
Introduction to Head Command in Linux
As by name it is clear that what head command does, typically it prints the first 10 lines(default in Unix-Linux) of any files or output of any files in n standard output format. Some times the head command does not provide the file name instead “-” is provided. So, in this case, it read the standard input of the user.
Syntax:
HEAD [options] [file]Options available for Head Command in Linux
1. -n, –lines=[-]num: Displays the first num lines instead of the first 10; with the leading ‘-‘, displays all but the last num lines of each file.
2. -v, –verbose: Always display the header name when file is identified.
3. –version: For version.
4. -c, –bytes=[-]num: Displays the first num bytes of each file; with a leading ‘-‘, displays all but the last num bytes of each file.
5. -q, –quiet, –silent: It restricts the printing of header name when file identified.
6. –help: For help.
- b 512
- M 1024*1024
- K 1024
- GB 1000*1000*1000
- MB 1000*1000
- kB 1000
- G 1024*1024*1024
Examples of Head Command in Linux
Given below are the examples of Head Command in Linux:
Example #1
Command:
head example.txtOutput:
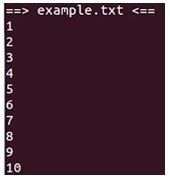
Explanation:
- Let’s just have a look at what’s in the example.txt file using cat you can see that it’s the numbers 1 to 20 all on separate lines so if I use the head command instead of cats and then type in the name of the file and hit enter you can see that it prints out the first 10 lines of the file which is 1 to 10 now.
Example #2
Command:
head -n 3 example.txtOutput:
![]()
Explanation:
- Head can actually do a little bit more than that with some options so if we type in heads and then dash n which stands for the number of lines we can actually tell it how many lines we want to print out so let’s just say 3 and we have to give it a file to actually do this operation on so same file again example.txt and hit enter and you can see that it’s printed out the first 3 lines now we can basically print out as many or as few lines as we want so.
Example #3
Command:
head -n -15 example.txt Output:

Explanation:
- Let’s just go for 15 there we go 1 to 15 now there is another thing that we can do with the same command just by editing it slightly and that is to put a minus sign in front of the number now what this does is it tells head that we actually want to print everything up to the last 15 lines.
- So, in this case, it prints how lines one to five and it won’t bother printing out the rest of the Alliance so if we hit enter you can see it’s printed outlines one to five now.
Example #4
Command:
head -n -2 example.txtOutput:
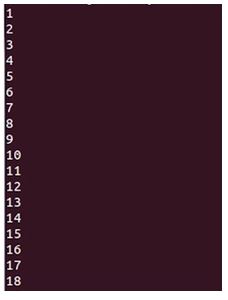
Explanation:
- If I do that again but I just tell it to not print out the last two lines we should get an output that is 1 to 18 so if I hit enter now you can see that that’s what we’ve got so by putting a minus sign in front of the number for this number option here we’re actually telling heads to print out everything apart from the last two lines or whatever number you have here.
- We can use for head which is a byte option which is -C and it works in exactly the same way as the -n option but rather than it printing outlines it prints out bytes now if I just cat out example.txt again
Example #5
Command:
head -c 2 example.txtOutput:
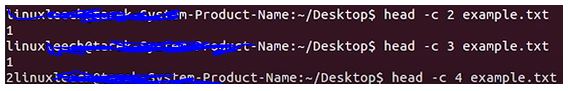
Explanation:
- So a byte is eight bits and the newline character which is actually at the end here which is hidden from our view but tells the computer to basically go to a new line and then print the next character is a byte as well so if I use the head command with the -C bytes option and then I tell it to print out the first two bytes of this file and the file name is example.txt again it’s actually just going to print out this one
- Here so if I hit enter you can see that’s what it’s done and it’s put the command prompt on to a new line now if I tell it to print out three you’ll see this printed out the numbers one the numbers two but the command prompt is on the same line as the two that’s because it hasn’t actually printed or recognized this newline character which is actually after the 2
Example #6
Command:
head -c 4 example.txtOutput:
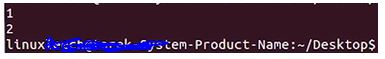
Explanation:
- So now if I change this to four and hit enter you can see that it’s printed out one and two and the command prompt on a new line so printing out bites is different from printing up lines basically.
Example #7
Command:
head -c -4 example.txtOutput:

Explanation:
- The minus sign with the white option so if I type in head -C which is the bite option and then minus four it’s gonna print out everything apart from the last four bytes of the file so example.txt and hit enter and there we go you can see that’s actually printed out everything up to the last four bytes of the file now.
Example #8
Command:
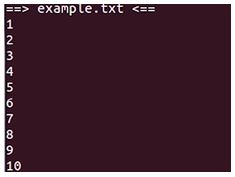
head -v example.txtOutput:
Explanation:
- – V for verbose and then the name of the file so example dot text so you can see it’s print out the first 10 lines and the name of the document.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Head Command in Linux. Here we discuss the introduction, options available for Head Command in Linux and respective examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


