Updated February 17, 2023
Introduction to JUnit Data Provider
The junit data provider is a static method used to generate the test data. The mandatory thing is that we need to use the test method with the same number and type of arguments with each line in the array of tests. Therefore, using the data provider of a junit is more beneficial than the parameterized runner we are using in junit.
What is JUnit Data Provider?
- We are using the provider of junit data only in annotation by its name. So, for example, the junit parameterized run will run every test method using the junit data provider.
- In a single class of tests, we provide different static methods and use the same in other test methods. Therefore, it is only possible using a junit data provider and not a junit parameterized runner.
- It is a library that makes easy data-driven testing of junit version 4. So if suppose we have an issue with Gradle, we can recommend using it.
How to Create Data Providers in JUnit?
To use a data provider feature in the tests, we need to declare the @DataProvider annotation. After declaring the annotation, we need to use the data provider attribute in this method.
We need to use @Test annotation while using the data provider in junit. The data provider name is used with the test method and the dataset provided in this method.
Below is the syntax to show how to create the same in our code as follows:
Syntax:
@DataProvider (name = "data provider name")
public object [] [] method_of_data_provider ()
{
Return new_object;
}While using the data provider in junit, we need to use the annotation of the data provider. With data provider annotation, we are using the name of the data provider. We must create a method object after providing the name of the data provider. Then we return the object method name as the return type. The below example shows how to create a data provider as follows.
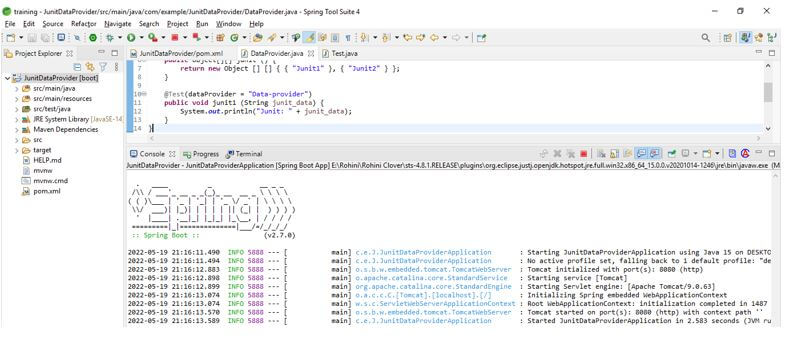
The below steps show how to create a junit data provider as follows. We are making the project name as JunitDataProvider.
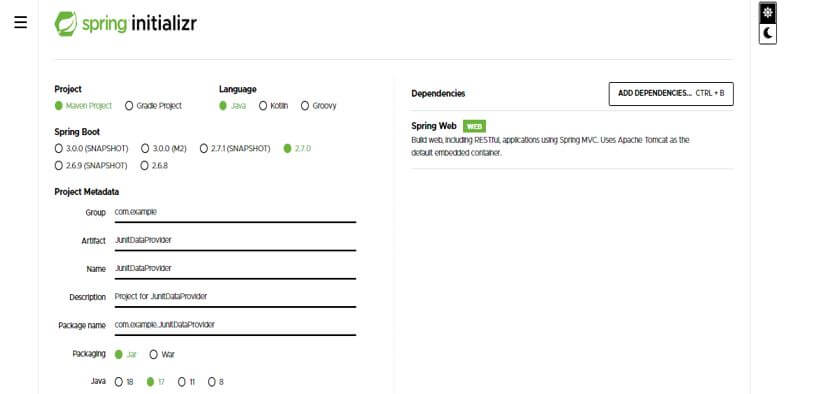
In this step, we create the project template in spring boot. We provide the project group name as com. For example, the artifact name is JunitDataProvider, the project name is JunitDataProvider, and the selected java version is 11. We are defining the version of spring boot as 2.6.7.
Group – com.example Artifact name – JunitDataProvider
Name – JunitDataProvider Spring boot – 2.7.0
Project – Maven Java – 11
Package name – com.example. JunitDataProvider
Project Description – Project for JunitDataProvider
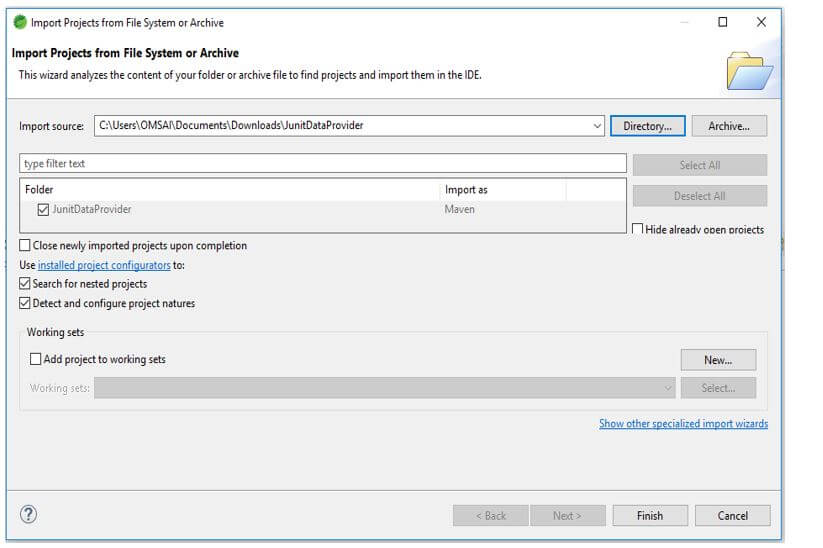
In this step, we extract the downloaded project and open the same by using the spring tool suite.
