Updated September 12, 2023
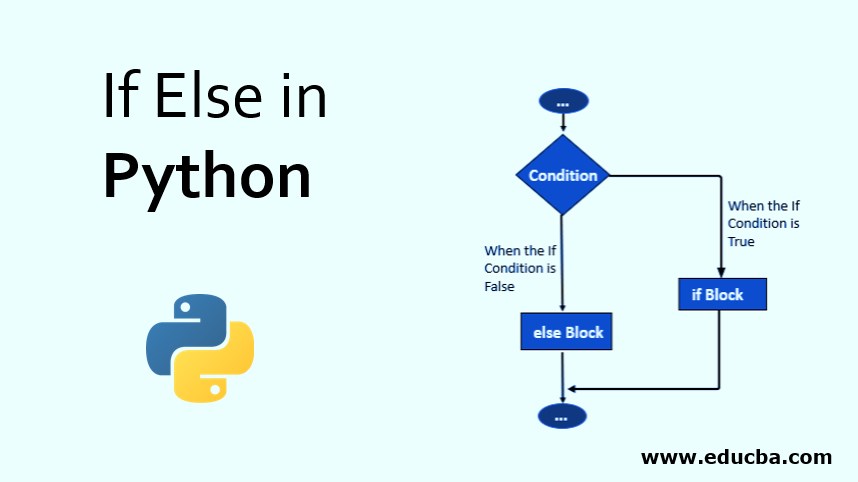
Table of Contents
Introduction to If Else in Python
An if-else statement executes different code blocks based on a specified condition. If the condition is true, the code inside the “if” block runs; otherwise, the code inside the “else” block executes.
You already know that a program is a series of written instructions. To no one’s surprise, there can be so many instances where a program may have to decide before proceeding. For example, deciding if the user is old enough to attend the exam or if the temperature is high enough to start the air conditioner, selecting the grade a student has passed, etc. These decisions are based on the input conditions and what to do in that situation.
When a program uses a condition statement, it executes a specific code block depending on the input and the conditions. Like any other fully-featured programming language, Python supports multiple decision-making methods; if else, it is one of the most used ways to get the job done.
Other decision-making statements in Python are the following:
- If Statement: It analyzes whether the condition is true or false. The code block below executes only when the condition is met.
- If Else Statement: This statement is similar to the If statement but adds another block of code executed when the conditions are not met. This article will look at this statement type and its example.
- Nested If: We use nested if statements when we need to check multiple conditions and execute instructions.
Syntax of Python If Else
The syntax of an If Else Statement is the following:
if condition:
# statements to execute when the conditions are met are inserted here
else:
# Statements to be executed when the conditions are not met.As you can see above, all if-else conditions have two statements and a condition written. Before the statements, the condition is made clear; once it has been processed, the program looks at the input and decides if it fulfills the conditions. If it does, statements in the first block are executed, and the program skips them in the syntax’s “else:” section.
If the condition is not met, the program skips the first block and executes statements in the “else:” block.
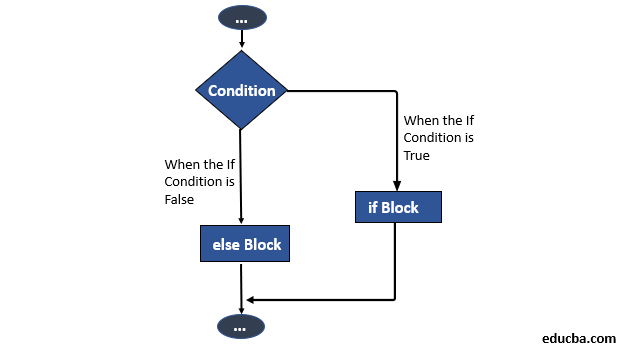
Flowchart of Python If Else Statement
As you can see in the flowchart above, the condition in an if-else statement creates two paths for the program to go on. If the condition is not met, the code below won’t execute, and the program proceeds to run the statement in the Else block.
On the other hand, when the “if” condition is met, only then if a block of code is executed and the program then jumps below, exiting the If else statement.
Examples of Python If Else
Now that we have seen the syntax, flowchart, and need of if-else statements, let’s take a look at some practical examples to see it in action:
Example #1
Code:
var = 100
if var>90:
print("True expression executed")
else:
print("False expression executed")Output:
As one can see, var = 100. If the value checked in the if condition is greater than 100, the program prints “True expression executed.” However, if a value is less than or equal to 90, see how this code would have behaved below.
