Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to Heap data structure C++
The following article provides an outline for Heap data structure C++. Heap data structure is a tree-based structure where all the nodes of the tree are in specific orders. Furthermore, it is a tree-based structure where the tree is a balanced binary tree in which the root node is compared with its children. For example, the complete binary tree is a tree in which the nodes have two children; the complete binary tree is a tree where all the levels except the final level, the leaf node must be full fill up, and all the other nodes must be arranged left-justified.
Syntax
Let’s see the heap data structure through an example; the heap is a balanced binary tree where root node keys are compared with their children; if x has child node y, then follow the format as,
key(x) ≥ key(y)How does Heap data structure work in C++?
Heap data structure is a tree-based structure where the tree is a balanced binary tree in which the root node is compared with its children. The heap function is of two types; they are min-heap and max-heap.
In min-heap, the parent node’s value must be less than or equal to both of its child nodes; let’s see with the format as below it explains the actual value of i is always greater than or equal to its parent value except the root node.
A[Parent(i)]<=A[i]Sample Code – For Min-Heap
void minHeap (int Arr[ ] , int i, int N)
{
int left = 2*i;
int right = 2*i+1;
int small;
if(left <= N and Arr[left] < Arr[ i ] )
small = left;
else
small = i;
if(right <= N and Arr[right] < Arr[small] )
small = right;
if(small!= i)
{
swap (Arr[ i ], Arr[small]);
min_heapify (Arr, small,N);
}
}In max-heap, the parent node’s value is always greater than n or equal to both of its child nodes; let’s see the format as follows below; it explains that the value of node i is always less than or equal to its parent value except the root node.
A[Parent(i)]>=A[i]Sample Program – For Max-Heap
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// to demonstrate the max-heap function
void Max_Heap(int arr[], int i, int n)
{
int left = 2*i + 1;
int right = 2*i + 2;
int big = i;
if (left < n && arr[left] > arr[i])
big = left;
if (right < n && arr[right] > arr[big])
big = right;
if (big != i)
{
swap(arr[i], arr[big]);
Max_Heap(arr, big, n);
}
}
//to build a max-heap function basically
void call_MaxHeap(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = (n-2)/2; i >= 0; --i)
Max_Heap(arr, i, n);
} // to print the array of given size
void DisplayResult(int* arr, int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}// to implement the max-heap function in the main()
int main()
{
// input values - array representing
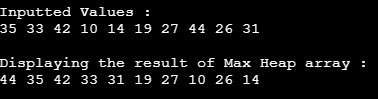
int arr[] = {35, 33, 42, 10, 14, 19, 27, 44, 26, 31};
printf("\nInputted Values : \n");
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
DisplayResult(arr, n);
call_MaxHeap(arr, n);
printf("\n\nDisplaying the result of Max Heap array : \n");
DisplayResult(arr, n);
return 0;
}Output:
Examples of Heap data structure C++
Heap data structure has some important operations which help in programming; let’s see the following examples,
For the max-heap, each key node is greater than their child nodes, and also root node key is the largest along with all other nodes, and for min-heap, each key node is always smaller than their child nodes, and also root key node is the smallest among several other nodes.
Program
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void swapping(int *x, int *y) // swap-function - to swapping two number
{
int t = *y;
*y = *x;
*x = t;
}
void insertHeapTree(vector<int> &hT, int val)
{
int treeSize = hT.size();
if (treeSize == 0)
{
hT.push_back(val);
}
else
{
hT.push_back(val);
}
}
void deleteValue(vector<int> &hT, int val)
{
int treeSize = hT.size();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < treeSize; i++)
{
if (val == hT[i])
break;
}
swapping(&hT[i], &hT[treeSize - 1]);
hT.pop_back();
}
void printArray(vector<int> &hT)
{
for (int i = 0; i < hT.size(); ++i)
cout << hT[i] << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
int main()
{
vector<int> heapTree;
int delValue;
insertHeapTree(heapTree, 3);
insertHeapTree(heapTree, 4);
insertHeapTree(heapTree, 9);
insertHeapTree(heapTree, 5);
insertHeapTree(heapTree, 12);
insertHeapTree(heapTree, 7);
insertHeapTree(heapTree, 15);
insertHeapTree(heapTree, 20);
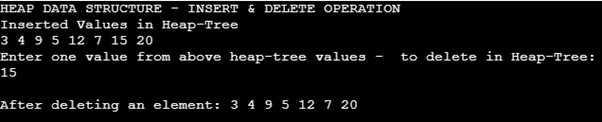
cout << "HEAP DATA STRUCTURE - INSERT & DELETE OPERATION\n";
cout << "Inserted Values in Heap-Tree\n";
printArray(heapTree);
cout << "Enter one value from above heap-tree values - to delete in Heap-Tree: \n";
cin>>delValue;
deleteValue(heapTree, delValue);
cout << "\nAfter deleting an element: ";
printArray(heapTree);
}Output:
Heap Data Structure Operations are of several types; let’s see those operations as shown below,
1. Heapify
Heapify is the process of rearranging values of heap trees to manage heap structure when such operation is performed, like insertion and deletion at that time; once the operation is done, the heap tree is re-arranged to return the final outcome for heap property.
2. Insertion in a heap
In the insertion heap, the new element/value will be added to the end of the heap; the newly inserted element/value will be added end of the heap first, then it will be rearranged to the correct position as the heap property follows the bottom-up approach.
Algorithm for Insertion
If there is no node,
Create new_Node.
else (node already available)
Then insert new_node at the end(the last node will be added from left to right.
Finally, arrange the heap structure.
Deletion in heap
In the delete heap, the particular element will be deleted by the last node in a heap. Thus, deletion is done from the last node in a heap. Once deletion did the heapify operation is done to rearrange the heap tree.
Algorithm for delete-heap
If the deleted_node is leafNode
Remove node
Else swap deleted_node with lastLeaf_node
Remove
Finally, arrange heap structure.
3. Peek operation
Peek operation is done by maximum value from Max-heap or the minimum value from Min-heap by not deleting the nodes. Thus, it returns max-heap and min-heap.
return root_nodeExtract Min-Max
It returns and deletes the minimum or maximum value in min-heap and max-heap, respectively.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about the Heap Data Structure, which is useful in several algorithms. Also, we discussed its syntax and example with usages of functions and different types available in heap functions.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Heap data structure C++. Here we discuss how Heap data structure works in C++ and, for example, the output. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –