Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to Hashing Function in C
This article has a brief note on hashing (hash table and hash function). The most important concept is ‘searching’ which determines time complexity. To reduce the time complexity than any other data structure hashing concept is introduced which has O(1) time in the average case and the worst case it will take O(n) time.
Hashing is a technique with faster access to elements that maps the given data with a lesser key for comparisons. In general, in this technique, the keys are traced using hash function into a table known as the hash table.
What is Hash Function?
The hash function is a function that uses the constant-time operation to store and retrieve the value from the hash table, which is applied on the keys as integers and this is used as the address for values in the hash table.
Types of Hashing Function in C
The types of Hashing Function in C are explained below:
1. Division method
In this method, the hash function is dependent upon the remainder of a division.
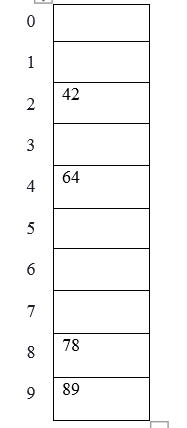
Example: elements to be placed in a hash table are 42,78,89,64 and let’s take table size as 10.
Hash (key) = Elements % table size;
2 = 42 % 10;
8 = 78 % 10;
9 = 89 % 10;
4 = 64 % 10;
The table representation can be seen as below:
2. Mid Square Method
In this method, the middle part of the squared element is taken as the index.
Element to be placed in the hash table are 210, 350, 99, 890 and the size of the table be 100.
210* 210 = 44100, index = 1 as the middle part of the result (44100) is 1.
350* 350 = 122500, index = 25 as the middle part of the result (122500) is 25.
99* 99 = 9801, index = 80 as the middle part of the result (9801) is 80.
890* 890 = 792100, index = 21 as the middle part of the result (792100) is 21.
3. Digit Folding Method
In this method the element to be placed in the table uh is sing hash key, which is obtained by dividing the elements into various parts and then combine the parts by performing some simple mathematical operations.
Element to be placed are 23576623, 34687734.
- hash (key) = 235+766+23 = 1024
- hash key) = 34+68+77+34 = 213
In these types of hashing suppose we have numbers from 1- 100 and size of hash table =10. Elements = 23, 12, 32
Hash (key) = 23 % 10 = 3;
Hash (key) = 12 % 10 = 2;
Hash (key) = 32 % 10 = 2;
From the above example notice that both elements 12 and 32 points to 2nd place in the table, where it is not possible to write both at the same place such problem is known as a collision. To avoid this kind of problems there are some techniques of hash functions that can be used.
Types of Collision Resolution Techniques
Let us discuss the types of collision resolution techniques:
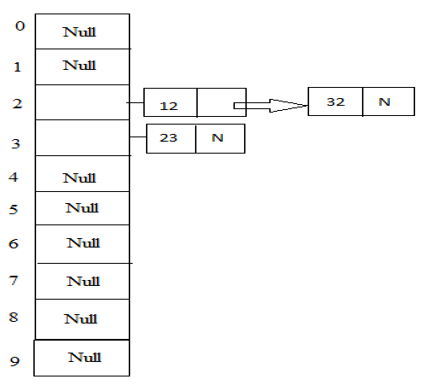
1. Chaining
In this method as the name suggests it provides a chain of boxes for the record in the table having two entries of elements. So whenever such collisions occur then the boxes act as a linked list will be formed.
Example: 23, 12, 32 with table size 10.
Hash (key) = 23 % 10 = 3;
Hash (key) = 12 % 10 =2;
Hash (key) = 32 % 10 =2;
2. Open Addressing
i. Linear Probing
This is another method for solving collision problems. As the name says whenever a collision occurs then two elements should be placed on the same entry in the table, but by this method, we can search for next empty space or entry in the table and place the second element. This can again lead to another problem; if we do not find any empty entry in the table then it leads to clustering. Thus this is known as a clustering problem, which can be solved by the following method.
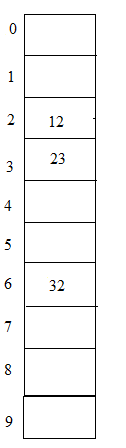
Example: 23, 12, 32 with table size 10
Hash (key) = 23 % 10 = 3;
Hash (key) = 12 % 10 =2;
Hash (key) = 32 % 10 =2;

In this diagram 12 and 32 can be placed in the same entry with index 2 but by this method, they are placed linearly.
ii. Quadratic probing
This method is a resolution for the clustering problem during linear probing. In this method the hash function with hash key is calculated as hash (key) = (hash (key) + x * x) % size of the table (where x =0, 1, 2 …).
Example: 23, 12, 32 with table size 10
Hash (key) = 23 % 10 = 3;
Hash (key) = 12 % 10 =2;
Hash (key) = 32 % 10 =2;
In this, we can see that 23 and 12 can be placed easily but 32 cannot as again 12 and 32 shares the same entry with the same index in the table, as per this method hash (key) = (32 + 1*1) % 10 = 3. But in this case table entry with index 3 is placed with 23 so we have to increment x value by 1. Hash (key) = (32 + 2 * 2) % 10 = 6. So we now can place 32 in the entry with index 6 in the table.
iii. Double hashing
This method we have to calculate 2 hash functions to resolve the collision problem. The first is calculated using a simple division method. Second has to satisfy two rules; it must not be equal to 0 and entries must be probed.
- 1 (key) = key % size of the table.
- 2 (key) = p – (key mod p), where p is prime numbers < size of the table.
Example: 23, 12, 32 with table size 10
Hash (key) = 23 % 10 = 3;
Hash (key) = 12 % 10 =2;
Hash (key) = 32 % 10 =2;

In this again the element 32 can be placed using hash2 (key) = 5 – (32 % 5) = 3. So 32 can be placed at index 5 in the table which is empty as we have to jump 3 entries to place it.
Conclusion
Hashing is one of the important techniques in terms of searching data provided with very efficient and quick methods using hash function and hash tables. Each element can be searched and placed using different hashing methods. This technique is very faster than any other data structure in terms of time coefficient.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Hashing function in C. Here we discussed brief overview, with types of Hashing Function in C and collision resolution techniques in detail. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–


