Updated April 6, 2023

Introduction to Java Matcher
Java Matcher class is one of the classes of the Java Regex package. Java Matcher class and pattern are part of the Regex package, which provides the facility of creating classes and interfaces for regular expressions. It helps to find the operations and the character sequence of the regular expression and then make a comparison with the other character sequence of the regular expression to hit a match. Once a match gets hit, it creates an interface which is called as MatchResult interface. A regex engine is used to perform the defined scenario of character sequence matching and creating the interface.
Java Matcher Class Methods
Given below are the class methods:
- public boolean matches()
- public boolean find()
- public boolean find(int start)
- public String group()
- public int start() and int start(int group)
- public int end() and int end(int group)
- public int groupCount()
- public boolean lookingAt()
- public Matcher appendReplacement()
- public StringBuffer appendTail()
- public String replaceAll()
- public String replaceFirst()
- public static String quoteReplacement()
1. public boolean matches()
boolean matches() is a method within the Java Matcher class that is used to test whether the regular expression matches the pattern.
Example:
This program illustrates the public boolean matches() method of the Java Matcher class with the pattern.
Code:
import java.util.regex.*;
public class BooleanRegMatches{
public static void main(String args[])
{
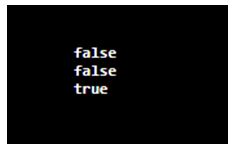
System.out.println(Pattern.matches("[banana]", "qda"));
System.out.println(Pattern.matches("[mango]", "mn"));
System.out.println(Pattern.matches("[orange]", "e"));
}
}Output:
2. public boolean find()
This method is part of the matcher class is used to find and match the next expression, which can match the pattern and can be used to create an interface.
Example:
This program is used to find and match the regular expression to match and compare with the pattern to create the interface.
Code:
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class Regx_Pattrn_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
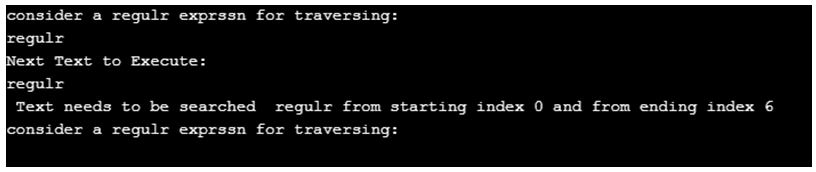
System.out.println("consider a regulr exprssn for traversing:");
Pattern pattern_k = Pattern.compile(sc.nextLine());
System.out.println("Next Text to Execute:");
Matcher matcher_g = pattern_k.matcher(sc.nextLine());
boolean found = false;
while (matcher_g.find()) {
System.out.println(" Text needs to be searched "+matcher_g.group()+" from starting index "+
matcher_g.start()+" and from ending index "+matcher_g.end());
found = true;
}
if(!found){
System.out.println("No match is found after comparison");
}
}
}
}Output:
3. public boolean find(int start)
This method is used to find out the method that matches the regular expression starting from the beginning or the ending index.
Example:
This program demonstrates the boolean find(int start) method, which gives the starting and ending index of the regular expression.
Code:
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class Java_Pattrn_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
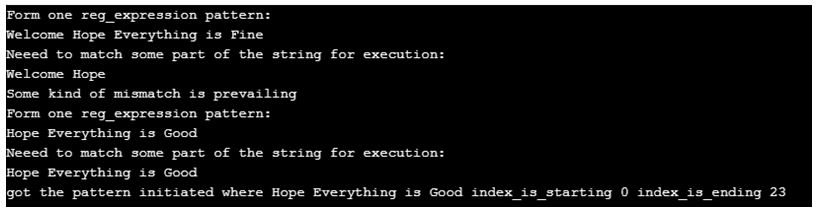
System.out.println("Form one reg_expression pattern:");
Pattern pattern_j = Pattern.compile(sc.nextLine());
System.out.println("Neeed to match some part of the string for execution:");
Matcher matcher_o = pattern_j.matcher(sc.nextLine());
boolean found1 = false;
while (matcher_o.find()) {
System.out.println("got the pattern initiated where "+matcher_o.group()+" index_is_starting "+
matcher_o.start()+" index_is_ending "+matcher_o.end());
found1 = true;
}
if(!found1){
System.out.println("Some kind of mismatch is prevailing");
}
}
}
}Output:
4. public String group()
This method is part of the Java Matcher class that returns the matched string of the regular expression subsequently.