Code:
var = 90
if var>90:
print("True expression executed")
else:
print("False expression executed")Output:
There could be a one-liner code for the above logic.
Code:
var = 100
print("True expression executed") if var>90 else print("False expression executed")Output:
Example #2
Now, let’s see some comparison of variables.
Code:
p = 90
q = 20
if p > q:
print("P is greater than q")
else:
print("P is less than q")Output:
As one can see, p and q are two variables holding values 90 and 20, respectively. The program compares these values in the ‘if’ and ‘else’ statements and prints the respective statements based on the comparison.
Example #3
Now, let’s see the use of the logical operator in an if-else statement:
Code:
p = 2000
q = 3330
r = 600
if p > r and q > r:
print("Both conditions are True")
else:
print("Nothing")Output:
As one can notice, if a statement contains logical operators “And” between two expressions, i.e., p>r and q>r. Then, as if both the statement were true, it resulted in printing “Both conditions are True”. Else, it would print “Nothing”.
The same way it can be done for “OR.”
Code:
p = 2000
q = 30
r = 600
if p > r or q > r:
print("Any one expression is true")
else:
print("Nothing")Output:
Here, one can notice only one expression is true, i.e., p>r and not q>r. The ‘Or’ operator caused the if statement to evaluate to ‘True,’ printing the message’ Anyone expression is true.’
You can use more than one variable and logical operator to evaluate expressions in the if-else statement.
Code:
p = 2000
q = 30
r = 600
s = 60
t = 60
if (p > r or q > r) and (s == t):
print("True")
else:
print("False")Output:
Example #4
Now, let’s see an if-else statement with a pass operator.
There are ample situations where one doesn’t know what logic to put at the writing program’s start. Use the pass operator at that time.
Code:
p = 2000
q = 30
r = 600
if (p > r or q > r):
pass
else:
print("Nothing")Output:
If a statement evaluates to true and contains a pass operator, the program doesn’t print anything
Example #5
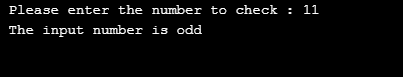
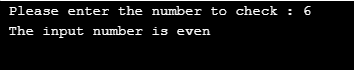
A Python Program to check if the input number is even or odd.
number = int(input(" Please enter the number to check : "))
if number %2 == 0:
print(" The input number is even ")
else:
print(" The input number is odd ")Output:
Example #6
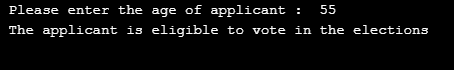
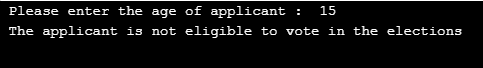
A Python Program to check whether the applicant is eligible to vote in the elections or not :
age = int (input(" Please enter the age of applicant: "))
if age>=18 :
print(" The applicant is eligible to vote in the elections " );
else :
print(" The applicant is not eligible to vote in the elections " );Output:
Example #7
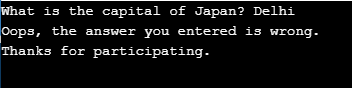
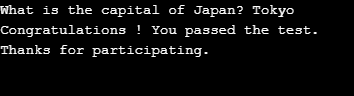
Python Program to check the input text for right or wrong answer :
code = input(" What is the capital of Japan? ")
if code == 'Tokyo':
print("Congratulations ! You passed the test.")
else:
print(" Oops, the answer you entered is wrong.")
print(" Thanks for participating. ")Output:
Conclusion – If Else Statement in Python
Decision-making is one of the core pillars of programming. Staying down proper conditional statements is necessary to get good at programming. Still, it is also essential to frequently accomplish tasks, and with a grasp of conditional statements like if, if-else, and nested if, you can use the program to make decisions and logically obtain accurate results.
FAQs
Q1. Can I have multiple conditions in an if-else statement?
Ans: Yes, you can use “elif” (short for “else if”) to check multiple conditions in sequence. It allows you to specify different code blocks for various conditions.
Q2. What is the difference between “if” and “elif”?
Ans: “if” is used for the primary condition, while “elif” is used for secondary conditions when you want to check additional conditions after the initial “if” condition is false.
Q3. Can I have multiple “else” blocks in a single if-else statement?
Ans: No, you can only have one “else” block in an if-else statement. However, multiple “elif” blocks can handle various conditions.
Q4. Can I use if-else statements in loops?
Ans: Yes, you can use if-else statements within loops to control the flow of your program based on conditions that change during each iteration of the loop.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “If Else in Python” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.