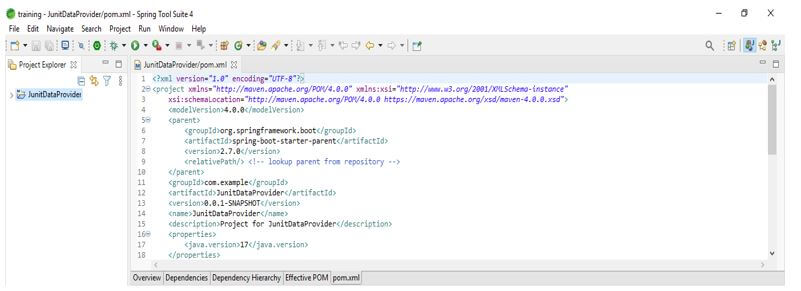
In this step, we check all the project structure and its files. Also, we are checking whether that pom.xml file is created or not. If this file is not created, we need to make the same manually. However, this file is created in the below example, so we do not need to create it manually.
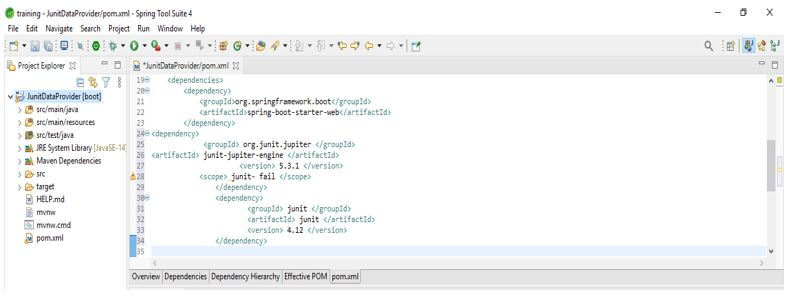
In this step, we are adding the junit dependency to the project. We are adding junit dependency.
Code:
<dependency>
<groupId> org.junit.jupiter </groupId>
<artifactId> junit-jupiter-engine </artifactId>
<version> 5.3.1 </version>
<scope> junit- fail </scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId> junit </groupId>
<artifactId> junit </artifactId>
<version> 4.12 </version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<reporting>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId> org.apache.maven.plugins </groupId>
<artifactId> maven-surefire-report-plugin </artifactId>
<version> 2.19.1 </version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</reporting>After adding the dependency in the below example, we use the @DataProvider and @Test methods in the same class. In the below example, we take the test class, which contains the test method, which takes one argument and prints it to the console when we execute test cases. The data provider method is available in the annotation of the data provider. We can mention the name of the data provider by using name attribute annotation. Data providers in junit will return a double array object using two data sets.
Code:
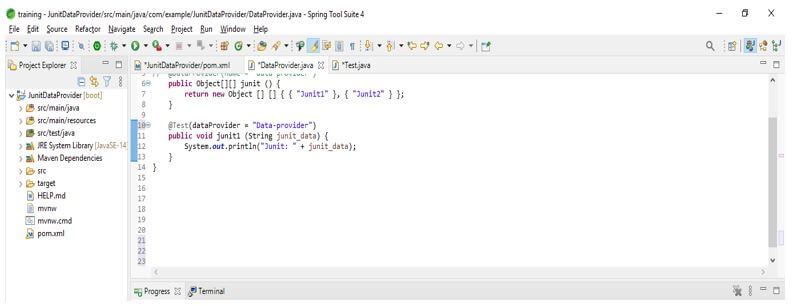
public class DataProvider
{
@DataProvider(name = "data-provider")
public Object[][] junit () {
return new Object [] [] { { "Junit1" }, { "Junit2" } };
}
@Test (dataProvider = "Data-provider")
public void junit1 (String junit_data) {
System.out.println ("Junit: " + junit_data);
}
}Example of JUnit Data Provider
In junit, we can use data provider and test annotation in the same class. Also, we can use the same in a different class. In the below example, we have declared the other classes for the data provider; we are creating a static method for that class. The example below shows how to use data provider and test annotation in a different class. First, we create the class of data provider, then create a class for test annotation.
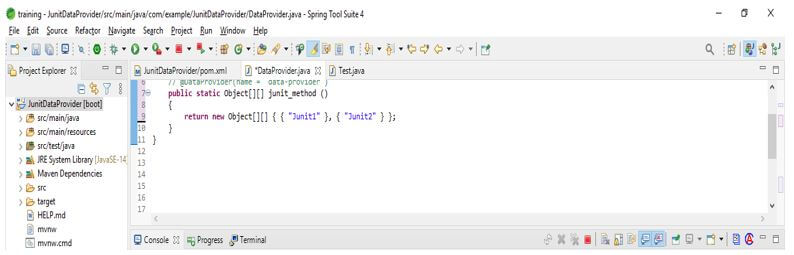
Data Provider Code: In the below code, we are creating a class name as DataProvider after creating the class, we are defining the DataProvider annotation with the data provider name. After determining the name, we call the static method with the string provider.