Example:
This program demonstrates the String group () method of the Java Matcher class, which tries to generate the regular expression’s subsequent substring after hitting the match string.
Code:
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class Regx_Pttrn_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
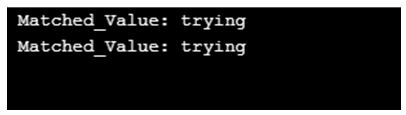
String reg_exprn_txt ="I am trying to learn something new, and trying to learning something from there," +
" and will one day become a skilled person. ";
String pattern_one_str = "(trying)";
Pattern pattrn_7 = Pattern.compile(pattern_one_str);
Matcher matchr_0 = pattrn_7.matcher(reg_exprn_txt);
while(matchr_0.find()) {
System.out.println(" Matched_Value: " + matchr_0.group(1));
}
}
}Output:
5. public int start() and int start(int group)
int start () and int start(int group)method as part of the Java Matcher class is used to get the subsequent values of the substring of the string with starting index of the grouped string.
Example:
This program demonstrates the string grouping followed by finding the subsequent matcher string to match the regular expression’s starting index.
Code:
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class Regx_Pttrn4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String reg_txt_exprssion =
"This text needs to be done " +
"with some careful attention 'done'.";
String string_grouping = "done";
Pattern pattern_l = Pattern.compile(string_grouping);
Matcher matcher_l = pattern_l.matcher(reg_txt_exprssion);
int count = 0;
while(matcher_l.find()) {
count++;
System.out.println("Matching_context: " + count + " : "
+ matcher_l.start());
}
}
}Output:
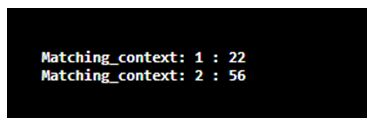
6. public int end() and int end(in group)
This method is used to return the ending index of the substring of the matched subsequent string pattern.
Example:
This program is used to demonstrate the int end (in group) method of the Java Matcher class.
Code:
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class Regx_Pattrn5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String Expression =
"Some special substring characters and escape characters need to be searched for. " +
"that to get the number of hits on the given expression of the text 'to'.";
String string_Pattrn = "to";
Pattern pattern_f = Pattern.compile(string_Pattrn);
Matcher matcher_f = pattern_f.matcher(Expression);
int count = 0;
while(matcher_f.find()) {
count++;
System.out.println("match_found: " + count + " : "
+ matcher_f.end());
}
}
}Output:
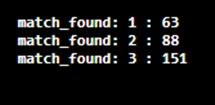
7. public int groupCount
This method is used to return the count of groups present as a set of regular expression after comparing the reg expression’s matched substring.
Example:
This program demonstrates the int group count method of the Java Matcher class.
Code:
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class Regx_Pattrn_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String run_Exp = " I am fond of eating delicious and yummy food everythime, and my mom is also fond of cooking that," +
" and dad also wants to taste the yummy food.";
String patternString1 = "(fond) (.+?) ";
Pattern pattern_s = Pattern.compile(patternString1);
Matcher matcher_s = pattern_s.matcher(run_Exp);
while(matcher_s.find()) {
System.out.println("matching_found_present: " + "count:"+ matcher_s.group(1) +
" " + matcher_s.group(2));
}
}
}Output:
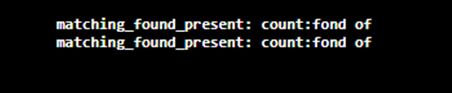
8. public boolean lookingat()
As part of the matcher class, this method only tries to match the beginning of the text, not the entire text, which means, unlike the matcher class, which considers the entire regular expression for matching and result.
Example:
This program demonstrates the boolean lookingat() method of the Java Matcher class.
Code:
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class Regx_Pattrn_7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String String_expr = "An expression to search and match the string pattern " + "make a search for the pattern.";
String String_ptrn = "pattern";
Pattern pattern_k = Pattern.compile(String_ptrn, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
Matcher matcher_k = pattern_k.matcher(String_expr);
System.out.println("currently_looking_At = " + matcher_k.lookingAt());
System.out.println("currently_matches = " + matcher_k.matches());
}
}Output:
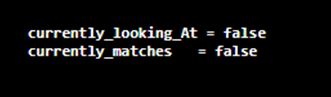
9. public Matcher appendReplacement()
This method is used to replace the set of text in the regular expression and then append that input string into the string buffer. It keeps a check on the string buffer what is being copied and what is needed to be replaced.
