Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to Keras MaxPooling2D
Keras MaxPooling2D is a pooling or max pooling operation which calculates the largest or maximum value in every patch and the feature map. The results will be down sampled, or it will pool features map which was highlighting the most present feature into the patch which contains the average feature presence from the average pooling. The max pooling is found to work well in average pooling for vision tasks.
Key Takeaways
- The keras max pooling two-dimensional layer executes the pooling operation of spatial data which is max. We need to define parameters while defining keras maxpooling2d.
- We can make the max pooling operations concrete by applying the output feature to the map of the line detector.
Overview of Keras MaxPooling2D
Keras maxpooling2d is a convolution layer that creates the convolution layer. This layer creates the convolution kernel which was winded with the layer of inputs which helps us to produce the outputs of the tensor. The kernel is an image processing matrix of mask which is used in blurring, sharpening edge detection and used to do the convolution between image and kernel. The keras maxpooling2d uses the class name as maxpool2d and it will use the tf keras layers, maxpooling2d class.
It contains the integer or 2 integer’s tuples factors which is used to downscale the spatial dimension. It contains the max pooling operation into the 2D spatial data. Down samples is nothing but the input along with the spatial dimensions which were taken from the input window’s maximum value for each channel. The window will be shifted by using strides along with every dimension.
Keras MaxPooling2D Layers
The keras max pooling two-dimensional layer executes the max pooling operations into the spatial data. To use the layer of maxpooling2d we need to import the maxpooling2d library from the keras module.
Below example shows the syntax of keras maxpooling2d as follows:
Syntax:
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(
……
)Output:

To use it we need to import the below module by using the import command as follows. We are importing the module name as an array, conv2d, sequential and maxpooling2d modules.
Code:
from numpy import as array
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Conv2D
from keras.layers import MaxPooling2DOutput:

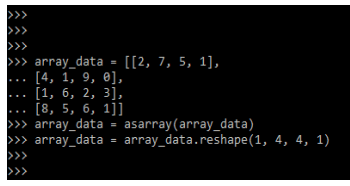
After importing the module now in this example, we are defining the input data as follows. We are defining the data in array format.
Code:
array_data = [[2, 7, 5, 1],
[4, 1, 9, 0],
[1, 6, 2, 3],
[8, 5, 6, 1]]
array_data = asarray(array_data)
array_data = array_data.reshape(1, 4, 4, 1)Output:
After defining the data input now, we can see that we are creating the model and using the maxpooling2d layer as follows.
Code:
mod = Sequential()
mod.add (Conv2D(1, (3,3), activation = 'relu', input_shape = (4, 4, 1)))
mod.add (MaxPooling2D())Output:

After creating the model now in this step we are summarizing the created model and defining the line detector of vertical as follows.
Code:
mod.summary()
det = [….]
weights = [asarray(det), asarray([0.0])]Output:

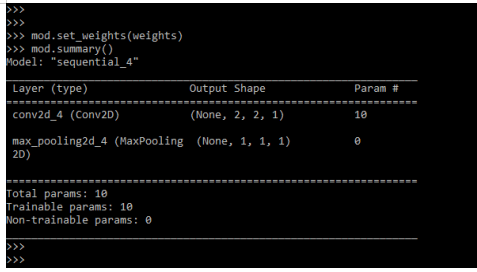
After summarizing the model now in this step, we are storing weights in the model and summarize the model.
Code:
mod.set_weights(weights)
mod.summary()Output:
Keras MaxPooling2D in Class
A convolution layer is used in ordering layers that were defined into the neural network and repeated once or more times from the given model as an addition to the pooling layer. This layer is defined in a common pattern. To create the same number of pooled features, the pooling layer operates on the feature map. The selection of the pooling process involves maximum pooling.
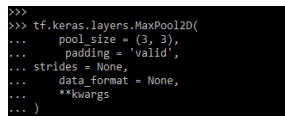
We are applying the features in the features map. The below example shows keras maxpooling2d in class as follows.
Code:
tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(
pool_size = (3, 3),
padding = 'valid',
strides = None,
data_format = None,
**kwargs
)Output:
The pooling operation size is smaller than the size of the feature map, specifically, it will be 2*2 pixels and the same is applied in 2 pixels. We can say that the maxpooling2d class reduces the size of the number of pixel values that were mapped to quarters. We can specify the pooling operation by specifying the common functions. The pooling layer result will create a down-sampled and contains the pooled features which were summarized into the input which was detected. The class of maxpooling2d is useful in small changes in the location of a convolutional layer. The keras maxpooling2d capability added into the pooling is called local translation.
Keras MaxPooling2D Arguments
Below are the arguments that we are using at the time of defining a keras maxpooling2d example as follows.
- pool_size – This is a defined integer or tuple of two integers. This is defined as the window size which takes the maximum value into the pooling window which was 2*2. If suppose we have specified a single integer then the same length is used for all dimensions.
- Strides – This is defined integer or tuple of two integers or it defines no value. This argument will specify how far our pooling window will be moving for every step of pooling. If suppose value is none then it will set the default as pool_size.
- Padding – It defines the one as the same or valid. Valid defines no padding. The same result in the padding is defined as up, down, left, or right input, such that our output contains the same input height and width.
- Data_format – This defines the string which contains the channel_last or channel_first. The dimensions ordering defines the input. Channels last will define the input shape channel first will correspond input with the shape. This string defaults to the value of the image data format which was found in a keras configuration file.
The keras maxpooling2d returns the maximum pooled values from the specified input. We can also define input and output shapes in keras maxpooling2d.
Examples of Keras MaxPooling2D
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
In the below example we are importing the keras module.
Code:
from numpy import asarray
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Conv2D
from keras.layers import MaxPooling2D
arr = [[3, 8, 6, 2],
[5, 1, 2, 3],
[2, 7, 5, 4],
[9, 6, 3, 1]]
arr = asarray(arr)
arr = arr.reshape(1, 4, 4, 1)
mod_1 = Sequential()
mod_1.add (Conv2D(1, (3,3), activation = 'relu', input_shape = (4, 4, 1)))
mod_1.add (MaxPooling2D())
det = [….]
keras = [asarray(det), asarray([0.0])]
mod_1.set_weights(keras)
mod_1.summary()Output:

Example #2
In the below example, we are defining the pool_size as 2, 2, and padding as the same.
Code:
maxpool = tf.constant ([])
maxpool = tf.reshape (maxpool, [])
max_pool_2d = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D (pool_size=(2, 2),
strides=(1, 1), padding = 'same')
max_pool_2d (maxpool)Output:

FAQ
Given below are the FAQs mentioned:
Q1. What is the use of max pooling two-dimensional in keras?
Answer: The keras max pooling two dimensional layer is used in executing the pooling and operation and is also used to calculate the largest value from the feature map.
Q2. How many arguments do we need to use while using keras maxpooling2d?
Answer: We need to define four arguments while using keras maxpooling2d i.e. pool_size, strides, padding, and data_format.
Q3. Which modules we are importing at the time of working with keras maxpooling2d?
Answer: We need to import the asarray, tensorflow, sequential, maxpooling2d, and conv2d while working with keras max pooling two-dimensional.
Conclusion
This layer creates the convolution kernel which was winded with the layer of inputs which helps us to produce the outputs of the tensor. It is a pooling or max pooling operation which calculates the largest or maximum value in every patch and the feature map.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Keras MaxPooling2D. Here we discuss the introduction, keras MaxPooling2D layers, arguments, and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

