Updated July 28, 2023
Introduction to Iterator in C++
Traversing through your highly complex data stored in different types of containers such as an Array, Vector, etc., in the smallest execution time is possible because of the Iterator in C++, a component of Standard Template Library (STL). Don’t worry; it is just a pointer like an object, but it’s smart because it doesn’t matter what container you are using; it will make your algorithm independent of Container type by providing a common interface for all types of container like a bridge between algorithm and container. Iterator not only reduces the complexity of a program instead makes execution time much faster.
For example, the sort()algorithm, which has two parameters, ending and starting iterator, will perform the sorting in order irrespective of what type of container you are using. Iterator allows the application of generic Algorithms to data structures. Data structures can use an Iterator to expose a range of elements.
Operations using the Iterator
- begin(): This function will return an iterator pointing to the first element of the container.
- end(): This function will return an iterator pointing to the past the last element of the container.
- advance(): This function will increment an iterator position to the specified argument.
- next(): This function will return the new iterator that the iterator will point after incrementing the positions in the arguments.
- previous(): This function will return the new iterator that the iterator will point after decrementing the positions in the arguments.
- inserter(): This function will insert the element at any position in the container.
Practical implementation
The practical implementation is as follows:
1. C++ code to implement the Iterator
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<iterator>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Declaring a Vector
std::vector<int> v{1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
//Declaring Iterator
vector<int>::iterator i;
//Function for iterating through vector elements
for(i=v.begin();i!=v.end();i++)
{
std::cout << *i <<" ";
}
return 0;
}Output:
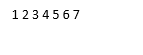
2. C++ code to show iterator functionality
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<iterator>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Declaring a Vector
vector<int> v{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
//Declaring Iterator
vector<int>::iterator i;
//Function
v.insert(v.begin()+1,10);
for(i=v.begin();i!=v.end();i++) {
cout << *i <<" ";
}
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
Iterator Categories
As of C++ 17, there are 5 different types of Iterators that can be classified depending upon the type of functionality, as shown in the flowchart below:
- Input Iterator(stdin): Because of limited functionality, they are the weakest of all iterators with read-only and forward-moving functionality. It can’t modify the container value. Dereference operator(*),Not equal operator(!=), Increment operator(++) and Equal operator(==) can be used as input iterators. Also, for sequential input operations.
- Output Iterator(stdout): Iterator only for storing, write-only iterator which is used to modify the value of a container. They also have very limited functionality. Iterator cannot access the element. The assignment operator(=) and Increment operator(++) can be used as output iterators, only in a single-pass algorithm.
- Forward Iterator(singly linked list): This Iterator contains the functionality of both Input and Output Iterators. It can move forward in direction one step at a time. Reading and writing to a container is the most preferred iterator, which supports reusing and saving. It supports all the above operators.
- Bidirectional Iterator(doubly linked list): As the name already suggests, bi-directional which makes it stronger than the above iterators. It also supports reading and writing to a container. It supports the Decrement operator(–).
- Random Access Iterator(arrays): The strongest iterator is the most powerful iterator as it can read, write, and access randomly. Pointer-like functionality like the pointer addition and subtraction.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Iterator in C++
Following are the advantages and disadvantages are given below.
Advantages
If you need to move from one element, iterator is currently pointing to another element that is potentially n steps away from your current iterator. The first four in the hierarchy will take a linear amount of time to do that, while a random access iterator can do that in constant time, and that is way more fascinating because that’s where time is saved. It is the most important feature that an Iterator provides. Some more are mentioned below.
- Code Efficiency: If we have P kinds of containers of data and Q things we want to do with them, then we will end up writing P * Q algorithms. If the data is also of R different types, then we might end up with the P * Q * R algorithm. So by using the iterators, we can do it in the P + Q algorithm. We saved 90% of the time and work. Taking the efficiency of code to the next level. The concept behind efficiency is that the input iterator over source and output iterator over the target sequence need not be of the same type.
- Dynamic Processing: Iterators have dynamic functionalities such as swapping in the same container, Copy-assignable, incrementing, dereferencing, and decrementing. The iterator provides the functionality to remove and dynamically add elements to the container. As all iterators can be incremented, input iterators can be compared and dereferenced to a value. Bidirectional iterators can be decremented. The main aspect is to write one function and use it for any container.
Disadvantages
- You can’t move from one data structure to another at the same time in some complex way. Iterator won’t work in that case.
- If you are processing through a list and forgot something, and now you want to go back, you can’t because iterators won’t work in that way.
- In case you need to update the structure during traversing, you can’t do that too because of the iterative way of storing its position.
Conclusion
While using iterators, keep these two things always in mind for making code efficient. Always pass the iterator into a function instead of containers. You should never return containers instead of return or pass iterator. You can get any element using an iterator, dereference, and pass a pair of the iterator to an algorithm.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Iterator in C++. Here we discuss operations in the iterator, categories, advantages, and disadvantages with codes and outputs. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


