Updated April 12, 2023
Introduction to JavaScript IIFE
The JavaScript Immediately Invoked Function Expression (IIFE) is a function which helps in providing a method that defines a sequence of a particular context. Once a variable is defined inside a function it is not possible to access it outside the function where it is defined. The functions which are created in JavaScript have named functions, anonymous functions and by making use of IIFE we can execute these as soon as they are mounted. This functionality makes them IIFE. Let us have a look in detail at how this function works
Syntax
Below is the syntax for JavaScript IIFE:
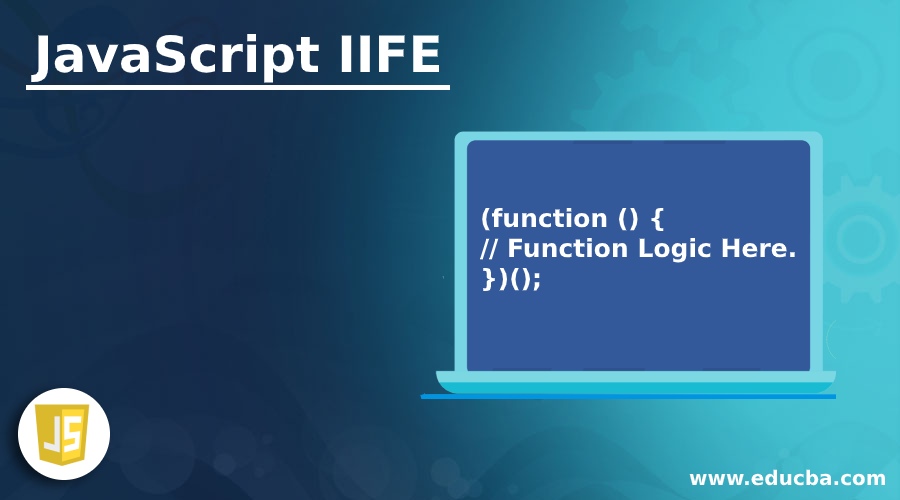
(function () {
// Function Logic Here.
})();Explanation: The primary use of this function is that the variables should be accessible only within the scope of the defined function that is there.
The declaration should begin with the keyword function(). In the function definition, you can define any statements which are to be performed. This function should be hoisted. A hoisted function is always placed at the start of the program or functional scope when the JavaScript code is being executed. You can also use the below syntax:
(() => { // Code that runs in your function })()The parentheses let JavaScript know that there is a function expression and the last pair of parentheses will invoke the function.
How does IIFE work in JavaScript?
Let us see how does it work:
Code:
(function () {
var userName = "Snehal";
function display(name)
{
alert("MyCode2.js: " + name);
}
display(userName);
})();The above code is an example of IIFE. The IIFE helps in including all functions and variables with the same name and they can be accessed globally. Here we define a function and in its definition, we are creating a variable username. We immediately write another function that will display this username. This is the display function where we are sending the username as a parameter. We have created an alert for the same where we display the code script name and then by making use of IIFE we have simply called the function at the end. In this way we have called two functions one after the other. We have rather immediately invoked. Let us check a few examples to understand better.
Examples to Implement JavaScript IIFE
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>JavaScript to check the working of Immediate Invoking Function Expression. </p>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
// anonymous function #1
var isLucky = function() {
var iife = Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
if (iife > 50) {
return "You are checking Immediate Invoking Function Expression!";
} else {
return "We are not in IIFE, better luck next time!";
}
};
var me = isLucky();
alert(me);
// anonymous function #2
window.setTimeout(function() {
alert("JavaScript and EduCBA is awesome!!!");
}, 2000);
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

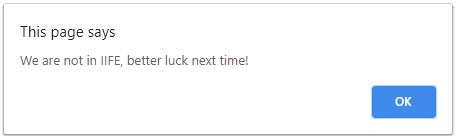
At first, the result is displayed as per the condition. When we again run the program the result is the else part. Once the time outspan is over then the output of the above program will be as below:
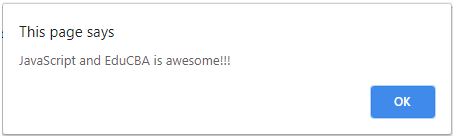
Explanation: The above script helps us understand the IIFE in Javascript better. Here we have created a function isLucky where we are rounding off a random number and then multiplying it by 100. The random number is being generated by the Math.random() function. After this number is generated then we check if the number is less or greater than 50. If the number is greater than 50 then the message will be displayed as: “You are checking Immediate Invoking Function Expression!”. Else the corresponding message for it will be displayed. Once this function is done we are calling it and storing it in a variable called me. Whatever message is returned it will be displayed in the form is an alert window in the browser. Just after this, another function is invoked. This function will time out and display another alert will be displayed. Below will be the output when we run for the first time.
Example #2
Let us take another example of IIFE. We can use this function without if else block as well.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>JavaScript to check the working of Immediate Invoking Function Expression. </p>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
(function() {
var create = "I have learnt what is Immediate Invoking Function Expression from EduCBA successfully !!!";
alert(create);
})();
// anonymous function #2
window.setTimeout(function() {
alert("JavaScript and Edu is awesome!!!");
}, 2000);
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

The message is displayed as soon as the above code is run. Once the timeout happens below alert window turns up automatically.
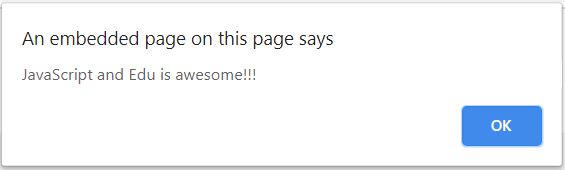
Explanation: The above code is an example of a classic and simple IIFE. We create a function and immediately call it. We have not named this function with any name. We have just created a variable create. This function then uses this to display this message as the sun as the function is invoked. As per the syntax, we are bound to use the parenthesis correctly. If there are any misses in the parenthesis then the code will not give the desired result. We can easily invoke the function as soon as the function is declared and defined. We will just pass empty parentheses in order to invoke the function that we have created. We send the variable to create as a parameter to an alert. When the program is run the alert will be called and whatever is present in the created variable will be displayed in the alert window. We also created a similar function as in Example 1. This will work in a similar way. It will wait for timeout and will again display an alert window with the specified message. The timeout time we have mentioned here is 2 milliseconds. Once this is over the message will be displayed automatically. Let us see the output of the above code.
Conclusion
The Immediate Invoking Function Expression is an easy way of calling a function just after it is created. It helps in keeping the local variables local or global variables as global whenever required. It is fast and hence very efficient to use. It fulfills the programmer’s purpose of keeping the variables intact. IIFE can be used with a name or without any name. They can also be used with unary operators when needed.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to JavaScript IIFE. Here we discuss an introduction to JavaScript IIFE, syntax, how does it work and programming examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