Example:
This program demonstrates the Matcher appendReplacement() method of Java Matcher.
Code:
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class Regex_Pttrn_8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
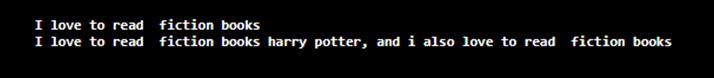
String sm_txt = "I love to read books of harry potter, and i also love to read books of JK Rowling" + " and My favourite writer writes all fiction books.";
String String_ptrn1 = "((books) (.+?)) ";
Pattern pattern_o = Pattern.compile(String_ptrn1);
Matcher matcher_o = pattern_o.matcher(sm_txt);
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
while(matcher_o.find()){
matcher_o.appendReplacement(stringBuffer, " fiction books ");
System.out.println(stringBuffer.toString());
}
}
}Output:
10. public StringBuffer appendTail()
This method also behaves in a similar fashion with a difference that if the last match is found from the input text and is not yet copied to the string buffer, then it is needed to check for the required text and can append at the end of the expression and then can be copied into the buffer.
Example:
This program demonstrates the StringBuffer append Tail() method of Java Matcher.
Code:
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class Regex_Pttrn_8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sm_txt = "I love to read books of harry potter, and i also love to read books of JK Rowling" + " and My favourite writer writes all fiction books.";
String String_ptrn1 = "((books) (.+?)) ";
Pattern pattern_p = Pattern.compile(String_ptrn1);
Matcher matcher_p = pattern_p.matcher(sm_txt);
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
while(matcher_p.find()){
matcher_p.appendReplacement(stringBuffer, " fiction books ");
System.out.println(stringBuffer.toString());
}
matcher_p.appendTail(stringBuffer);
System.out.println(stringBuffer.toString());
}
}Output:

11. public String replaceAll()
As its name suggests, the String replaceAll () method can replace all the found matches and matched groups with the regular expression.
Example:
This program demonstrates the String replaceAll() method of Java Matcher.
Code:
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class Java_Reg_Replace {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String one_ptrn ="I want to have a cup of tea, and I also want to have a cup of coffe at the same time," +
" and also want to have toffee.";
String ptrn_ex_strng = "((cofee) (.+?)) ";
Pattern pattern1 = Pattern.compile(ptrn_ex_strng);
Matcher matcherb = pattern1.matcher(one_ptrn);
String replaceAll = matcherb.replaceAll("tea or coffee ");
System.out.println("replaceAll = " + replaceAll);
}
}Output:

12. public String replaceFirst()
This method is used for replacing the string text from the beginning of the regular expression as soon as the first match gets hit.
Example:
This program demonstrates the replaceFirst() method of Java Matcher.
Code:
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class Java_Reg_Replace {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String one_ptrn ="I want to have a cup of tea, and I also want to have a cup of coffe at the same time," + " and also want to have toffee.";
String ptrn_ex_strng = "((cofee) (.+?)) ";
Pattern pattern1 = Pattern.compile(ptrn_ex_strng);
Matcher matcherb = pattern1.matcher(one_ptrn);
String replaceAll = matcherb.replaceAll("tea or coffee ");
System.out.println("replaceAll = " + replaceAll);
String replaceFirst = matcherb.replaceFirst("tea or coffee ");
System.out.println("replaceFirst = " + replaceFirst);
}
}Output:

13. public static String quoteReplacement()
It is a mediator method of all the replace methods and is used when the string and the characters in the string need to be replaced with the parameters passed as a replaced parameter.
Example:
This program demonstrates the String quoteReplacement() method of Java Matcher.
Code:
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
public class reg_quote_replcment {
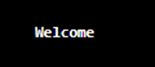
public static void main(String[] args) {
String reg_exprsn = "Welcome Everyone";
Pattern pattern_a = Pattern.compile(reg_exprsn);
String stringNeedsToMatch = "Welcome evryone to the laerning portal of educba";
Matcher matcher_b = pattern_a.matcher(stringNeedsToMatch);
String stringToBeReplaced = "Welcome";
System.out.println(matcher_b .quoteReplacement(stringToBeReplaced));
}
}Output:
Conclusion
Java Matcher class is a class which is part of Java regex package and mainly deals with the regular expressions and its functioning with the other regular function at the index level, replacement methods and quotereplacement method. It has simplified the overall manipulation of the strings and characters of the string for regular expressions.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java Matcher. Here we discuss the introduction to java matcher class methods, top 12 methods with respective example. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


