Updated July 6, 2023
Introduction to JDBC Architecture
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an API (Application Program Interface) or platform-independent interface which helps to connect java programs with various databases such as Oracle, My SQL, MS Access and SQL Server. It provides ways to query and update the database using Structured Query Language (SQL) update statements such as CREATE, DELETE, INSERT and UPDATE and query statements like SELECT. It is almost similar to ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) that was provided by Microsoft.
To connect the java program or application with the database there are five steps to be followed:
1. Load the Driver: Driver helps to make a connection to the database hence driver must be loaded once in the program. This can be done by two methods:
- Class.forName(): By using this, the driver’s class file is loaded in the memory during run time. There is no need to create a new object. For example:
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");- DriverManager.registerDriver(): Here DriverManager is an inbuilt Java class where the register is its static member. By using this, the constructor of the driver class is called during compile time. In this new object is created. For example:
DriverManager.registerDriver(new oracle.jdbd.driver.OracleDriver());2. Creating Connections: After the driver is loaded, the connection is set up. The connection object uses username, password, and URL to set up the connection. URL has a predefined format which contains database name, the driver used, IP address where the database is stored, Port number and the service provider. The connection can be set up by using the command:
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, user, password);3. Creating Statement: After establishing the connection, the user can interact with the database. The interfaces such as JDBC statement, PreparedStatement, CallableStatement provides methods that allow a user to send SQL statements and get data from the database. Command used to create statement is;
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();4. Executing Query: The SQL query is executed to interact with the database. A query can be for updating/inserting in the database or for retrieving data. Statement interface provides two methods i.e. executeQuery() method to execute queries for retrieving data while executeUpdate() method to execute queries for updating or inserting. For Example:
int n = stmt.executeUpdate("DELETE TABLENAME");
if(n==1)
System.out.println("Success");
else
System.out.println("Failed");5. Closing Connection: After executing our query, the data user wanted to update or retrieve has been done so now it’s time to close the established connection. The connection interface provides a method close() to close the connection. For example:
con.close();JDBC Architecture
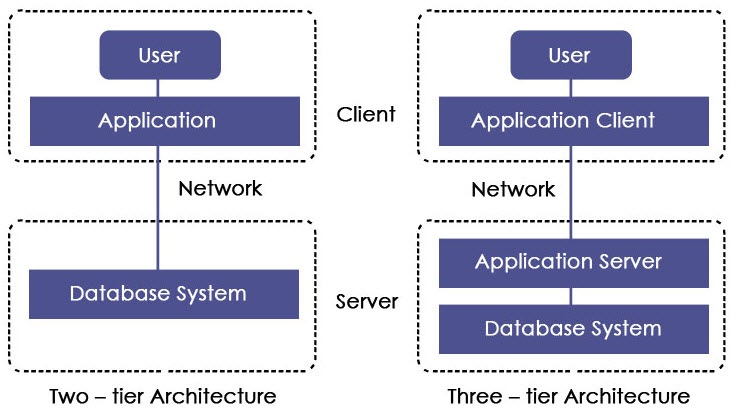
JDBC supports two types of processing models for accessing database i.e. two-tier and three-tier.
1. Two-tier Architecture
This architecture helps java program or application to directly communicate with the database. It needs a JDBC driver to communicate with a specific database. Query or request is sent by the user to the database and results are received back by the user. The database may be present on the same machine or any remote machine connected via a network. This approach is called client-server architecture or configuration.
2. Three-tier Architecture
In this, there is no direct communication. Requests are sent to the middle tier i.e. HTML browser sends a request to java application which is then further sent to the database. Database processes the request and sends the result back to the middle tier which then communicates with the user. It increases the performance and simplifies the application deployment.
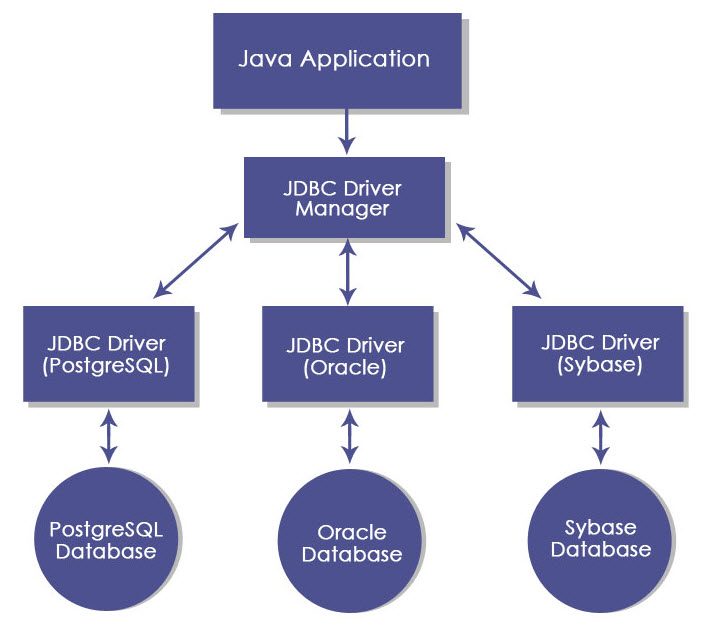
Components of JDBC Architecture
The components are explained below.
