Updated July 10, 2023

Introduction to Java Collection Generics
Java collection generics are used to add a way in the specified concrete types, and it’s the general purpose of classes and methods that operate objects for performing and abstracting it so that it will look at some more typically used in the collections. The Java generics with other classes rather than the collection classes is the easiest way to show the basics of Java generics. Still, it’s the quickest way to show the basics of Java generics with referencing and de-referencing. It uses settings for the generic type of a Collection and other classes like HashSet, HashMap, etc.
Java Collection Generics Overview
The Java generics are more important for creating the sort and its method; it first performs the cast and then uses the datatype arrays like Integer, String, char, or any other array that supports ordering in the user datas. Java programmers use generic methods and generic classes to allow and declare a group of related methods with specified types in a single method declaration using the class declaration, respectively. Generics classes also provide safety at a specified build time, allowing programmers to catch erroneous types with particular transformations. Additionally, we could construct a generic method for sorting an array of objects using the Java Generic idea rather than the generic method using Integer arrays, Double arrays, String arrays, and other data types filters, and so on to sort the array contents.
Uses of Generic Collections in Java
In Java programming language, the generic collections are most important, allowing the object creation of a single type using the Type safety. If the type is Type safety, it means that the compiler will validate the specific types while using the compilation time, even though it will throw the error if the type value is not supported. If suppose we used Type Casting, means its no need for casting the types like String, Integer, double, etc. But mostly, the generics are not needed for this operation while we performed in the application. Before generics, we could store any objects with the specified collections that may be any of the types like both generic and non-generic now the generics will enforce the java coder to perform the object creation and its operations like storing and retrieving the values from the backend to the front end. If we disable generic collections, then we should use typecasting to achieve the desired outcome, and there is no need for typecasting within the context of generics.
The generic collections have some default methods to achieve the functionality that takes the array of objects and the collections for putting and getting the data from all the objects in the array collection. As in MapK, V>, the generic Map interface (and map implementations) are defined with two parameterized types. Each key’s type is K, and a key’s associated value’s type is V. So, we’d declare MapString, Integer> to store a map indicating how often each word appears in a text file. We would create MapString, ListInteger>> if we needed a map defining the lines on which each word appears in a text file. It’s worth noting that we can combine (or layer) generic type instantiations.
Advantages of Java Generics
This has been a rapid tour of Java generics’ most important features. “Most crucial” in this context refers to “more important when compared to all other language programmers who use generics.” But the main goal is to have enough knowledge about generics to utilize generics written by other programs. Put another way; we must understand generics well enough to get the compiler to accept our program without warnings or errors. If Java accepts our program, the generic mechanism should ensure its type of safety.
Type safety is one of the advantages, and it can only store one type of object. It does not allow for the storage of other items. We can store any object without Generics.
It is unnecessary to use typecasting when the object does not need to be typecast.
Before that we can use Generics, we must first typecast the values, and then it should perform Generics.
Compile-Time Checking ensures that an issue does not arise at runtime. According to the excellent programming approach, it is considerably better to handle the problem at compile time than at runtime.
Example #1
Code:
import java.util.*;
class TestGenerics1{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList<String> lst=new ArrayList<String>();
lst.add("January is the first month ");
lst.add("February is the second month");
lst.add("March is the third month");
lst.add("April is the fourth month");
lst.add("May is the fifth month");
lst.add("June is the sixth month ");
lst.add("July is the seventh month");
lst.add("August is the eigth month");
lst.add("September is the ninth month");
lst.add("October is the tenth month");
lst.add("November is the eleventh month");
lst.add("December is the twelth month");
String str=lst.get(7);
System.out.println("Welcome To My Domain its the first example: "+str);
Iterator<String> iterators=lst.iterator();
while(iterators.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterators.next());
}
}
}Output:
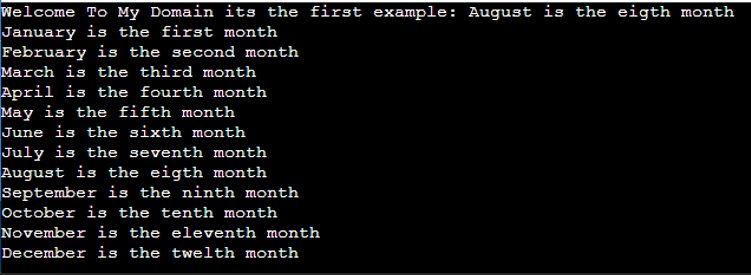
In the above example, we used Array List collection classes in the generics. With the help of add() method we can add n number of input values and get() method to retrieve the values.
Example #2
Code:
import java.util.*;
class TestGenerics1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Map<Integer,String> first=new HashMap<Integer,String>();
first.put(1,"Tv is the electronic device");
first.put(2,"Laptop is the electronic device");
first.put(3,"Computer is the electronic device");
first.put(4,"Mobile is the electronic device");
first.put(5,"Tablet is the electronic device");
Set<Map.Entry<Integer,String>> second=first.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer,String>> iterators=second.iterator();
while(iterators.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<Integer, String>result=iterators.next();
System.out.println(result.getKey()+" "+result.getValue());
}
}}Output:

In the above example, we used generic collections by using the Map interface. It contains some default and customized methods for achieving the operations. With the help of iterators, the values are listed on the loop.
Conclusion
Generally, it makes the programmer’s job easier and less error-prone when we use Java Generics. It’s a powerful addition to the Java language. It provides any correctness at compile time and, more crucially, implements generic algorithms without adding overhead to the Java programmers compared to the other language.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Java Collection Generics” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


