function?
These lambda functions play a great role in the following instances,
1. When a function is expected to available only for a short period.
2. When a function is being conceded as an argument for a superior function in respect of the order of the function. So this is a scenario where one function picks other function as an argument of it.
Lambda with python map() function
Map function in python takes a function object and a set of iterables. So it performs this map function object for every element of iterables in it and produces the output. The iterables could be a list, tuple, or any collective datatypes. The syntax of the map function is specified below,
Syntax :
map(function_object, iterable1, iterable2,...)Code without Lambda :
def multiply2(x):
return x * 2
a = map(multiply2, [1, 2, 3, 4])
print(a)Output:
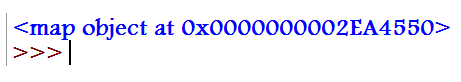
Code with Lambda :
map(lambda x : x*2, [1, 2, 3, 4])Complete Code Snippet :
dict_a = [{'name': 'python3', 'points': 9}, {'name': 'java', 'points': 7}]
list_a = [1, 2, 3]
list_b = [11, 21, 31]
a=map(lambda x : x['name'], dict_a) # Output: ['python3', 'java']
b=map(lambda x : x['points']*10, dict_a) # Output: [90, 70]
c=map(lambda x : x['name'] == "python3", dict_a) # Output: [True, False]
d=map(lambda x, y: x + y, list_a, list_b) # Output: [12, 23, 34]
print(a,b,c,d)Output:

Lambda with python Filter() function
The filter function implies two arguments, namely the function object and the iterable value. The function object always produces a boolean value, and for every element in the iterable segment and every element for which the function object is returned as true are produced as output by the filter function. here the filter function can hold only one iterable as input for it. This is among the key differences of the filter() function about the map() function where the map function can hold more than one iterables. in the other view, both the filter and map function could produce more than one value as output.
- An index level accessing is not a possible instance with these filter objects in place.
- On top of the fact that the index cannot be used for values in a filter object, even its length cannot be determined in any predefined manner.
Syntax :
filter(function_object, iterable)Complete Code Snippet :
listing_a = [1, 3, 2, 4, 1]
dictionary_a = [{'name': 'python3', 'points': 11}, {'name': 'java', 'points': 9}]
a = filter(lambda x : x['name'] == 'python', dictionary_a)
print(a)
b = filter_obj = filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, listing_a) # filter object
print(b)
even_num = list(filter_obj) # Converts the filer obj to a list
print(even_num)Output:
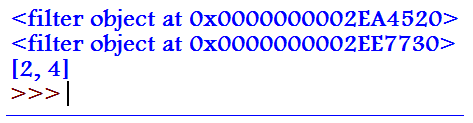
Conclusion
These anonymous functions largely help code reduction and encourage optimized use of python elements; they play a significant role specifically in two neccessive instances, One when a function is expected to available only for a short period in the overall life cycle of the program involved. When a function is being conceded as an argument for a superior function in respect of the order of the function, this is the state of affairs where one function chooses another function as an argument.these instances bring in larger code optimization into python boundaries which make python among the most flexible programming languages in the current world.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Lambda in Python” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


