Updated March 31, 2023

Introduction to Java ServerSocket
The following article provides an outline on Java ServerSocket. In web technology, we have used front end and backend codes separately for creating web applications for the secure purpose.The web application contains servers for receiving the client request and sent to the response for the clients’ particular request. In java technology, with the help of socket programs, we can achieve these tasks when we will send multiple requests with the help of multiple pcs, which has to be connected with the protocols like tcp and udp. We can write the server codes like ServerSocket class, connect with the specified ports, and send them to the data.
Syntax:
The serversocket class is used for the client and server transfer process.
Server Class:
java packages import(import java.io.*,import java.net.*)
class serverclassname
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
--some logic—
}
catch()
{
}
}
}Client class:
Java packages import(import java.io.*,import java.net.*)
class clientclassname
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
--some logic—
}
catch()
{
}
}
}How to use Java ServerSocket?
- Java server socket connections will use the two types of protocols for sent and receive the data.
- TCP(transfer control protocol) and udp(user datagram protocol) will use the sockets class to transfer the data.
- We also see some difference between these two protocols while we use in the socket class when we use udp, it means is a connection less, and there are no sessions for storing the log data regarding client and server transmissions, but in tcp, it is a connection-oriented, so the client and server have the session storages in the log folders.
- The socket programs will be used for communications between the web applications running with the different jre.
- The serversocket class are mainly with the connection-oriented socket programs.
- When we connect the applications with the help of socket, we need to get the information’s like IP Address of the servers and port numbers which has to be connected with the applications for a specified way so that the data transmission will not be interpreted.
- Basically, the socket class between client and server is one-way data transmission. The client will send the request messages to the server, servers read the client messages, and send the response to the client, or else it will display the data on the client screen like browsers.
- So that we will use two types of java net classes are used a socket and serversocket classes; the socket class is responsible for client-server communications, serversocket class is used for server-side applications it will authenticate the request from the client-side until the client machine is connected with the socket class after the successful connections it will return the socket class instance in the server-side applications.
Examples of Java ServerSocket
Given below are the examples:
Example #1
Code: Client Example
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class clientSample {
public static void main(String arg[]) throws UnknownHostException,IOException
{
int n,n1;
String s;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
Socket s1=new Socket("127.0.0.1",1408);
Scanner sc1=new Scanner(s1.getInputStream());
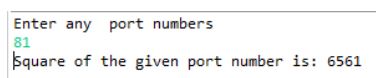
System.out.println("Enter any port numbers");
n=sc.nextInt();
PrintStream p=new PrintStream(s1.getOutputStream());
p.println(n);
n1=sc1.nextInt();
System.out.println("Square of the given port number is: "+n1);
}
}Output:
Code: Server Example
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ServerSample {
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {
int n,n1;
String s;
ServerSocket s1=new ServerSocket(1408);
Socket s2=s1.accept();
Scanner sc=new Scanner(s2.getInputStream());
s=s2.toString();
n =sc.nextInt();
n1=n*n;
PrintStream p=new PrintStream(s2.getOutputStream());
p.println(n1);
System.out.println("Server started and working.. ");
}
} Output:
![]()
Example #2
Code: Client Example
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class clientSample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try{
Socket s=new Socket("127.0.0.1",8888);
DataInputStream d=new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream out=new DataOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String client="",server="";
while(!client.equals("")){
System.out.println("Enter the number :");
client=br.readLine();
out.writeUTF(client);
out.flush();
server=d.readUTF();
System.out.println(server);
}
out.close();
out.close();
s.close();
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}Code: Server Client
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
class ServerClients extends Thread {
Socket sockets;
int clients;
int squre;
ServerClients(Socket s,int count){
sockets = s;
clients=count;
}
public void run(){
try{
DataInputStream inStream = new DataInputStream(sockets.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream outStream = new DataOutputStream(sockets.getOutputStream());
String client="", server="";
while(!client.equals("")){
client=inStream.readUTF();
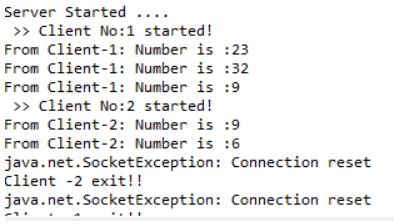
System.out.println("From Client side-" +clients+ ": Number of client is :"+client);
squre = Integer.parseInt(client) * Integer.parseInt(client);
server="From Server to Client request-" + clients + " Square of the client " + client + " is " +squre;
outStream.writeUTF(server);
outStream.flush();
}
inStream.close();
outStream.close();
sockets.close();
}catch(Exception ex){
System.out.println(ex);
}finally{
System.out.println("Client -" + clients + " exit!! ");
}
}
}Code: Server Example
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class ServerSample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try{
ServerSocket s=new ServerSocket(8888);
int count=0;
System.out.println("Server is Started ....");
while(true){
count++;
Socket socket=s.accept();
System.out.println(" >> " + "ClientNo:" + count + " started!");
ServerClients sc = new ServerClients(socket,count);
sc.start();
}
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}Output:
Example #3
Code: Client Program
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class ClientMain
{
public static void main (String[] args ) throws IOException {
int size=1022388; int bytess; int c = 0;
Socket sockets = new Socket("localhost",12345);
byte [] bytes = new byte [size];
InputStream in = sockets.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("F:\\copy.doc");
BufferedOutputStream b = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
bytess= in.read(bytes,0,bytes.length);
c = bytess;
do {
bytess = in.read(bytes, c, (bytes.length-c));
if(bytess >= 0) c += bytess;
}
while(bytess > -1);
b.write(bytes, 0 , c);
b.flush();
b.close();
sockets.close();
} }Code: Server Program
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main (String [] args ) throws IOException
{ ServerSocket serverSockets = new ServerSocket(12345);
Socket sockets = serverSockets.accept();
System.out.println("Server connection Accepted : " + sockets);
File f = new File ("F:\\Sample.docx");
byte [] bytes = new byte [(int)f.length()];
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(f);
BufferedInputStream b = new BufferedInputStream(input);
b.read(bytes,0,bytes.length);
OutputStream output = sockets.getOutputStream();
System.out.println("Sending Files...");
output.write(bytes,0,bytes.length);
output.flush(); sockets.close();
System.out.println("File transfer complete");
} } Output:

Conclusion
In java programming technology, the package is called java.net.* In that each version of java it may vary the classes in the package the server socket connection is a basic networking feature for file transmission, upload and even though we have sent an email from one client to another client with the help of socket connections
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java ServerSocket. Here we discuss the introduction, how to use Java ServerSocket, along with respective examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