Code:
public class DataProvider
{
@DataProvider (name = "data-provider")
public static Object [] [] junit_method ()
{
return new Object[][] { { "Junit1" }, { "Junit2" } };
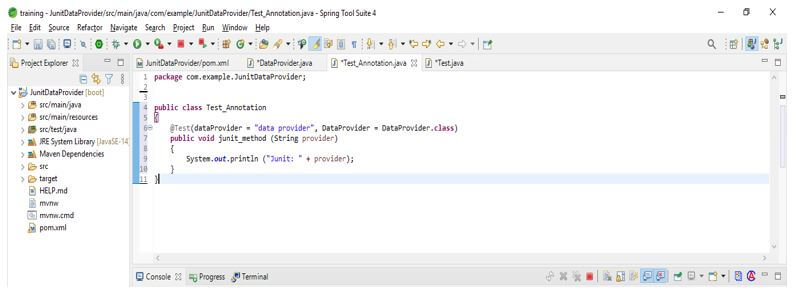
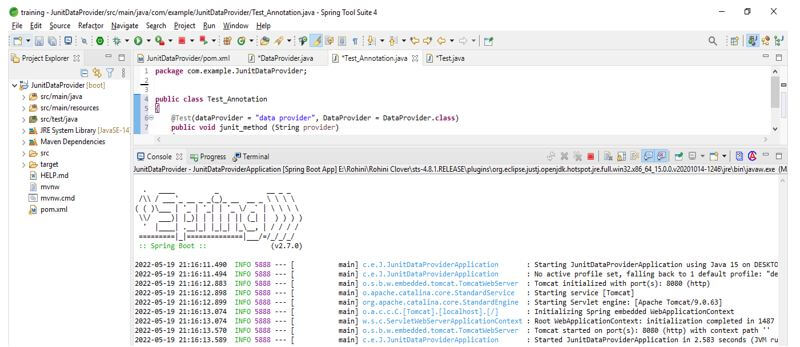
} }Test Annotation Code: In the below code, we are creating a class name as Test_Annotation after creating the class, we define the test annotation with the data provider class name. After determining the class name, we call the method with the string provider.
Code:
public class Test_Annotation
{
public void junit_method (String provider)
{
System.out.println ("Junit: " + provider);
}
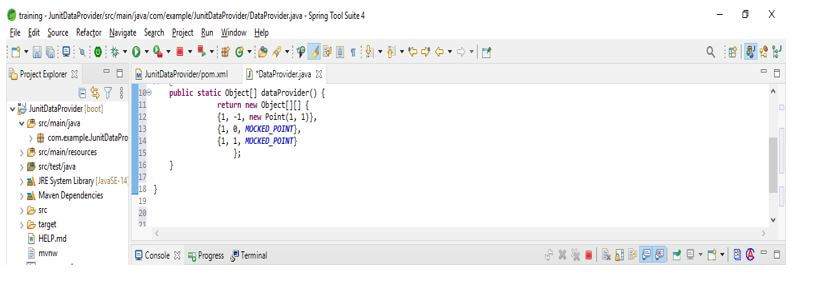
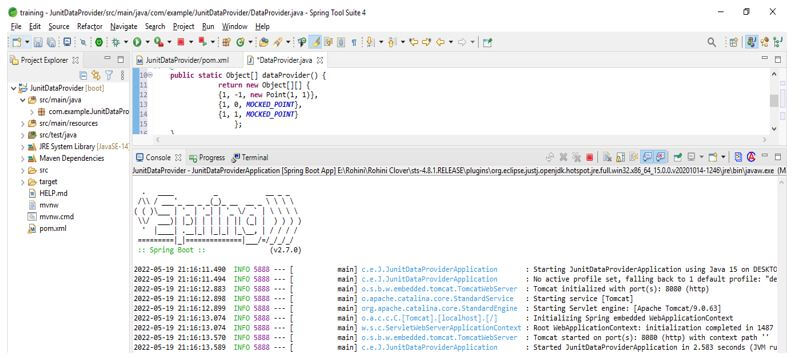
}Using it, we can also define test data using the static method. This method returns the object of the array where each array contains the input and expected output.
Code:
public class DataProvider
@DataProvider
public static Object[] dataProvider() {
return new Object[][] {
{1, -1, new Point(1, 1)},
{1, 0, MOCKED_POINT},
{1, 1, MOCKED_POINT}
};
}
}Conclusion
It is a library that makes easy data-driven testing of junit version 4. If suppose we have an issue with Gradle, we can recommend using the junit data provider. It is a static method used to generate the test data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to JUnit Data Provider. Here we discuss the introduction, example, and how to create data providers in JUnit. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –