Updated April 10, 2023

Introduction to Java BufferedReader
The Java BufferedReader Class of Java Programming Language involves with reading the text from the character-input stream; buffered characters will provide the most efficient characters reading, arrays reading, and lines reading. For each and every read request made of a Reader, which can cause corresponding request reading, which is needed to be made of some underlying character or some byte stream. Therefore, now it is advisable to wrap a BufferedReader around the reader who’s read() function operations may be somewhat costly like inputStreamReaders and FileReaders.
Syntax:
Public class BufferedReader Extends ReaderHow does Java BufferedReader Class work?
The Java BufferedReader Class basically works just by reading the text of the character input stream and the buffering characters, which are about to provide the efficient reading of arrays, characters, and lines. There are some of the important points to make the BufferedReader Class work. They are buffer size can be specified or may have some default size. The default size of it is somewhat large enough for each and most of the purposes. The programs that actually use the DataInputStreams for some textual input localized by replacing for each and every DataInputStream along with an appropriate BufferedReader.
Constructors of Java BufferedReader
Given below are the two different types of constructors:
- BufferedReader(Reader in)
- BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz)
1. BufferedReader(Reader in): This constructor will create one buffering character input stream, which actually used as a default sized input buffer or buffering.
2. BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz): This constructor will create a buffering input character stream that actually uses input buffering of some specific size.
Methods of Java BufferedReader
Given below are the methods:
1. Void Close() Method of BufferedReader Class: The void close() method will help close the streaming or stream and release any type of system resources that actually associate with it.
2. Void mark(int readAheadLimit) Method of BufferedReader Class: The Void mark (int readAheadLimit) method will help in marking the present position/spot in the stream.
3. Boolean markSupported() Method of BufferedReader Class: The Boolean markSupported() method will tell the support stream the mark() function operation, which it actually does.
4. Int read() Method of BufferedReader: The int read() method will read a single character.
5. Int read(char[] cbuf , int off, int len) Method of BufferedReader Class: The int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) method will read the character into some array portion.
6. String readLine() Method of Java BufferedReader Class: The string readLine () method will read the text line / lines as needed.
7. Boolean ready() Method of Java BufferedReader Class: The Boolean ready () method will actually tell if/whether the particular stream is actually ready in reading.
8. Void reset() Method of Java BufferedReader Class: The void reset() method will reset the stream so easily.
9. Long skip(long n) Method of Java BufferedReader Class: The Long skip (long n) method will easily skip the characters.
Examples of Java BufferedReader
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
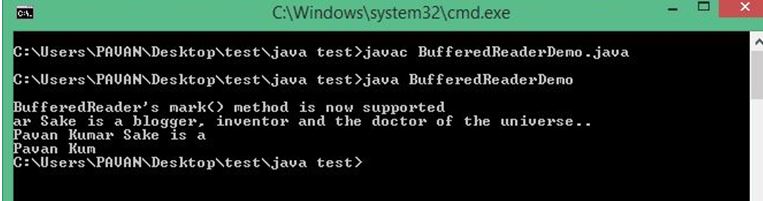
This is an example of implementing the Java BufferedReader methods. At first, some libraries are imported using the import function. Then main() is created to create the needed program. Then fr1 FileReader and br1 BufferedReader are created. Then character array with 21 lengths is created then IF Loop is created to illustrate markSupported() function/method. Then again, IF is created for illustrating the ready() method.
The br.skip() is used to skip the first 8 characters of the text, which is in the file1.txt. Inside of the IF LOOP readLine() method and read () are illustrated. Then FOR LOOP is created with 21 lengths as a condition to print the characters which are within the 21 characters. Then line break will be printed. Then reset() method is illustrated. Then FOR LOOP for illustrating reset() and read() method.
Code:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
//importing bufferreader java library
import java.io.FileReader;
//importing FileReader java library
import java.io.IOException;
//importing IOException java library
public class BufferedReaderDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
FileReader fr1 = new FileReader("file1.txt");
BufferedReader br1 = new BufferedReader(fr1);
char c1[]=new char[21];
if(br1.markSupported())
{
System.out.println("\nBufferedReader's mark() method is now supported");
br1.mark(101);
}
br1.skip(9);
if(br1.ready())
{
System.out.println(br1.readLine());
br1.read(c1);
for (int i = 0; i <21 ; i++)
{
System.out.print(c1[i]);
}
System.out.println();
br1.reset();
for (int i = 0; i <9 ; i++)
{
System.out.print((char)br1.read());
}
}
}
}Output:
Example #2
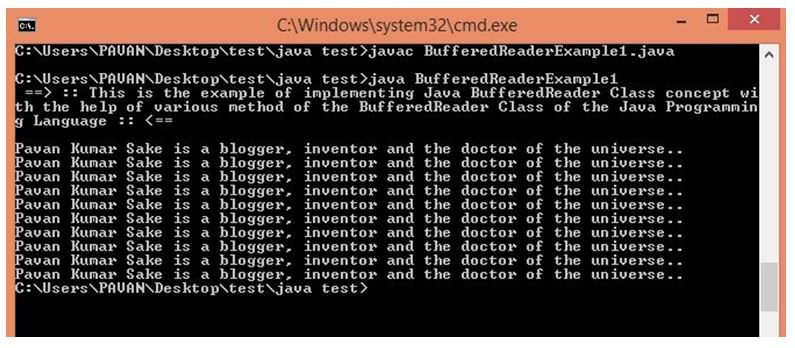
This is an example of implementing the Java BufferedReader Class Methods. At first, here, java IO function libraries are included. Then a public class called “BufferedReaderExample1” is created, and then the main() function is created to write the user needed code which throws the exception. Then the “fr1” variable is created for file reading (file1.txt), and then the “br1” variable is created, which is the buffered reader for fr1. Then int i1 is created, and then WHILE LOOP is created to implement read() method/function with the condition not equal to -1. Inside of the loop system.out.println() is used to print the whole characters of the file1.txt.
Code:
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedReaderExample1 {
public static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
System.out.println(" ==> :: This is the example of implementing Java BufferedReader Class concept with the help of various method of the BufferedReader Class of the Java Programming Language :: <== \n");
FileReader fr1=new FileReader("file1.txt");
BufferedReader br1=new BufferedReader(fr1);
int i1;
while((i1=br1.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)i1);
}
br1.close();
fr1.close();
}
}Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we saw the definition of BufferedReader class along with its syntax, how the java BufferedReader class works, constructors of java BufferedReader class, methods of java BufferedReader class along with some of the examples.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java BufferedReader. Here we discuss introducing the java BufferedReader class, along with constructors, methods, and how it works and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


