Updated July 19, 2023
Difference Between IaaS and PaaS and SaaS
Cloud Computing is divided into three types: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. In terms of popularity, Saas has gained the most, with 38.5 % in 2022, and is expected to rise by 2023. IaaS gains popularity by 22.2 %, with PaaS at 19.2 %. With these clouds, computing is becoming the key to end businesses. These three cloud computing techniques explain the best way of using the cloud in businesses. SaaS is the software platform available through a third party via the internet. PaaS is a model where a third party provides hardware and software tools over the internet. The same is for IaaS, a cloud computing service where a user is billed on a “pay per use” scheme for using services such as storage, networking, etc.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Infographics
Below are the top 9 differences between IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS:
Key Differences between IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
Following are the key differences between IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS:
SaaS (Known as Software as a Service) gives access to software and its functions. Here no need to invest in additional hardware, as the software is hosted remotely. SaaS reduces the hardware setup, installation, and maintenance. Also known as Storage as a service, it provides storage space from third-party providers, and users utilize those space when data is been transferred from users to the service provider.
Features of SaaS
- No manual installation of hardware is required as everything is virtually available on the internet once we log in. It consists of software applications that your personalized logins can access.
- No need for any technical specialist to update or upgrade the software applications. Cloud takes care of this.
- The billed amount for the services taken for SaaS is based mainly on a fixed monthly fee. Thus it gives a clear estimation of Software and other subscriptions taken.
- SaaS offers security and maintenance within the cost given to software applications.
PaaS (Known as a Platform as a service) provides hardware and software tools to develop applications over the Internet. Developers mostly use the PaaS cloud platform to design and develop software applications.
Features of PaaS
- PaaS provides a Web-based User interface that multiple users can access.
- It provides many features, like developing applications with testing, hosting, and maintenance.
- It is quite flexible, scalable, and portable.
- PaaS cloud computing platform is quite portable as when the user needs more storage capacity; he can opt for a public cloud.
- PaaS is quite secure as it provides data security, backup, and recovery of lost data.
- IaaS (Known as Infrastructure as a Service) uses the model of “pay per use” or “pay as you go” for storage, networking, and virtualization. IaaS services are delivered over the Internet, and users only pay for the services that are taken. In the IaaS model, users utilize the resources such as software, hardware, and storage space from third-party service providers, and they also host user applications with maintenance. Here the consumer or user saves time and money.
Features of IaaS
- IaaS services are highly scalable and flexible.
- Here hardware is configured by service providers, reducing high investments and time.
- No waste of unused storage capacity; whenever more storage space is needed, it gets in time.
- There is no single point of failure, as the IaaS service still runs if there is any fault in the network, server, or switch.
- IaaS provides more security as its services are hosted externally.
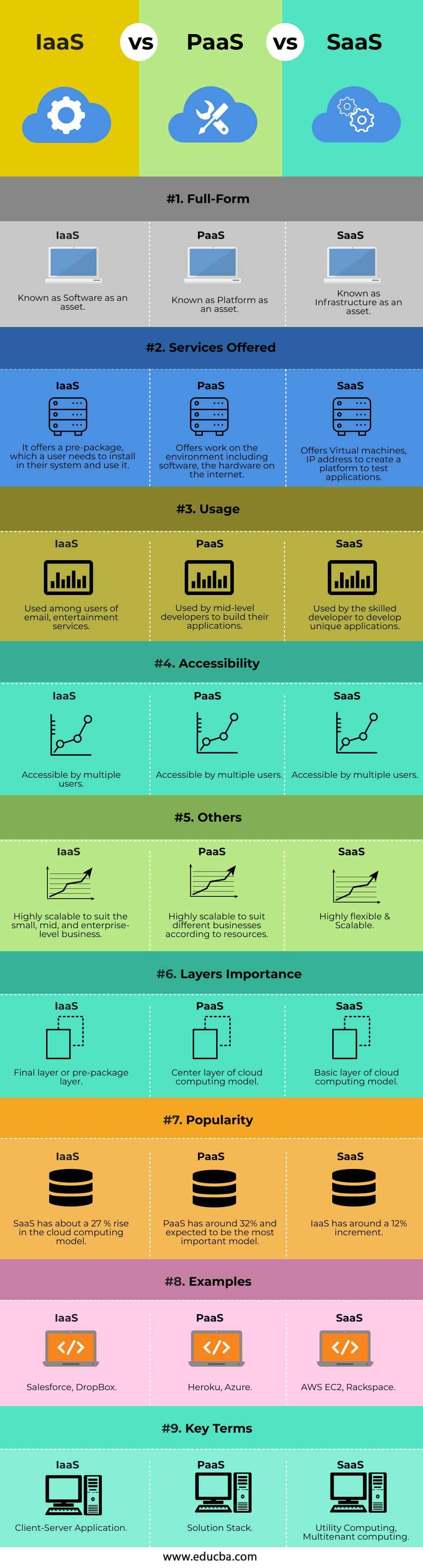
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS Comparison Table
Let us look at the comparison table of IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS.
|
Features |
SaaS | PaaS |
IaaS |
| Full-Form | Known as Software as an asset | Known as Platform as an asset | Known as Infrastructure as an asset |
| Services Offered | It offers a pre-package, which a user needs to install and use in their system. | Offers work on the environment, including software and internet hardware. | Offers Virtual machines and IP addresses to create a platform to test applications. |
| Usage | Used among users of email and entertainment services. | Used by mid-level developers to build their applications. | Used by the skilled developer to develop unique applications. |
| Accessibility | Accessible by multiple users. | Accessible by multiple users. | Accessible by multiple users. |
| Others | Highly scalable to suit small, mid, and enterprise-level businesses. | Highly scalable to suit different businesses according to resources. | Highly flexible & Scalable |
| Layers Importance | Final layer or pre-package layer. | The center layer of the cloud computing model. | Basic layer of cloud computing model. |
| Popularity | SaaS has about a 27 % rise in the cloud computing model. | PaaS has around 32% and is expected to be the most important model | IaaS has around a 12% increment. |
| Examples | Salesforce, DropBox | Heroku, Azure | AWS EC2, Rackspace |
| Key Terms | Client-Server Application | Solution Stack | Utility Computing, Multitenant computing |
Conclusion
The cloud computing concept arises from the network diagram mentioning the internet as a cloud. The services offered by either of the cloud computing models (i.e., Platform as a service, Software as a service, and Infrastructure as a service) are related to mobility, and it depends on the quality of service and security provided by the service providers for user experience.
In choosing the best service delivery model, a user must know his business requirements. Every service model has its pros and cons; where SaaS uses packaged content as it does not have any control over maintenance issues, and PaaS and IaaS are not suitable for all types of workloads. Companies have been moving their IT infrastructures to a cloud platform as the cloud has been booming for a few years. Cloud computing technology has several cloud products, such as cloud storage, namely public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. A recent move towards cloud computing solutions by various organizations depends on their needs only.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.