Updated March 28, 2023

Introduction to Java Parallel Stream
A parallel stream is a parallel flow of objects that supports various functions which can be intended to produce the expected output. Parallel stream is not a data structure that allows the user to enter input from Collections, Arrays, Java Input and Output APIs. Parallel stream does not change the functionality’s actual behaviour, but it can provide the output based on the applied filter (pipeline). Parallel stream is part of Java functional programming that comes into existence after the Java 8th version. Parallel stream is an added advantage to the Lambda expressions.
Ways to do Parallel Stream in Java
- parallelStream() method
- parallel() method
How does Parallel Stream work in Java?
It is based on the applied parallelStream() method on collections or parallel() method on streams.
Syntax:
List<Object> list=new ArrayList<Object>();
list.parallelStream();Explanation:
- First, we create an array list collection.
- On array collection applied paralleStream() method.
- We conclude that parallelStream() applied only on collections.
Syntax:
IntStream inStream=IntStream.rangeClosed(initialValue, finalValue);
inStream.parallel();Explanation:
- First, we create an IntStream stream.
- On stream applied parallel() method.
- We conclude that parallel() applied only on streams.
Examples
Given below are the examples:
Example #1
parallelStream() applied on Capital Alphabets.
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ParalleStreamOnAlphabets {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Capital Alphabets before Parallel Stream");
// creating array list for adding alphabets
List<String> capitalAlphabets = new ArrayList<>();
int ascilCode = 65; // Ascii value of A=65 and Z=90
while (ascilCode <= 90) { // iterating ascii values
char alphabets = (char) ascilCode; // converting integer to character
capitalAlphabets.add(String.valueOf(alphabets)); // adding Capital alphabets to list
ascilCode++;// pre increment operator
}
// displaying initial Alphabets
capitalAlphabets.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("Capital Alphabets after Parallel Stream");
// inserting all elements to another list to apply parallelStream
// operation without modifying previous array list
List<String> captatlAlphabetsParalleStream = capitalAlphabets;
//applying parallelStream() on new array list
captatlAlphabetsParalleStream.parallelStream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}Output:


Explanation:
- As you can see the output before applying parallel stream, we got output sequentially.
- But when we applied the parallel stream, then we got output zig-zag manner means parallelly.
Example #2
parallelStream() applied on Even Numbers.
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ParallelStreamEvenNumbers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Even Numbers before Parallel Stream");
// creating array list for adding alphabets
List<Integer> evenNumbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int number=0;number<=10;number++) { // iterating numbers
if(number%2==0) //if number even go inside the condition
evenNumbers.add(number); //added all even numbers
}
// displaying initial even numbers
evenNumbers.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("Even Numbers before Parallel Stream");
// inserting all elements to another list to apply parallelStream
// operation without modifying previous array list
List<Integer> captatlAlphabetsParalleStream = evenNumbers;
// applying parallelStream() on new array list
captatlAlphabetsParalleStream.parallelStream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}Output:
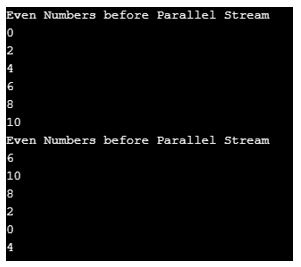
Explanation:
- As you can see the output before applying parallel stream, we got output sequentially.
- But when we applied the parallel stream, then we got output zig-zag manner means parallelly.
Example #3
parallelStream() applied on courses fee.