- Driver Manager: It is a class that contains a list of all drivers. When a connection request is received, it matches the request with the appropriate database driver using a protocol called communication sub-protocol. The driver that matches is used to establish a connection.
- Driver: It is an interface which controls the communication with the database server. DriverManager objects are used to perform communication.
- Connection: It is an interface which contains methods to contact a database.
- Statement: This interface creates an object to submit SQL queries or statements to the database.
- ResultSet: This contains the results retrieved after the execution of the SQL statements or queries.
- SQLException: Any errors that occur in database application are handled by this class.
Basic JDBC architectural diagram is shown below with the positioning of all components:
Interfaces
The java.sql package consists of many interfaces. Some popular interfaces are mentioned below:
- Driver Interface: This interface allows for multiple database drivers. DriverManager objects are created to communicate with the database. These objects are created by DriverManager.registerDriver();
- Connection Interface: Connection interface establishes the connection i.e. session between java program and the database. It has many methods like rollback(), close() etc.
- Statement Interface: This interface provides methods for the execution of the SQL queries. It provides factory methods to get a ResultSet object. Some methods of statement interface are executeQuery(), executeUpdate() etc.
- PreparedStatement Interface: This interface helps when the SQL queries need to implement many times. It accepts input parameters during runtime.
- CallableStatement Interface: This interface is used when stored procedures are to be accessed. It also accepts parameters during run time.
- ResultSet Interface: This interface helps to store the result returned after the execution of the SQL queries.
Types of JDBC drivers
There are four types of JDBC drivers:
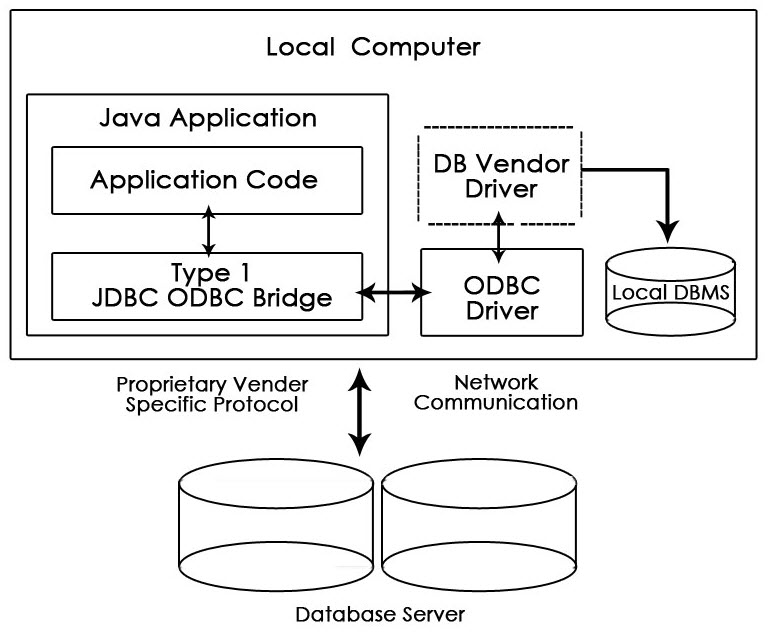
1. Type-1 Driver or JDBC-ODBC Bridge
This driver acts as a bridge between JDBC and ODBC. It converts JDBC calls into ODBC calls and then sends the request to ODBC driver. It is easy to use but execution time is slow.
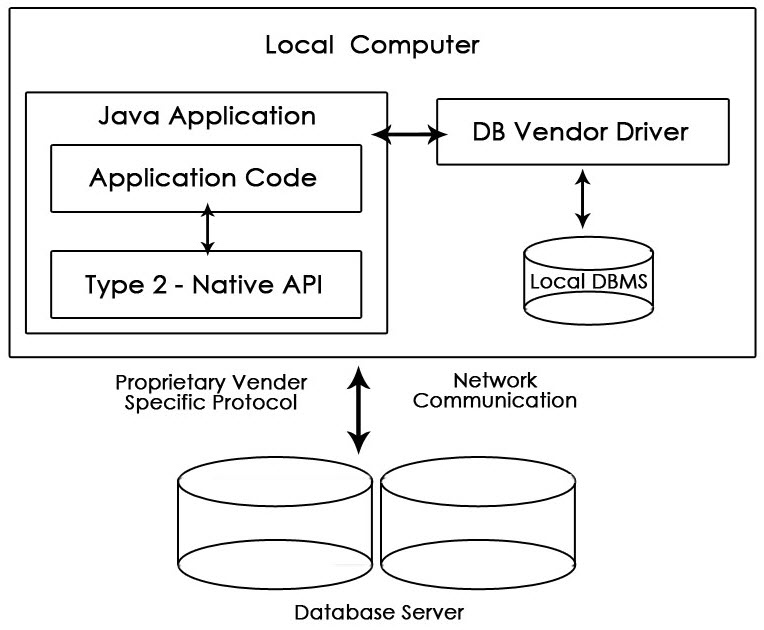
2. Type-2 Driver or Native API Partly Java Driver
This driver uses JNI (Java Native Interface) call on database specific native client API. It is comparatively faster than Type-1 driver but it requires native library and cost of application also increases.
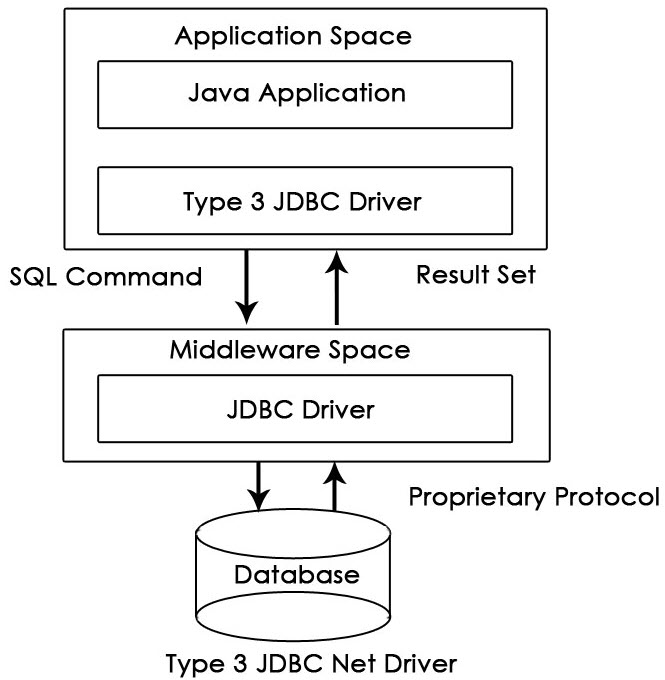
3. Type-3 Driver or Network Protocol Driver
These drivers communicate to JDBC middleware server using proprietary network protocol. This middleware translates the network protocol to database specific calls. They are database independent. They can switch from one database to another but are slow due to many network calls.
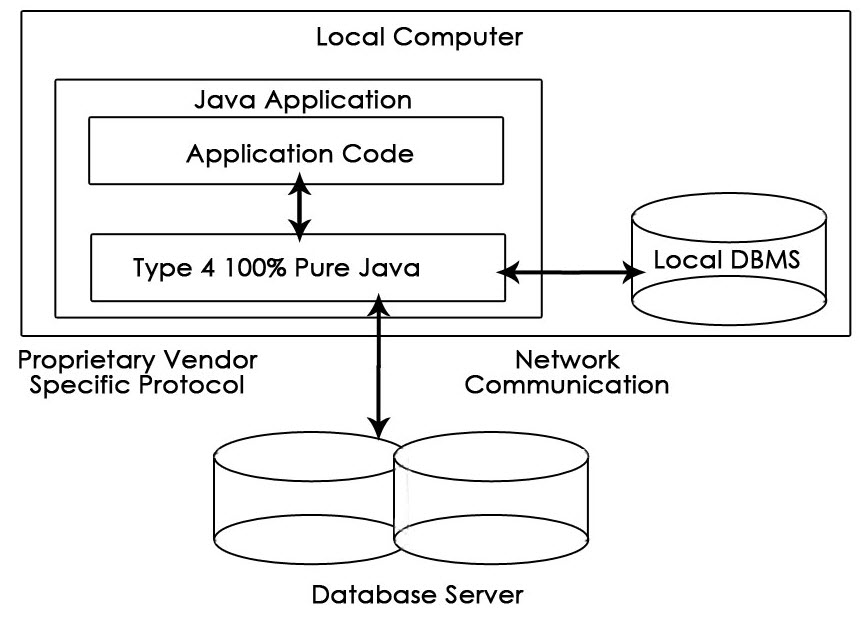
4. Type-4 or Thin Driver
This driver is also called pure Java driver because they directly interact with the database. It neither requires any native library nor middleware server. It has better performance than other drivers but comparatively slow due to an increase in a number of network calls.
Conclusion
This article specifies the JDBC architecture, its interfaces and types of drivers to communicate or interact with the database.
Now a day’s databases are maintained in every sector hence updating them and retrieving data from them is necessary. So understanding the architecture would help to understand the basic JDBC concepts.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “jdbc architecture” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.