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class ParallelStreamCourseFee {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("How many number would you like to enter=>");
int inputNumber = scanner.nextInt(); // asking user for number count
List<Courses> courseWithFee = new ArrayList<Courses>();// creating array
String coursename = "";
int courseFee = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < inputNumber; i++) {
coursename = scanner.next();//taking course name input
courseFee = scanner.nextInt();//taking course fee input
courseWithFee.add(new Courses(coursename, courseFee));//adding course name and fee
}
//get the stream list which courses fee is >1000
Stream<Courses> list = courseWithFee.parallelStream().filter(e -> e.getCourseFee() > 1000);
//displaying courses count which is fee is >1000
System.out.println("Course Fee above 1000 is=> " + list.count());
scanner.close();
}
}
//courses class
class Courses {
String course;
int courseFee;
public Courses(String course, int courseFee) {
this.course = course;
this.courseFee = courseFee;
}
public String getCourse() {
return course;
}
public void setCourse(String course) {
this.course = course;
}
public int getCourseFee() {
return courseFee;
}
public void setCourseFee(int courseFee) {
this.courseFee = courseFee;
}
}Output:
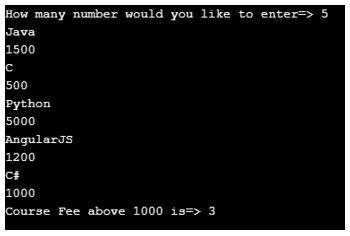
Explanation:
- As you can see in the output, we got to count for course fee is >1000.
Example #4
parallel() applied on Odd Number count.
Code:
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Taking InStream with range of 1 to 1000
//On rane() applied parallel method
//On parallel() method applied filter to decide whether given number odd or not
//after getting odd numbers we simply displaying odd numnbers count
int oddNumberCount = (int) IntStream.range(1, 1000).parallel().filter(value -> oddOrNot(value)).count();
//displaying odd number count
System.out.println("Count of Odd Number from 1-1000 range is => " + oddNumberCount);
}
public static boolean oddOrNot(int inputNumber) {
//checking first number >0 and then checking range from 1 tom 1000
//next checking odd number or not within nonMatch method
return inputNumber > 0
&& IntStream.rangeClosed(1, inputNumber).noneMatch(temp -> inputNumber % 2 == 0);
}
}Output:
![]()
Explanation:
- As you can see parallel method can be applied with streams only.
Example #5
parallel() applied on Prime number.
Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.function.IntPredicate;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class ParallelPrimeNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("How many number would you like to enter=>");
int inputNumber = scanner.nextInt(); //asking user for number count
System.out.print("Enter your numbers =>");
List<Integer> listNumbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();//creating array list
for (int i = 0; i < inputNumber; i++) {
listNumbers.add(scanner.nextInt());//adding user elements into an array
}
//checking the entered numbers are prime or not
//filter(ParallelCount::isPrime) ParallelCount is class name and primeNumberOrNot method
List<Integer> primeOut = listNumbers.stream().filter(ParallelPrimeNumber::primeNumberOrNot).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.print("Prime number set from your entered numbers is/are=>");
for (Integer i : primeOut) {
System.out.print(i+" ");//displaying prime numbers
}
scanner.close();
}
public static boolean primeNumberOrNot(int i) {
//IntPredicate checks the number whether even, odd, prime etc. based on condition
IntPredicate trueOrNot = index -> i % index == 0;
//return true if entered number is prime else returns false
return i > 1 && IntStream.range(2, i).noneMatch(trueOrNot);
}
}Output:
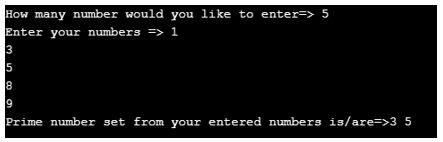
Explanation:
- As you can see in the above code, even the parallel method on streams also performs prime number, even number, odd number, etc., logic.
Advantages and Applications of Java Parallel Stream
Given below are the advantages and applications:
Advantages
- Improves CPU utilization more efficiently than normal filters.
- Parallel stream process multiple data at a time.
Applications
- Used with Aggregate functionality.
- Used with more sized collection frameworks.
- Used with sequential streams.
Conclusion
It is achieved with parallelStream() method on collections and parallel() method on streams. Parallel stream reduces processing time, so it mostly used large collection data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java Parallel Stream. Here we discuss the introduction, how parallel stream work in Java, and examples, advantages, and applications. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


